hdu 2196 Computer 树形dp模板题
2014-04-29 16:15
369 查看
Computer
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2850 Accepted Submission(s): 1450
Problem Description
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the
net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.
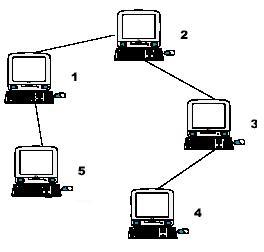
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also
get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
Input
Input file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N (N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers - number of computer, to which i-th computer is connected
and length of cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9. Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
Output
For each case output N lines. i-th line must contain number Si for i-th computer (1<=i<=N).
Sample Input
5
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
Sample Output
3
2
3
4
4
/***
分析:以编号的i的节点为例(非根节点),最长的路径长度只有俩种可能,
1)子树中存在最长路径;
2)通过父节点的路径中存在最长路径
所以,只有分别求出每一节点对应的那俩种路径取大最大值即可,其中,根节点只存在第一种可能
***/
#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
#define N 10005
struct node{
int x,y;
int weight;
int next;
}edge[4*N];
int idx,head
;
void Init(){idx=0; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));}
void Add(int x,int y,int weight)
{
edge[idx].x = x;
edge[idx].y = y;
edge[idx].weight = weight;
edge[idx].next = head[x];
head[x] = idx++;
}
struct point{
int id;
int value;
}dp1
,dp2
; //dp1[i]记录点i的最远距离,dp2[i]记录点i的次远距离,
void swap(point &a,point &b)
{
point c;
c = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
void DFS1(int x,int father)
{
int i,y;
dp1[x].value = dp2[x].value = 0;
for(i=head[x]; i!=-1; i=edge[i].next)
{
y = edge[i].y;
if(y==father) continue;
DFS1(y,x);
if(dp1[y].value + edge[i].weight > dp2[x].value)
{
dp2[x].value = dp1[y].value + edge[i].weight;
dp2[x].id = y;
if(dp1[x].value < dp2[x].value) //dp1[i]记录点i的最远距离,dp2[i]记录点i的次远距离,
swap(dp1[x],dp2[x]);
}
}
}
void DFS2(int x,int father)
{
int i,y;
for(i=head[x]; i!=-1; i=edge[i].next)
{
y = edge[i].y;
if(y==father) continue;
if(dp1[x].id == y) //点y是父亲x的最远距离的下一个节点
{
if(dp2[y].value < dp2[x].value+edge[i].weight) //,那么看点y的次元距离能否通过父亲x的其他节点更新
{
dp2[y].value = dp2[x].value + edge[i].weight;
dp2[y].id = x;
if(dp1[y].value < dp2[y].value)
swap(dp1[y],dp2[y]);
}
}
else
{
if(dp2[y].value < dp1[x].value+edge[i].weight)
{
dp2[y].value = dp1[x].value+edge[i].weight;
dp2[y].id = x;
if(dp1[y].value < dp2[y].value)
swap(dp1[y],dp2[y]);
}
}
DFS2(y,x);
}
}
int main()
{
int i,n;
int x,y,k;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
Init();
for(y=2; y<=n; ++y)
{
scanf("%d %d",&x,&k);
Add(x,y,k);
Add(y,x,k);
}
DFS1(1,-1);
DFS2(1,-1);
for(i=1; i<=n; ++i)
printf("%d\n",dp1[i].value);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- hdu 2196 Computer 树形dp模板题
- HDU 2196 Computer 树形DP
- HDU_2196_Computer_2次树形DP
- HDU 2196 Computer 树形DP(2个dfs)
- 【树形DP】 HDU 2196 Computer
- HDU - 2196 Computer 【树形dp必做题?】
- hdu 2196 Computer(树形dp)
- HDU 2196 Computer (树形DP)
- HDU 2196 Computer (树形DP 求树上每个点能到达的最远距离)
- HDU 2196 Computer(树形DP)
- HDU 2196 Computer【树形DP】
- Hdu 2196 Computer(树形dp)
- hdu 2196 Computer(树形dp)
- HDU--2196---Computer(树形DP)
- HDU 2196 Computer(经典树形DP)
- HDU 2196 Computer 树形DP 经典题
- Computer - HDU 2196 树形dp
- hdu 2196 Computer(树形DP)
- HDU 2196-Computer(树形dp)
- hdu 2196 computer(树形dp)
