我的服务端之内存池
2014-01-08 17:43
369 查看
分类: 我的服务端 C/C++2014-01-05
00:03 1836人阅读 评论(9) 收藏 举报
C++memorypool服务端内存碎片内存池
内存池(Memory Pool)
一、前言
1、操作系统的内存分配方式
1.1、连续分配方式
顾名思义,这种分配方式,会将进程分配在连续的空间。
连续分配方式一般可以分为固定分配方式、动态分配方式和伙伴系统(固定分配方式与动态分配方式的折衷方案)。
1.2、基本分页存储管理方式
1.3、基本分段存储管理方式
注:以上说的分配方式,自个可以到网上去搜索一下,方便理解以下内容。
二、为什么要添加内存池?内存池到底有什么作用?
1、避免内存碎片化。
1.1、什么是内存碎片?
内存碎片就是系统中程序频繁分配内存,会留下许多难以利用、很小的空闲分区,这些小分区被称为“零头”或“碎片”。
1.2、内存碎片的危害。
1.2.1、造成内存的浪费。
这是毫无疑问的。如下图所示。
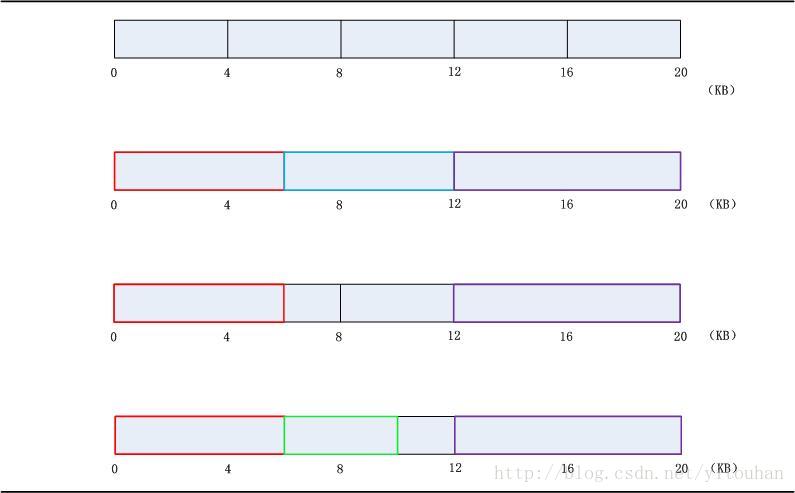
当第一次分配6KB、6KB和8KB之后,蓝色部分的内被程序释放,系统收回。在之后又被另一个绿色程序分配了4KB。绿色与紫色之间只剩下2KB,当其它程序需要分
配大于2KB时候,剩下的空间不足够,这就成了碎片,浪费内存。极端的情况下会耗尽所有内存(这个情况很少会出现,毕竟现在的内存是白菜价)
1.2.2、降低内存的分配效率
一般来说操作系统都是查找空闲分区表或链表来分配空间的。就像之前说的一样,剩下2KB的碎片(假设不能再被分配),系统每次分配内存的时候都会来判断这
2KB能不能被分配。因此降低了内存的分配效率。
1.3、为什么能避免内存碎片化?
添加内存池,由于内存池会在初始化的时候分配一定长度的空间。因此内存池分配出来的内存结构很可能会像第一次分配出来的结果一样(红、蓝、紫)。而且一
般情况下程序运行过程中,内存池的内存都不会释放,直到程序结束。因此,内存池能很好地避免内存碎片。
2、提高内存分配与释放效率
有了上面的了解,我们知道无论系统的内存分配算法有多么地快速,也是不可能比我们从池中取出来内存快。
在服务端中,C++分配堆内存大小一般是类的长度(new出一个新对象)。因此下面讲解一下定长、列表的内存池。
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?


