环形队列实现原理 /链式实现
2014-03-13 09:17
323 查看
环形队列实现原理 /链式实现
环形队列是在实际编程极为有用的数据结构,它有如下特点。
它是一个首尾相连的FIFO的数据结构,采用数组的线性空间,数据组织简单。能很快知道队列是否满为空。能以很快速度的来存取数据。
因为有简单高效的原因,甚至在硬件都实现了环形队列.
环形队列广泛用于网络数据收发,和不同程序间数据交换(比如内核与应用程序大量交换数据,从硬件接收大量数据)均使用了环形队列.
一.环形队列实现原理
------------------------------------------------------------
内存上没有环形的结构,因此环形队列实上是数组的线性空间来实现。那当数据到了尾部如何处理呢?它将转回到0位置来处理。这个的转回是通过取模操作来执行的。
因此环列队列的是逻辑上将数组元素q[0]与q[MAXN-1]连接,形成一个存放队列的环形空间。
为了方便读写,还要用数组下标来指明队列的读写位置。head/tail.其中head指向可以读的位置,tail指向可以写的位置。
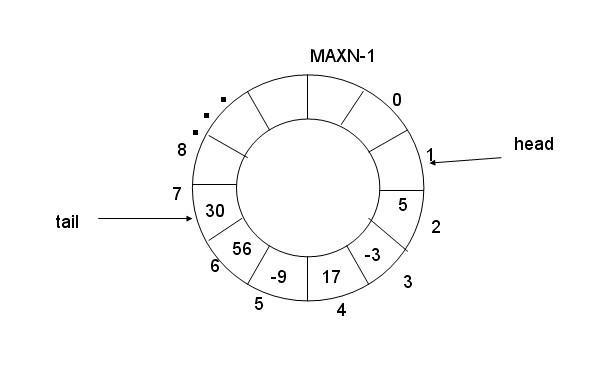
环形队列的关键是判断队列为空,还是为满。当tail追上head时,队列为满时,当head追上tail时,队列为空。但如何知道谁追上谁。还需要一些辅助的手段来判断.
如何判断环形队列为空,为满有两种判断方法。
一.是附加一个标志位tag
当head赶上tail,队列空,则令tag=0,
当tail赶上head,队列满,则令tag=1,
二.限制tail赶上head,即队尾结点与队首结点之间至少留有一个元素的空间。
队列空: head==tail
队列满: (tail+1)% MAXN ==head
二.附加标志实现算法
采用第一个环形队列有如下结构
初始化状态: q->head = q->tail = q->tag = 0;
队列为空:(q->head == q->tail) && (q->tag == 0)
队列为满: ((q->head == q->tail) && (q->tag == 1))
入队操作:如队列不满,则写入
q->tail = (q->tail + 1) % q->size ;
出队操作:如果队列不空,则从head处读出。
下一个可读的位置在 q->head = (q->head + 1) % q->size
完整代码
头文件ringq.h
实现代码 ringq.c
测试代码
三.预留空间环境队列
-------------------------------------------------------------------
不采用tag,只留一个空间
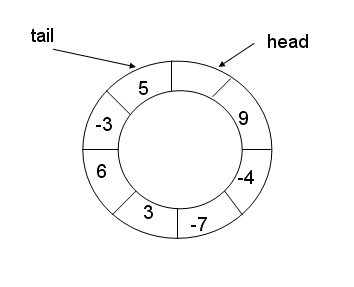
初始化状态: q->head = q->tail = q->tag = 0;
队列为空:(q->head == q->tail)
队列为满: (((q->tail+1)%q->size) == q->head )
入队操作:如队列不满,则写入
q->tail = (q->tail + 1) % q->size ;
出队操作:如果队列不空,则从head处读出。
下一个可读的位置在 q->head = (q->head + 1) % q->size
头文件
ringq.h
实现代码ringq.c
作者:Andrew Huang bluedrum@163.com
程序是用codeblock写的,中间碰到了一个又一个的问题,都最终解决了。这个结构可以作为所有结构体的实现的一个模式。写写这些程序可以不断让自己更加深入认识指针,更加熟悉指针的各种使用。经常锻炼C基础,心里写程序更有底.
