RTP打包发送H264(上)
2014-03-20 19:03
309 查看
RTP打包发送H264
一开始当然是看有没有现成的源码了,资源充分利用的同时也可以边看代码边去理解所涉及到的基础知识,我利用的的是网上非常流行的NALDecode,这个工程包含三个文件,一个是H264所涉及的一些结构,它在一个头文件h264.h中定义了很多结构体来表示。#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//#include "mem.h"
#define PACKET_BUFFER_END (unsigned int)0x00000000
#define MAX_RTP_PKT_LENGTH 1400
#define DEST_IP "180.101.59.185"
#define DEST_PORT 1234
#define H264 96
typedef struct
{
/**//* byte 0 */
unsigned char csrc_len:4; /**//* expect 0 */
unsigned char extension:1; /**//* expect 1, see RTP_OP below */
unsigned char padding:1; /**//* expect 0 */
unsigned char version:2; /**//* expect 2 */
/**//* byte 1 */
unsigned char payload:7; /**//* RTP_PAYLOAD_RTSP */
unsigned char marker:1; /**//* expect 1 */
/**//* bytes 2, 3 */
unsigned short seq_no;
/**//* bytes 4-7 */
unsigned long timestamp;
/**//* bytes 8-11 */
unsigned long ssrc; /**//* stream number is used here. */
} RTP_FIXED_HEADER;
typedef struct {
//byte 0
unsigned char TYPE:5;
unsigned char NRI:2;
unsigned char F:1;
} NALU_HEADER; /**//* 1 BYTES */
typedef struct {
//byte 0
unsigned char TYPE:5;
unsigned char NRI:2;
unsigned char F:1;
} FU_INDICATOR; /**//* 1 BYTES */
typedef struct {
//byte 0
unsigned char TYPE:5;
unsigned char R:1;
unsigned char E:1;
unsigned char S:1;
} FU_HEADER; /**//* 1 BYTES */
BOOL InitWinsock();// NALDecoder.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "h264.h"
#pragma comment(lib,"ws2_32.lib")
typedef struct
{
int startcodeprefix_len; //! 4 for parameter sets and first slice in picture, 3 for everything else (suggested)
unsigned len; //! Length of the NAL unit (Excluding the start code, which does not belong to the NALU)
unsigned max_size; //! Nal Unit Buffer size
int forbidden_bit; //! should be always FALSE
int nal_reference_idc; //! NALU_PRIORITY_xxxx
int nal_unit_type; //! NALU_TYPE_xxxx
char *buf; //! contains the first byte followed by the EBSP
unsigned short lost_packets; //! true, if packet loss is detected
} NALU_t;
FILE *bits = NULL; //!< the bit stream file
static int FindStartCode2 (unsigned char *Buf);//查找开始字符0x000001
static int FindStartCode3 (unsigned char *Buf);//查找开始字符0x00000001
//static bool flag = true;
static int info2=0, info3=0;
RTP_FIXED_HEADER *rtp_hdr;
NALU_HEADER *nalu_hdr;
FU_INDICATOR *fu_ind;
FU_HEADER *fu_hdr;
BOOL InitWinsock()
{
int Error;
WORD VersionRequested;
WSADATA WsaData;
VersionRequested=MAKEWORD(2,2);
Error=WSAStartup(VersionRequested,&WsaData); //启动WinSock2