#ifndef MEMORYPOOL_H
#define MEMORYPOOL_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct MemoryList
{
void * memory;
MemoryList * next;
};
class MemoryPool
{
public:
MemoryPool(unsigned int size, unsigned int increase = 64);
~MemoryPool();
void * Alloc();
void Free(void *m);
private:
unsigned int m_size;
unsigned int m_increase;
MemoryList * m_memory_list_header;
MemoryList * m_handle;
};
#define REGISTER_MEMORYPOOL(PoolNameSpace, ClassName, IncreaseNum) \
namespace PoolNameSpace\
{\
MemoryPool g_##ClassName##_mem_pool(sizeof(ClassName), IncreaseNum);\
}\
void *ClassName::operator new(size_t size)\
{\
void *mem = PoolNameSpace::g_##ClassName##_mem_pool.Alloc();\
return mem;\
}\
void ClassName::operator delete(void *m)\
{\
PoolNameSpace::g_##ClassName##_mem_pool.Free(m);\
}
#endif
memorypool.cpp
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?


#include "memorypool.h"
MemoryPool::MemoryPool( unsigned int size, unsigned int increase /*= 64*/ )
{
m_size = size;
m_increase = increase;
MemoryList *list = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
m_handle = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
if (list == NULL || m_handle == NULL)
{
return;
}
list->memory = malloc(size);
m_memory_list_header = list;
MemoryList *handle = NULL;
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < m_increase * 2; ++i)
{
handle = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
handle->memory = malloc(size);
list->next = handle;
list = list->next;
}
list->next = NULL;
}
MemoryPool::~MemoryPool()
{
MemoryList *handle = NULL;
while(m_memory_list_header->next != NULL)
{
handle = m_memory_list_header;
m_memory_list_header = m_memory_list_header->next;
free(handle);
}
}
void * MemoryPool::Alloc()
{
static void * handle = NULL;
if (m_memory_list_header->next == NULL)
{
// ÖØзÖÅäÄÚ´æ½øÀ´
MemoryList *handle = NULL;
MemoryList *list = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
if (list == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
list->memory = malloc(m_size);
m_memory_list_header->next = list;
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < m_increase ; ++i)
{
handle = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
if (handle == NULL)
{
break;
}
handle->memory = malloc(m_size);
list->next = handle;
list = list->next;
}
list->next = NULL;
}
handle = m_memory_list_header->memory;
m_memory_list_header = m_memory_list_header->next;
return handle;
}
void MemoryPool::Free(void *m)
{
if (m == NULL)
{
return ;
}
if ( m_handle == NULL)
{
m_handle = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
}
m_handle->memory = m;
m_handle->next = m_memory_list_header;
m_memory_list_header = m_handle;
}
memorypoolconfig.cpp
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?


#include "memorypool.h"
#include "test.h"
REGISTER_MEMORYPOOL(gamememorypool, Test, 64)
Test 类
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?


#ifndef TEST_H
#define TEST_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
class Test
{
public:
Test(){}
~Test(){}
void Show();
void Init();
void * operator new(size_t size);
void operator delete(void *m);
private:
int a;
float b;
char c;
double d;
char * e;
};
#endif
void Test::Init()
{
a = 1;
b = 2;
c = 3;
d = 4;
e = (char *)malloc(16 * sizeof(char));
memcpy(e, "一头汗", sizeof("一头汗"));
}
void Test::Show()
{
printf("%d\n",a);
printf("%f\n",b);
printf("%c\n",c);
printf("%f\n",d);
printf("%s\n",e);
}
下面是测试用例
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?


#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "globalvariable.h"
#include "luaengine.h"
#include "gamesocket.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "dll.h"
#include "MyDll.h"
#include "gametime.h"
#include "frame.h"
#include "datatable.h"
#include "showcrash.h"
#include "globalfunction.h"
#include "commonconfig.h"
#include "scene/areamanager.h"
#include "memorypool/test.h"
class Test1
{
public:
Test1(){}
~Test1(){}
void Show();
void Init();
private:
int a;
float b;
char c;
double d;
char * e;
};
void Test1::Init()
{
a = 1;
b = 2;
c = 3;
d = 4;
e = (char *)malloc(16 * sizeof(char));
memcpy(e, "一头汗", sizeof("一头汗"));
}
void Test1::Show()
{
printf("%d\n",a);
printf("%f\n",b);
printf("%c\n",c);
printf("%f\n",d);
printf("%s\n",e);
}
#define TESTNUM 100000000
int main()
{
clock_t start;
start = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < TESTNUM; ++i)
{
Test *t = new Test;
delete t;
}
printf("use pool = %dms\n",(clock() - start)/1000);
start = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < TESTNUM; ++i)
{
Test1 *t = new Test1;
delete t;
}
printf("normal = %dms\n",(clock() - start)/1000);
return 0;
}
输出结果:

Test类与Test1类不同的是,Test在memorypoolconfig.cpp重载了new/delete。
上面的代码为了方便排版,做了调整,如果有问题可以及时通知我。
如果上面的代码有错误,或者您有更好的方法都可以与我讨论!
交流群:315249378
欢迎交流与讨论!
00:03 1836人阅读 评论(9) 收藏 举报
C++memorypool服务端内存碎片内存池
内存池(Memory Pool)
一、前言
1、操作系统的内存分配方式
1.1、连续分配方式
顾名思义,这种分配方式,会将进程分配在连续的空间。
连续分配方式一般可以分为固定分配方式、动态分配方式和伙伴系统(固定分配方式与动态分配方式的折衷方案)。
1.2、基本分页存储管理方式
1.3、基本分段存储管理方式
注:以上说的分配方式,自个可以到网上去搜索一下,方便理解以下内容。
二、为什么要添加内存池?内存池到底有什么作用?
1、避免内存碎片化。
1.1、什么是内存碎片?
内存碎片就是系统中程序频繁分配内存,会留下许多难以利用、很小的空闲分区,这些小分区被称为“零头”或“碎片”。
1.2、内存碎片的危害。
1.2.1、造成内存的浪费。
这是毫无疑问的。如下图所示。

当第一次分配6KB、6KB和8KB之后,蓝色部分的内被程序释放,系统收回。在之后又被另一个绿色程序分配了4KB。绿色与紫色之间只剩下2KB,当其它程序需要分
配大于2KB时候,剩下的空间不足够,这就成了碎片,浪费内存。极端的情况下会耗尽所有内存(这个情况很少会出现,毕竟现在的内存是白菜价)
1.2.2、降低内存的分配效率
一般来说操作系统都是查找空闲分区表或链表来分配空间的。就像之前说的一样,剩下2KB的碎片(假设不能再被分配),系统每次分配内存的时候都会来判断这
2KB能不能被分配。因此降低了内存的分配效率。
1.3、为什么能避免内存碎片化?
添加内存池,由于内存池会在初始化的时候分配一定长度的空间。因此内存池分配出来的内存结构很可能会像第一次分配出来的结果一样(红、蓝、紫)。而且一
般情况下程序运行过程中,内存池的内存都不会释放,直到程序结束。因此,内存池能很好地避免内存碎片。
2、提高内存分配与释放效率
有了上面的了解,我们知道无论系统的内存分配算法有多么地快速,也是不可能比我们从池中取出来内存快。
在服务端中,C++分配堆内存大小一般是类的长度(new出一个新对象)。因此下面讲解一下定长、列表的内存池。
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?

#ifndef MEMORYPOOL_H
#define MEMORYPOOL_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct MemoryList
{
void * memory;
MemoryList * next;
};
class MemoryPool
{
public:
MemoryPool(unsigned int size, unsigned int increase = 64);
~MemoryPool();
void * Alloc();
void Free(void *m);
private:
unsigned int m_size;
unsigned int m_increase;
MemoryList * m_memory_list_header;
MemoryList * m_handle;
};
#define REGISTER_MEMORYPOOL(PoolNameSpace, ClassName, IncreaseNum) \
namespace PoolNameSpace\
{\
MemoryPool g_##ClassName##_mem_pool(sizeof(ClassName), IncreaseNum);\
}\
void *ClassName::operator new(size_t size)\
{\
void *mem = PoolNameSpace::g_##ClassName##_mem_pool.Alloc();\
return mem;\
}\
void ClassName::operator delete(void *m)\
{\
PoolNameSpace::g_##ClassName##_mem_pool.Free(m);\
}
#endif
memorypool.cpp
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?