需要特别注意几个问题:
一,结构作为参数传递。这个传递方式也是和其他一样的,当需要改变传入参数的值的时候,用地址传递,使用指针参数。参数的传递类似于一般的int了,使用结构体指针就行。
二,结构体参数值传递和地址传递的调用方式的不同。结构体参数如果是以普通值传递进入参数,使用结构体.成员来访问。如果是以地址传递,也就是传入的是指针参数,就是结构体->成员来访问。这个就是结构体和结构体指针访问数据成员的差异。
三,像队列这种包含头尾队列点的结构体,在初始化的时候,要为每个一个指针结构申请空间,也就是里面的
L->front = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
L->retail = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
四,在取结构体成员指针指向的数据的时候,不要使用 结构体指针->指针成员->指针成员指向的数据。 这样多个"->"连接会导致编译不能识别“结构体指针->指针成员”这个指针类型,会报错的。相应的处理方法是申请一个指针指向它就行。然后 操作这个指针。
五, 对于特定临界点情况的处理要慎重,比如队列数据点为0,1,2这几个情况对于环形队列是不同的,需要额外注意。
具体的算法,上面的程序里面都有了。都经过了简单的测试,应该没什么问题。
顺道说下CODEBLOCK的debug,到现在我不太知道,怎样使用,几次加入Watch变量都没反应囧,出错了,只能一个一个自己分析。
注:这个问题后来查了相关的论坛,原来codeblock不允许项目路径有空格和中文字符导致
环形队列是在实际编程极为有用的数据结构,它有如下特点。
它是一个首尾相连的FIFO的数据结构,采用数组的线性空间,数据组织简单。能很快知道队列是否满为空。能以很快速度的来存取数据。
因为有简单高效的原因,甚至在硬件都实现了环形队列.
环形队列广泛用于网络数据收发,和不同程序间数据交换(比如内核与应用程序大量交换数据,从硬件接收大量数据)均使用了环形队列.
一.环形队列实现原理
------------------------------------------------------------
内存上没有环形的结构,因此环形队列实上是数组的线性空间来实现。那当数据到了尾部如何处理呢?它将转回到0位置来处理。这个的转回是通过取模操作来执行的。
因此环列队列的是逻辑上将数组元素q[0]与q[MAXN-1]连接,形成一个存放队列的环形空间。
为了方便读写,还要用数组下标来指明队列的读写位置。head/tail.其中head指向可以读的位置,tail指向可以写的位置。

环形队列的关键是判断队列为空,还是为满。当tail追上head时,队列为满时,当head追上tail时,队列为空。但如何知道谁追上谁。还需要一些辅助的手段来判断.
如何判断环形队列为空,为满有两种判断方法。
一.是附加一个标志位tag
当head赶上tail,队列空,则令tag=0,
当tail赶上head,队列满,则令tag=1,
二.限制tail赶上head,即队尾结点与队首结点之间至少留有一个元素的空间。
队列空: head==tail
队列满: (tail+1)% MAXN ==head
二.附加标志实现算法
采用第一个环形队列有如下结构
typedef struct ringq{
int head; /* 头部,出队列方向*/
int tail; /* 尾部,入队列方向*/
int tag ;
int size ; /* 队列总尺寸 */
int space[RINGQ_MAX]; /* 队列空间 */
}RINGQ;初始化状态: q->head = q->tail = q->tag = 0;
队列为空:(q->head == q->tail) && (q->tag == 0)
队列为满: ((q->head == q->tail) && (q->tag == 1))
入队操作:如队列不满,则写入
q->tail = (q->tail + 1) % q->size ;
出队操作:如果队列不空,则从head处读出。
下一个可读的位置在 q->head = (q->head + 1) % q->size
完整代码
头文件ringq.h
#ifndef __RINGQ_H__
#define __RINGQ_H__
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
#define QUEUE_MAX 20
typedef struct ringq{
int head; /* 头部,出队列方向*/
int tail; /* 尾部,入队列方向*/
int tag ; /* 为空还是为满的标志位*/
int size ; /* 队列总尺寸 */
int space[QUEUE_MAX]; /* 队列空间 */
}RINGQ;
/*
第一种设计方法:
当head == tail 时,tag = 0 为空,等于 = 1 为满。
*/
extern int ringq_init(RINGQ * p_queue);
extern int ringq_free(RINGQ * p_queue);
/* 加入数据到队列 */
extern int ringq_push(RINGQ * p_queue,int data);
/* 从队列取数据 */
extern int ringq_poll(RINGQ * p_queue,int *p_data);
#define ringq_is_empty(q) ( (q->head == q->tail) && (q->tag == 0))