if(Error!=0)
{
return FALSE;
}
else
{
if(LOBYTE(WsaData.wVersion)!=2||HIBYTE(WsaData.wHighVersion)!=2)
{
WSACleanup();
return FALSE;
}
}
return TRUE;
}
//为NALU_t结构体分配内存空间
NALU_t *AllocNALU(int buffersize)
{
NALU_t *n;
if ((n = (NALU_t*)calloc (1, sizeof (NALU_t))) == NULL)
{
printf("AllocNALU: n");
exit(0);
}
n->max_size=buffersize;
if ((n->buf = (char*)calloc (buffersize, sizeof (char))) == NULL)
{
free (n);
printf ("AllocNALU: n->buf");
exit(0);
}
return n;
}
//释放
void FreeNALU(NALU_t *n)
{
if (n)
{
if (n->buf)
{
free(n->buf);
n->buf=NULL;
}
free (n);
}
}
void OpenBitstreamFile (char *fn)
{
if (NULL == (bits=fopen(fn, "rb")))
{
printf("open file error\n");
exit(0);
}
}
//这个函数输入为一个NAL结构体,主要功能为得到一个完整的NALU并保存在NALU_t的buf中,获取他的长度,填充F,IDC,TYPE位。
//并且返回两个开始字符之间间隔的字节数,即包含有前缀的NALU的长度
int GetAnnexbNALU (NALU_t *nalu)
{
int pos = 0;
int StartCodeFound, rewind;
unsigned char *Buf;
if ((Buf = (unsigned char*)calloc (nalu->max_size , sizeof(char))) == NULL)
printf ("GetAnnexbNALU: Could not allocate Buf memory\n");
nalu->startcodeprefix_len=3;//初始化码流序列的开始字符为3个字节
if (3 != fread (Buf, 1, 3, bits))//从码流中读3个字节
{
free(Buf);
return 0;
}
info2 = FindStartCode2 (Buf);//判断是否为0x000001
if(info2 != 1)
{
//如果不是,再读一个字节
if(1 != fread(Buf+3, 1, 1, bits))//读一个字节
{
free(Buf);
return 0;
}
info3 = FindStartCode3 (Buf);//判断是否为0x00000001
if (info3 != 1)//如果不是,返回-1
{
free(Buf);
return -1;
}
else
{
//如果是0x00000001,得到开始前缀为4个字节
pos = 4;
nalu->startcodeprefix_len = 4;
}
}
else
{
//如果是0x000001,得到开始前缀为3个字节
nalu->startcodeprefix_len = 3;
pos = 3;
}
//查找下一个开始字符的标志位
StartCodeFound = 0;
info2 = 0;
info3 = 0;
while (!StartCodeFound)
{
if (feof (bits))//判断是否到了文件尾
{
nalu->len = (pos-1)-nalu->startcodeprefix_len;
memcpy (nalu->buf, &Buf[nalu->startcodeprefix_len], nalu->len);
nalu->forbidden_bit = nalu->buf[0] & 0x80; //1 bit
nalu->nal_reference_idc = nalu->buf[0] & 0x60; // 2 bit
nalu->nal_unit_type = (nalu->buf[0]) & 0x1f;// 5 bit
free(Buf);
return pos-1;
}
Buf[pos++] = fgetc (bits);//读一个字节到BUF中
info3 = FindStartCode3(&Buf[pos-4]);//判断是否为0x00000001
if(info3 != 1)
info2 = FindStartCode2(&Buf[pos-3]);//判断是否为0x000001
StartCodeFound = (info2 == 1 || info3 == 1);
}
// Here, we have found another start code (and read length of startcode bytes more than we should
// have. Hence, go back in the file
rewind = (info3 == 1)? -4 : -3;
if (0 != fseek (bits, rewind, SEEK_CUR))//把文件指针指向前一个NALU的末尾
{
free(Buf);
printf("GetAnnexbNALU: Cannot fseek in the bit stream file");
