RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams
2014-04-28 19:58
288 查看
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive (Independent) Disks.On most situations you will be using one of the following four levels of RAIDs.RAID 0
RAID 1
RAID 5
RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0)
This article explains the main difference between these raid levels along with an easy to understand diagram.
In all the diagrams mentioned below:A, B, C, D, E and F – represents blocks
p1, p2, and p3 – represents parity
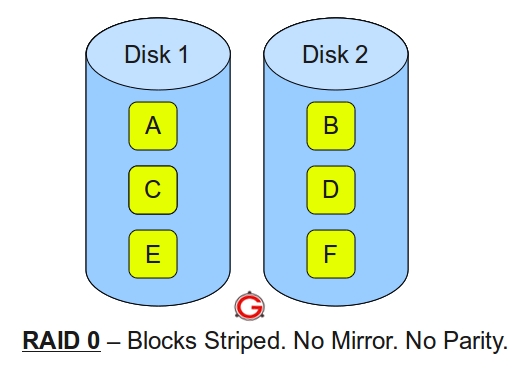
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 0.Minimum 2 disks.
Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped ).
No redundancy ( no mirror, no parity ).
Don’t use this for any critical system.
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 1.Minimum 2 disks.
Good performance ( no striping. no parity ).
Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored ).
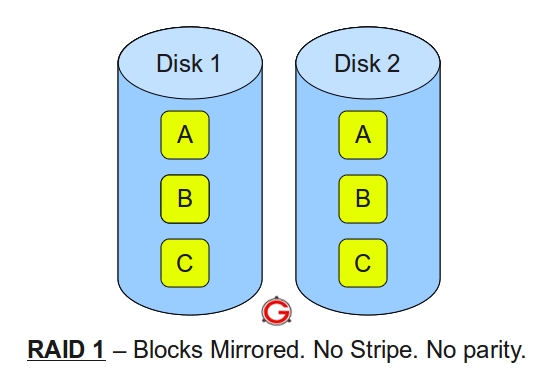
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 1.Minimum 2 disks.
Good performance ( no striping. no parity ).
Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored ).
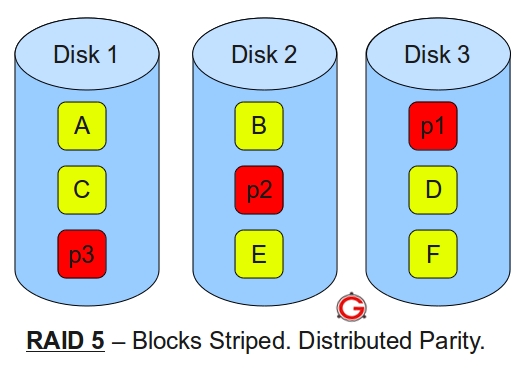
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 5.Minimum 3 disks.
Good performance ( as blocks are striped ).
Good redundancy ( distributed parity ).
Best cost effective option providing both performance and redundancy. Use this for DB that is heavily read oriented. Write operations will be slow.
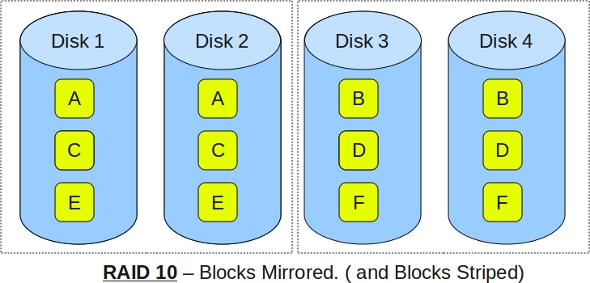
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 10.
Minimum 4 disks.
This is also called as “stripe of mirrors”
Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored )
Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped )
If you can afford the dollar, this is the BEST option for any mission critical applications (especially databases).
RAID 1
RAID 5
RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0)
This article explains the main difference between these raid levels along with an easy to understand diagram.
In all the diagrams mentioned below:A, B, C, D, E and F – represents blocks
p1, p2, and p3 – represents parity
RAID LEVEL 0

Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 0.Minimum 2 disks.
Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped ).
No redundancy ( no mirror, no parity ).
Don’t use this for any critical system.
RAID LEVEL 1
Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 1.Minimum 2 disks.
Good performance ( no striping. no parity ).
Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored ).

Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 1.Minimum 2 disks.
Good performance ( no striping. no parity ).
Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored ).
RAID LEVEL 5

Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 5.Minimum 3 disks.
Good performance ( as blocks are striped ).
Good redundancy ( distributed parity ).
Best cost effective option providing both performance and redundancy. Use this for DB that is heavily read oriented. Write operations will be slow.
RAID LEVEL 10

Following are the key points to remember for RAID level 10.
Minimum 4 disks.
This is also called as “stripe of mirrors”
Excellent redundancy ( as blocks are mirrored )
Excellent performance ( as blocks are striped )
If you can afford the dollar, this is the BEST option for any mission critical applications (especially databases).
相关文章推荐
- RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams
- RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10 Explained with Diagrams
- RAID 10 Vs RAID 01 (RAID 1+0 Vs RAID 0+1) Explained with Diagram
- RAID 2, RAID 3, RAID 4, RAID 6 Explained with Diagram
- svn add 报错 is too old (format 10) to work with client version '1.8.8
- SSD阵列卡方案优化:考虑使用RAID 50替代RAID 10
- Solaris 10 Advance Administrator 310-202 读书笔记 第八章 ---- Describing RAID and the Solaris™ Volume Manager Software
- RAID 10和raid 01
- tensorflow 笔记10:tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits 函数
- SQL点滴10—使用with语句来写一个稍微复杂sql语句,附加和子查询的性能对比
- Top 10 Java Debugging Tips with Eclipse
- RAID 01 和RAID 10的区别
- 10 Tips to Boost Your Productivity with C# and Visual Studio 2008 -- John W Powell
- Introduction to Programming with c++ 10-2 replace strings and split strings
- 【Python】ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10的错误
- 【转】Top 10 Java Debugging Tips with Eclipse
- 使用磁盘阵列卡测试RAID 0、1、5、10等功能 推荐
- SQL Server 在RAID 10 vs. RAID 5性能
- Top 10 Java Debugging Tips with Eclipse