#define ringq_is_full(q) ( (q->head == q->tail) && (q->tag == 1))
#define print_ringq(q) printf("ring head %d,tail %d,tag %d\n", q->head,q->tail,q->tag);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* __RINGQ_H__ */实现代码 ringq.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "ringq.h"
int ringq_init(RINGQ * p_queue)
{
p_queue->size = QUEUE_MAX ;
p_queue->head = 0;
p_queue->tail = 0;
p_queue->tag = 0;
return 0;
}
int ringq_free(RINGQ * p_queue)
{
return 0;
}
int ringq_push(RINGQ * p_queue,int data)
{
print_ringq(p_queue);
if(ringq_is_full(p_queue))
{
printf("ringq is full\n");
return -1;
}
p_queue->space[p_queue->tail] = data;
p_queue->tail = (p_queue->tail + 1) % p_queue->size ;
/* 这个时候一定队列满了*/
if(p_queue->tail == p_queue->head)
{
p_queue->tag = 1;
}
return p_queue->tag ;
}
int ringq_poll(RINGQ * p_queue,int * p_data)
{
print_ringq(p_queue);
if(ringq_is_empty(p_queue))
{
printf("ringq is empty\n");
return -1;
}
*p_data = p_queue->space[p_queue->head];
p_queue->head = (p_queue->head + 1) % p_queue->size ;
/* 这个时候一定队列空了*/
if(p_queue->tail == p_queue->head)
{
p_queue->tag = 0;
}
return p_queue->tag ;
}测试代码
/* 测试第一种环形队列*/
void test5()
{
RINGQ rq, * p_queue;
int i,data;
p_queue = &rq;
ringq_init(p_queue);
for(i=0; i < QUEUE_MAX +2 ; i++)
{
ringq_push(p_queue,i+1);
}
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
ringq_free(p_queue);
}
/* 测试第一种环形队列,更加复杂的情况*/
void test6()
{
RINGQ rq, * p_queue;
int i,data;
p_queue = &rq;
ringq_init(p_queue);
ringq_push(p_queue,1);
ringq_push(p_queue,2);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
ringq_push(p_queue,3);
ringq_push(p_queue,4);
ringq_push(p_queue,5);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
ringq_push(p_queue,6);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
if(ringq_poll(p_queue,&data)>=0)
PRINT_INT(data);
ringq_free(p_queue);
}三.预留空间环境队列
-------------------------------------------------------------------
不采用tag,只留一个空间

初始化状态: q->head = q->tail = q->tag = 0;
队列为空:(q->head == q->tail)
队列为满: (((q->tail+1)%q->size) == q->head )
入队操作:如队列不满,则写入
q->tail = (q->tail + 1) % q->size ;
出队操作:如果队列不空,则从head处读出。
下一个可读的位置在 q->head = (q->head + 1) % q->size
头文件
ringq.h
#ifndef __RINGQ_H__
#define __RINGQ_H__
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
#define RINGQ_MAX 20
typedef struct ringq{
int head; /* 头部,出队列方向*/
int tail; /* 尾部,入队列方向*/
int size ; /* 队列总尺寸 */
int space[RINGQ_MAX]; /* 队列空间 */
}RINGQ;
/*
取消tag .限制读与写之间至少要留一个空间
队列空 head == tail .