}
// Here the Start code, the complete NALU, and the next start code is in the Buf.
// The size of Buf is pos, pos+rewind are the number of bytes excluding the next
// start code, and (pos+rewind)-startcodeprefix_len is the size of the NALU excluding the start code
nalu->len = (pos+rewind)-nalu->startcodeprefix_len;
memcpy (nalu->buf, &Buf[nalu->startcodeprefix_len], nalu->len);//拷贝一个完整NALU,不拷贝起始前缀0x000001或0x00000001
nalu->forbidden_bit = nalu->buf[0] & 0x80; //1 bit
nalu->nal_reference_idc = nalu->buf[0] & 0x60; // 2 bit
nalu->nal_unit_type = (nalu->buf[0]) & 0x1f;// 5 bit
free(Buf);
return (pos+rewind);//返回两个开始字符之间间隔的字节数,即包含有前缀的NALU的长度
}
//输出NALU长度和TYPE
void dump(NALU_t *n)
{
if (!n)return;
//printf("a new nal:");
printf(" len: %d ", n->len);
printf("nal_unit_type: %x\n", n->nal_unit_type);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
OpenBitstreamFile("./test2.264");//打开264文件,并将文件指针赋给bits,在此修改文件名实现打开别的264文件。
NALU_t *n;
char* nalu_payload;
char sendbuf[1500];
unsigned short seq_num =0;
int bytes=0;
InitWinsock(); //初始化套接字库
SOCKET socket1;
struct sockaddr_in server;
int len =sizeof(server);
float framerate=15;
unsigned int timestamp_increse=0,ts_current=0;
timestamp_increse=(unsigned int)(90000.0 / framerate); //+0.5);
server.sin_family=AF_INET;
server.sin_port=htons(DEST_PORT);
server.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(DEST_IP);
socket1=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM,0);
connect(socket1, (const sockaddr *)&server, len) ;//申请UDP套接字
n = AllocNALU(8000000);//为结构体nalu_t及其成员buf分配空间。返回值为指向nalu_t存储空间的指针
while(!feof(bits))
{
GetAnnexbNALU(n);//每执行一次,文件的指针指向本次找到的NALU的末尾,下一个位置即为下个NALU的起始码0x000001
dump(n);//输出NALU长度和TYPE
memset(sendbuf,0,1500);//清空sendbuf;此时会将上次的时间戳清空,因此需要ts_current来保存上次的时间戳值
//rtp固定包头,为12字节,该句将sendbuf[0]的地址赋给rtp_hdr,以后对rtp_hdr的写入操作将直接写入sendbuf。
rtp_hdr =(RTP_FIXED_HEADER*)&sendbuf[0];
//设置RTP HEADER,
rtp_hdr->payload = H264; //负载类型号,
rtp_hdr->version = 2; //版本号,此版本固定为2
rtp_hdr->marker = 0; //标志位,由具体协议规定其值。
rtp_hdr->ssrc = htonl(10); //随机指定为10,并且在本RTP会话中全局唯一
// 当一个NALU小于1400字节的时候,采用一个单RTP包发送
if(n->len<=1400)
{
//设置rtp M 位;
rtp_hdr->marker=1;
rtp_hdr->seq_no = htons(seq_num ++); //序列号,每发送一个RTP包增1
//设置NALU HEADER,并将这个HEADER填入sendbuf[12]
nalu_hdr =(NALU_HEADER*)&sendbuf[12]; //将sendbuf[12]的地址赋给nalu_hdr,之后对nalu_hdr的写入就将写入sendbuf中;
nalu_hdr->F=n->forbidden_bit;
nalu_hdr->NRI=n->nal_reference_idc>>5;//有效数据在n->nal_reference_idc的第6,7位,需要右移5位才能将其值赋给nalu_hdr->NRI。
