CF:402D - Upgrading Array 数分解为素数之积滴判定
2014-03-18 16:51
267 查看
D. Upgrading Array
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
You have an array of positive integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] and a set of bad prime
numbers b1, b2, ..., bm.
The prime numbers that do not occur in the set b are considered good. The beauty of
array a is the sum
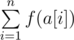
,
where function f(s) is determined as follows:
f(1) = 0;
Let's assume that p is the minimum prime divisor of s.
If p is a good prime, then
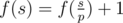
,
otherwise
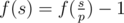
.
You are allowed to perform an arbitrary (probably zero) number of operations to improve array a. The operation
of improvement is the following sequence of actions:
Choose some number r (1 ≤ r ≤ n) and calculate
the value g = GCD(a[1], a[2], ..., a[r]).
Apply the assignments:
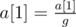
,

, ...,
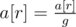
.
What is the maximum beauty of the array you can get?
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 5000)
showing how many numbers are in the array and how many bad prime numbers there are.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109)
— array a. The third line contains m space-separated
integers b1, b2, ..., bm (2 ≤ b1 < b2 < ... < bm ≤ 109)
— the set of bad prime numbers.
Output
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem.
Sample test(s)
input
output
input
output
Note
Note that the answer to the problem can be negative.
The GCD(x1, x2,
..., xk) is
the maximum positive integer that divides each xi.
这题有点神啊……题意看了好久都没太理解,又研究队友那时过的代码,也好久了才懂什么意思,太神了,以前知道怎么分解一个数为素数之积,不过没写过代码,这题就作为模板了吧……
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
You have an array of positive integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] and a set of bad prime
numbers b1, b2, ..., bm.
The prime numbers that do not occur in the set b are considered good. The beauty of
array a is the sum
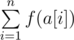
,
where function f(s) is determined as follows:
f(1) = 0;
Let's assume that p is the minimum prime divisor of s.
If p is a good prime, then
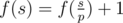
,
otherwise
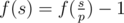
.
You are allowed to perform an arbitrary (probably zero) number of operations to improve array a. The operation
of improvement is the following sequence of actions:
Choose some number r (1 ≤ r ≤ n) and calculate
the value g = GCD(a[1], a[2], ..., a[r]).
Apply the assignments:
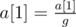
,

, ...,
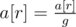
.
What is the maximum beauty of the array you can get?
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 5000)
showing how many numbers are in the array and how many bad prime numbers there are.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109)
— array a. The third line contains m space-separated
integers b1, b2, ..., bm (2 ≤ b1 < b2 < ... < bm ≤ 109)
— the set of bad prime numbers.
Output
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem.
Sample test(s)
input
5 2 4 20 34 10 10 2 5
output
-2
input
4 5 2 4 8 16 3 5 7 11 17
output
10
Note
Note that the answer to the problem can be negative.
The GCD(x1, x2,
..., xk) is
the maximum positive integer that divides each xi.
这题有点神啊……题意看了好久都没太理解,又研究队友那时过的代码,也好久了才懂什么意思,太神了,以前知道怎么分解一个数为素数之积,不过没写过代码,这题就作为模板了吧……
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define sca(a) scanf("%d",&a)
#define pri(a) printf("%d\n",a)
#define MM 1000000000
#define MN 5005
#define INF 10000007
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
int n,m,bad[MN],a[MN],is[MN*200],ans,prime[MN*2],gcd[MN];
void get_prime()
{
int i,j,k=sqrt(MM+0.5);
for(i=2;i<=k;i++)
if(!is[i])
{
prime[ans++]=i;
for(j=i*i;j<=k;j+=i) is[j]=1;
}
}
int fenjie(int x)
{
int cnt=0,i,t,pos;
for(i=0;i<ans&&x>1;i++)
if(!(x%prime[i]))
{
t=0;
while(!(x%prime[i])) x/=prime[i],t++;
pos=lower_bound(bad,bad+m,prime[i])-bad;
if(pos<m&&bad[pos]==prime[i]) cnt-=t;
else cnt+=t;
}
if(x>1) //说明x比prime中最大的数还大,那么就在bad里面找了
{
pos=lower_bound(bad,bad+m,x)-bad;
if(pos<m&&bad[pos]==x) cnt--;
else cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
ll sum=0;
int i,j;
get_prime();
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&a[0]);
gcd[0]=a[0];
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
sca(a[i]),gcd[i]=__gcd(gcd[i-1],a[i]);
for(i=0;i<m;i++) sca(bad[i]);
for(i=0;i<n;i++) sum+=fenjie(a[i]);
for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
if(gcd[i]>0)
{
int d=fenjie(gcd[i]);
if(d<0)
{
for(j=0;j<=i;j++)
a[j]/=gcd[i],gcd[j]/=gcd[i];
sum-=d*(i+1);
}
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- poj 1811 Prime Test(数论:大素数判定-分解)
- 大数分解与素数判定
- pku 1811 Prime Test 大素数判定和大数分解
- 大数分解与素数判定
- POJ 1811 Prime Test【大素数判定】【素因子分解】
- 【知识点】大数分解与素数判定 --- 【Miller-rabin算法】【pollard-rho算法】
- 素数判定(Miller_Rabin) & 大数分解(Pollard_Pho)
- 素数判定、埃氏筛法与整数分解
- poj 2191 大数素数判定 && 大数素数分解
- 【世界数学难题】素数判定与大数因子分解问题(上)
- HDU 4344 大数分解大素数判定
- 学习笔记:素数的判定以及整数的唯一分解定理
- 【世界数学难题】素数判定与大数因子分解问题(下)
- poj 2429 GCD & LCM Inverse miller_rabin素数判定和pollard_rho因数分解
- BZOJ 4802 欧拉函数(素数判定Miller-Rabin+素因子分解Pollard-rho+欧拉函数)
- 数学#素数判定Miller_Rabin+大数因数分解Pollard_rho算法 POJ 1811&2429
- cf D. Dima and Lisa (三素数定理_素数打表+判定)
- POJ 2429 GCD & LCM Inverse(素数判定Miller-Rabin+素因子分解Pollard-rho)
- poj 1811(大素数模版 miller_rabbin素数判定+pollard_rho分解)
- 大素数分解与素数判定