队列满是 (tail+1)%MAX == head
初始化是head = tail = 0;
*/
extern int ringq_init(RINGQ * p_ringq);
extern int ringq_free(RINGQ * p_ringq);
extern int ringq_push(RINGQ * p_ringq,int data);
extern int ringq_poll(RINGQ * p_ringq,int * p_data);
#define ringq_is_empty(q) (q->head == q->tail)
#define ringq_is_full(q) (((q->tail+1)%q->size) == q->head )
#define print_ringq2(q,d) printf("ring head %d,tail %d,data %d\n", q->head,q->tail,d);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* __QUEUE_H__ */实现代码ringq.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "ringq.h"
int ringq_init(RINGQ * p_ringq)
{
p_ringq->size = RINGQ_MAX;
p_ringq->head = 0;
p_ringq->tail = 0;
return p_ringq->size;
}
int ringq_free(RINGQ * p_ringq)
{
return 0;
}
/* 往队列加入数据 */
int ringq_push(RINGQ * p_ringq,int data)
{
print_ringq(p_ringq,data);
if(ringq_is_full(p_ringq))
{
printf("ringq is full,data %d\n",data);
return -1;
}
p_ringq->space[p_ringq->tail] = data;
p_ringq->tail = (p_ringq->tail + 1) % p_ringq->size ;
return p_ringq->tail ;
}
int ringq_poll(RINGQ * p_ringq,int * p_data)
{
print_ringq(p_ringq,-1);
if(ringq_is_empty(p_ringq))
{
printf("ringq is empty\n");
return -1;
}
*p_data = p_ringq->space[p_ringq->head];
p_ringq->head = (p_ringq->head + 1) % p_ringq->size ;
return p_ringq->head;
}
作者:Andrew Huang bluedrum@163.com
环形队列的链式实现
from:/article/6513730.html程序是用codeblock写的,中间碰到了一个又一个的问题,都最终解决了。这个结构可以作为所有结构体的实现的一个模式。写写这些程序可以不断让自己更加深入认识指针,更加熟悉指针的各种使用。经常锻炼C基础,心里写程序更有底.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int Queue_Type;
// 定义队列节点结构
typedef struct CQUEUE_NODE
{
Queue_Type value;
struct CQUEUE_NODE *next;
}QNode, *PNode;
// 定义队列结构
typedef struct CQUEUE
{
unsigned int size;
PNode front, retail;
}LQueue;
//创建环形队列
void Create_Queue(LQueue *L, int n)
{
PNode front = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
PNode retail = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(front == NULL || retail == NULL)
exit(1);
scanf("%d", &front->value);
front->next = NULL;
// 只有一个节点的时候,头尾指向同一个点
retail = front;
// 多个点情况
int i;
for(i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
PNode p = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(p == NULL)
exit(1);
scanf("%d", &p->value);
retail->next = p;
retail = p;
}
// 结束后,尾节点指向头节点
retail->next = front;
L->front = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
L->retail = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(L->front == NULL || L->retail == NULL)
exit(1);
L->front = front;
L->retail = retail;
L->size = n;
}
// 销毁队列
void Destory_Queue(LQueue *L)
{
// 如果队列为空
if(L->front == NULL)
exit(1);
// 这里注意必须重新申请一个节点
// 直接使用L->retail->next会有类型不能识别的错误
PNode p = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(p == NULL)
exit(1);
p = L->front;
int size = L->size;
// 队列是多个节点情况
while(size != 0)
{
L->front = p->next;
free(p);
p = L->front;
size--;
}
// 这里一定要记得处理
// 将front retail指向NULL 在上面的处理过程中,只是free并没有指向NULL
// 如果不指向NULL, front,retail将是野指针
// 还要记得将L->size重新赋值,上面size只是读取size,并不改变size的值
L->front = NULL;
L->retail = NULL;
L->size = size;
}
// 入列操作 在尾节点插入
void Enqueue(LQueue *L, Queue_Type value)
{
PNode p = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(p == NULL)
exit(1);
p->value = value;
int size = L->size;
//如果队列是个空队列
if(size == 0)
{
L->front = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
L->retail = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
L->front = p;
L->retail = p;
p->next = NULL;
size ++;
}
// 如果队列不是空队列
// 头节点倒是没有必要重新开辟空间