nalu_hdr->TYPE=n->nal_unit_type;
nalu_payload=&sendbuf[13];//同理将sendbuf[13]赋给nalu_payload
memcpy(nalu_payload,n->buf+1,n->len-1);//去掉nalu头的nalu剩余内容写入sendbuf[13]开始的字符串。
ts_current=ts_current+timestamp_increse;
rtp_hdr->timestamp=htonl(ts_current);
bytes=n->len + 12 ; //获得sendbuf的长度,为nalu的长度(包含NALU头但除去起始前缀)加上rtp_header的固定长度12字节
send( socket1, sendbuf, bytes, 0 );//发送rtp包
// Sleep(100);
}
else if(n->len>1400)
{
//得到该nalu需要用多少长度为1400字节的RTP包来发送
int k=0,l=0;
k=n->len/1400;//需要k个1400字节的RTP包
l=n->len%1400;//最后一个RTP包的需要装载的字节数
int t=0;//用于指示当前发送的是第几个分片RTP包
ts_current=ts_current+timestamp_increse;
rtp_hdr->timestamp=htonl(ts_current);
while(t<=k)
{
rtp_hdr->seq_no = htons(seq_num ++); //序列号,每发送一个RTP包增1
if(!t)//发送一个需要分片的NALU的第一个分片,置FU HEADER的S位
{
//设置rtp M 位;
rtp_hdr->marker=0;
//设置FU INDICATOR,并将这个HEADER填入sendbuf[12]
fu_ind =(FU_INDICATOR*)&sendbuf[12]; //将sendbuf[12]的地址赋给fu_ind,之后对fu_ind的写入就将写入sendbuf中;
fu_ind->F=n->forbidden_bit;
fu_ind->NRI=n->nal_reference_idc>>5;
fu_ind->TYPE=28;
//设置FU HEADER,并将这个HEADER填入sendbuf[13]
fu_hdr =(FU_HEADER*)&sendbuf[13];
fu_hdr->E=0;
fu_hdr->R=0;
fu_hdr->S=1;
fu_hdr->TYPE=n->nal_unit_type;
nalu_payload=&sendbuf[14];//同理将sendbuf[14]赋给nalu_payload
memcpy(nalu_payload,n->buf+1,1400);//去掉NALU头
bytes=1400+14; //获得sendbuf的长度,为nalu的长度(除去起始前缀和NALU头)加上rtp_header,fu_ind,fu_hdr的固定长度14字节
send( socket1, sendbuf, bytes, 0 );//发送rtp包
t++;
}
//发送一个需要分片的NALU的非第一个分片,清零FU HEADER的S位,如果该分片是该NALU的最后一个分片,置FU HEADER的E位
else if(k==t)//发送的是最后一个分片,注意最后一个分片的长度可能超过1400字节(当l>1386时)。
{
//设置rtp M 位;当前传输的是最后一个分片时该位置1
rtp_hdr->marker=1;
//设置FU INDICATOR,并将这个HEADER填入sendbuf[12]
fu_ind =(FU_INDICATOR*)&sendbuf[12]; //将sendbuf[12]的地址赋给fu_ind,之后对fu_ind的写入就将写入sendbuf中;
fu_ind->F=n->forbidden_bit;
fu_ind->NRI=n->nal_reference_idc>>5;
fu_ind->TYPE=28;
//设置FU HEADER,并将这个HEADER填入sendbuf[13]
fu_hdr =(FU_HEADER*)&sendbuf[13];
fu_hdr->R=0;
fu_hdr->S=0;
fu_hdr->TYPE=n->nal_unit_type;
fu_hdr->E=1;
nalu_payload=&sendbuf[14];//同理将sendbuf[14]的地址赋给nalu_payload
memcpy(nalu_payload,n->buf+t*1400+1,l-1);//将nalu最后剩余的l-1(去掉了一个字节的NALU头)字节内容写入sendbuf[14]开始的字符串。
bytes=l-1+14; //获得sendbuf的长度,为剩余nalu的长度l-1加上rtp_header,FU_INDICATOR,FU_HEADER三个包头共14字节
send( socket1, sendbuf, bytes, 0 );//发送rtp包
t++;
// Sleep(100);
}
else if(tmarker=0;
//设置FU INDICATOR,并将这个HEADER填入sendbuf[12]
fu_ind =(FU_INDICATOR*)&sendbuf[12]; //将sendbuf[12]的地址赋给fu_ind,之后对fu_ind的写入就将写入sendbuf中;
fu_ind->F=n->forbidden_bit;
fu_ind->NRI=n->nal_reference_idc>>5;
fu_ind->TYPE=28;
//设置FU HEADER,并将这个HEADER填入sendbuf[13]
fu_hdr =(FU_HEADER*)&sendbuf[13];
//fu_hdr->E=0;
fu_hdr->R=0;
fu_hdr->S=0;
fu_hdr->E=0;
fu_hdr->TYPE=n->nal_unit_type;
nalu_payload=&sendbuf[14];//同理将sendbuf[14]的地址赋给nalu_payload
memcpy(nalu_payload,n->buf+t*1400+1,1400);//去掉起始前缀的nalu剩余内容写入sendbuf[14]开始的字符串。
bytes=1400+14; //获得sendbuf的长度,为nalu的长度(除去原NALU头)加上rtp_header,fu_ind,fu_hdr的固定长度14字节
send( socket1, sendbuf, bytes, 0 );//发送rtp包
t++;
}
}
}
}
FreeNALU(n);
return 0;
}
static int FindStartCode2 (unsigned char *Buf)
{
if(Buf[0]!=0 || Buf[1]!=0 || Buf[2] !=1) return 0; //判断是否为0x000001,如果是返回1
else return 1;
}
static int FindStartCode3 (unsigned char *Buf)
{
if(Buf[0]!=0 || Buf[1]!=0 || Buf[2] !=0 || Buf[3] !=1) return 0;//判断是否为0x00000001,如果是返回1
else return 1;
}ok,现在就把这段代码搞明白。
可以看到是用Socket发的,但是发的是从一个test2.264的文件中读取的数据流,这里就是一个H264的裸流,什么样的呢?我们都知道,H264有三种帧,I、P、B,在一般的监控视频中为了降低编码复杂度,都没有B帧,也就是采用baseline。裸流文件中就是这样的一些帧,大概是IPPPPPP......IPPPPPPP.......IPPPPPP格式的一些帧,两个I帧中间到底有几个P帧,我没有具体数,大家可以对照我上传的码流文件用Notepad++打开后自己研究下,每个帧都是以00
00 00 01开头,后面跟着的65表示I帧,41就表示P帧,可以发现每个I帧前面还有两个00 00 00 01开头的,那是SPS(67)和PPS(68),其实每个帧就是一个NAL单元,00 00 00 01的起始头就是区分每个NAL。
这样就知道代码中GetAnnexbNALU(n)的含义了,提取出来后就开始打印NALU的信息,是根据起始头00 00 00 01后面的一个字节来判断的,称为NAL头,NAL头信息由8位1个字节:
forbidden_bit(隐藏比特位)---(1位)
nal_reference_bit(优先级)---(2位)
nal_unit_type(类型)---(3位)
NAL 头信息的隐藏比特位,在 H.264 编码器中默认为 0,当网络识别到单元中存在比特错误时,可将其置为 1。NAL 头信息的 nal_referrence_idc(NRI)用于在重建过程中标记一个 NAL 单元的重要性,值为 0 表示这个 NAL 单元没有用预测,因此可以被解码器抛弃而不会有错误扩散,值高于 0 表示 NAL 单元要用于无漂移重构,且值越高,对此 NAL 单元丢失的影响越大。NAL单元的类型见图1。
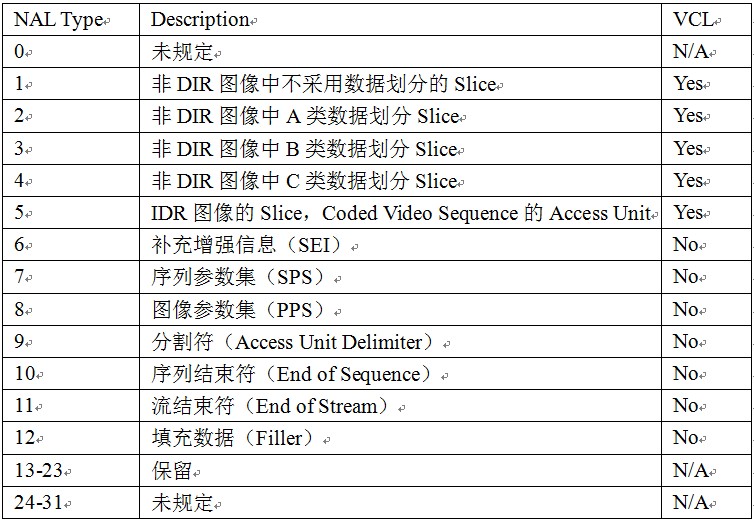
NAL的头占用了一个字节,按照比特自高至低排列可以表示:0AABBBBB,(这里强调下自高至低),因为后面会涉及到一个网络字节与机器字节的大小端问题)。其中,AA用于表示该NAL是否可以丢弃(有无被其后的NAL参考),00表示没有参考作用,可丢弃,如B slice、SEI等,非零——包括01、10、11——表示该NAL不可丢弃,如SPS、PPS、I Slice、P Slice等。
常用的NAL头的取值如:
0x67: SPS
0x68: PPS
0x65: IDR
0x61: non-IDR Slice
0x01: B Slice
0x06: SEI
0x09: AU Delimiter
0x41: P Slice
裸流文件test2.264在我的资源中可以下载。
(原谅我这么啰嗦,讲了这么多还没到重点,对于各位都懂的大神就没什么说的啦,给不懂的人一些参考吧)
相关文章推荐
- RTP打包发送H264
- H264 RTP打包发送
- RTP打包发送H264(下)
- 论如何是用RTP打包H264数据(发送单包的情况,分包发送还需要另外分析)
- rtp打包发送H264文件
- H264 RTP打包发送 12323
- 对标准H264码流的RTP打包 VLC播放RTP打包发送的.264文件
- 论如何是用RTP打包H264数据(发送单包的情况,分包发送还需要另外分析)
- H264 RTP打包发送
- h264打包rtp发送
- H264 RTP打包发送 2222
- 论如何是用RTP打包H264数据(发送分包发送分析)
- RTP打包发送H264(中)
- 关于H264通过RTP传输的打包方式
- H264 NALU 使用PS封装 RTP发送
- 基于RTP的H264视频数据打包解包类
- live555学习笔记-RTP打包与发送
- H264码流结构分析和rtp打包结构详解
- jrtplib打包发送H264
- H264的打包与发送,SPS、PPS提取与作用