PNode p1 = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(p1 == NULL)
exit(1);
p1 = L->retail;
p1->next = p;
p->next = L->front;
L->retail = p; //这里没发现啊,害我找了很久
size++;
L->size = size;
}
// 出列操作
Queue_Type Dequeue(LQueue *L)
{
int size = L->size;
Queue_Type n;
//如果队列为空
if(size == 0)
{
printf("The queue is empty.\n");
exit(1);
}
PNode p = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(p == NULL)
exit(1);
p = L->front;
//如果队列只有一个节点
if(size == 1)
{
n = p->value;
free(p);
L->front = L->retail = NULL;
p = NULL;
size--;
L->size = size;
return n;
}
if(size == 2)
{
n = p->value;
L->front = L->retail;
free(p);
p = NULL;
size--;
L->size = size;
return n;
}
// 头节点倒是没有必要重新开辟空间
PNode p1 = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(p1 == NULL)
exit(1);
p1 = L->retail;
n = p->value;
L->front = p->next;
p1->next = L->front;
free(p);
p = NULL;
size--;
L->size = size;
return n;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
bool Is_Empty(LQueue L)
{
if(L.size == 0)
return false;
else
return true;
}
// 打印队列
void Print_Queue(LQueue L)
{
// 如果队列为空
if(L.size == 0)
{
printf("The size of the queue is: %d\n", L.size);
exit(1);
}
printf("The size of the queue is: %d\n", L.size);
printf("The following are the elements of the queue:\n");
PNode p = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(p == NULL)
exit(1);
p = L.front;
while(p != L.retail)
{
printf("%d\n", p->value);
p = p->next;
}
if(p == L.retail)
{
printf("%d\n", p->value);
}
}
int main()
{
LQueue L;
int n;
printf("Input the number of the nodes of the queue:\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("-------------------------------------------\n");
Create_Queue(&L, n);
printf("-------------------------------------------\n");
Print_Queue(L);
printf("-------------------------------------------\n");
printf("Enqueue a node:\n");
int n1, n2,n3;
scanf("%d", &n1);
Enqueue(&L, n1);
printf("-------------------------------------------\n");
Print_Queue(L);
printf("Dequeue one node -------------------------\n");
n2 = Dequeue(&L);
printf("Node1 is %d\n",n2);
Print_Queue(L);
printf("Dequeue another node -------------------------\n");
n3 =Dequeue(&L);
printf("Node2 is %d\n",n3);
Print_Queue(L);
printf("-------------------------------------------\n");
printf("Destory the queue---------------------------\n");
Destory_Queue(&L);
Print_Queue(L);
return 0;
}
关于指针可能碰到的问题,在注释里差不多都说明了。需要特别注意几个问题:
一,结构作为参数传递。这个传递方式也是和其他一样的,当需要改变传入参数的值的时候,用地址传递,使用指针参数。参数的传递类似于一般的int了,使用结构体指针就行。
二,结构体参数值传递和地址传递的调用方式的不同。结构体参数如果是以普通值传递进入参数,使用结构体.成员来访问。如果是以地址传递,也就是传入的是指针参数,就是结构体->成员来访问。这个就是结构体和结构体指针访问数据成员的差异。
三,像队列这种包含头尾队列点的结构体,在初始化的时候,要为每个一个指针结构申请空间,也就是里面的
L->front = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
L->retail = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
四,在取结构体成员指针指向的数据的时候,不要使用 结构体指针->指针成员->指针成员指向的数据。 这样多个"->"连接会导致编译不能识别“结构体指针->指针成员”这个指针类型,会报错的。相应的处理方法是申请一个指针指向它就行。然后 操作这个指针。
五, 对于特定临界点情况的处理要慎重,比如队列数据点为0,1,2这几个情况对于环形队列是不同的,需要额外注意。
具体的算法,上面的程序里面都有了。都经过了简单的测试,应该没什么问题。
顺道说下CODEBLOCK的debug,到现在我不太知道,怎样使用,几次加入Watch变量都没反应囧,出错了,只能一个一个自己分析。
注:这个问题后来查了相关的论坛,原来codeblock不允许项目路径有空格和中文字符导致
相关文章推荐
- 环形队列的实现原理
- 环形队列的链式实现(原创)
- 环形队列实现原理
- 环形队列实现原理
- 链式队列实现原理
- 环形队列的实现原理
- Java阻塞队列ArrayBlockingQueue和LinkedBlockingQueue实现原理分析
- 环形无锁队列的简易实现
- PHP实现队列及队列原理
- Java并发包中的同步队列SynchronousQueue实现原理
- C 算法精介----队列->链式队列->分析与实现
- 链式队列的实现
- 无锁队列的原理与实现
- 简单环形队列实现
- java自己实现的链式队列
- PHP实现队列及队列原理
- 队列的链式存储结构及实现
- 队列的顺序存储和链式存储实现
- java队列实现方法(顺序队列,链式队列,循环队列)
- 拓扑排序(链式前向星+队列实现)