#include "memorypool.h"
MemoryPool::MemoryPool( unsigned int size, unsigned int increase /*= 64*/ )
{
m_size = size;
m_increase = increase;
MemoryList *list = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
m_handle = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
if (list == NULL || m_handle == NULL)
{
return;
}
list->memory = malloc(size);
m_memory_list_header = list;
MemoryList *handle = NULL;
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < m_increase * 2; ++i)
{
handle = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
handle->memory = malloc(size);
list->next = handle;
list = list->next;
}
list->next = NULL;
}
MemoryPool::~MemoryPool()
{
MemoryList *handle = NULL;
while(m_memory_list_header->next != NULL)
{
handle = m_memory_list_header;
m_memory_list_header = m_memory_list_header->next;
free(handle);
}
}
void * MemoryPool::Alloc()
{
static void * handle = NULL;
if (m_memory_list_header->next == NULL)
{
// ÖØзÖÅäÄÚ´æ½øÀ´
MemoryList *handle = NULL;
MemoryList *list = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
if (list == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
list->memory = malloc(m_size);
m_memory_list_header->next = list;
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < m_increase ; ++i)
{
handle = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
if (handle == NULL)
{
break;
}
handle->memory = malloc(m_size);
list->next = handle;
list = list->next;
}
list->next = NULL;
}
handle = m_memory_list_header->memory;
m_memory_list_header = m_memory_list_header->next;
return handle;
}
void MemoryPool::Free(void *m)
{
if (m == NULL)
{
return ;
}
if ( m_handle == NULL)
{
m_handle = (MemoryList*)malloc(sizeof(MemoryList));
}
m_handle->memory = m;
m_handle->next = m_memory_list_header;
m_memory_list_header = m_handle;
}
memorypoolconfig.cpp
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?

#include "memorypool.h"
#include "test.h"
REGISTER_MEMORYPOOL(gamememorypool, Test, 64)
Test 类
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?

#ifndef TEST_H
#define TEST_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
class Test
{
public:
Test(){}
~Test(){}
void Show();
void Init();
void * operator new(size_t size);
void operator delete(void *m);
private:
int a;
float b;
char c;
double d;
char * e;
};
#endif
void Test::Init()
{
a = 1;
b = 2;
c = 3;
d = 4;
e = (char *)malloc(16 * sizeof(char));
memcpy(e, "一头汗", sizeof("一头汗"));
}
void Test::Show()
{
printf("%d\n",a);
printf("%f\n",b);
printf("%c\n",c);
printf("%f\n",d);
printf("%s\n",e);
}
下面是测试用例
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?

#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "globalvariable.h"
#include "luaengine.h"
#include "gamesocket.h"
#include "log.h"
#include "dll.h"
#include "MyDll.h"
#include "gametime.h"
#include "frame.h"
#include "datatable.h"
#include "showcrash.h"
#include "globalfunction.h"
#include "commonconfig.h"
#include "scene/areamanager.h"
#include "memorypool/test.h"
class Test1
{
public:
Test1(){}
~Test1(){}
void Show();
void Init();
private:
int a;
float b;
char c;
double d;
char * e;
};
void Test1::Init()
{
a = 1;
b = 2;
c = 3;
d = 4;
e = (char *)malloc(16 * sizeof(char));
memcpy(e, "一头汗", sizeof("一头汗"));
}
void Test1::Show()
{
printf("%d\n",a);
printf("%f\n",b);
printf("%c\n",c);
printf("%f\n",d);
printf("%s\n",e);
}
#define TESTNUM 100000000
int main()
{
clock_t start;
start = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < TESTNUM; ++i)
{
Test *t = new Test;
delete t;
}
printf("use pool = %dms\n",(clock() - start)/1000);
start = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < TESTNUM; ++i)
{
Test1 *t = new Test1;
delete t;
}
printf("normal = %dms\n",(clock() - start)/1000);
return 0;
}
输出结果:

Test类与Test1类不同的是,Test在memorypoolconfig.cpp重载了new/delete。
上面的代码为了方便排版,做了调整,如果有问题可以及时通知我。
如果上面的代码有错误,或者您有更好的方法都可以与我讨论!
交流群:315249378
欢迎交流与讨论!
相关文章推荐
- 监控sql语句执行时间
- python 安装 scrapy 源码 ,并 调试 scrapy-tutorial 工程
- 每日英语:Booming Tech Sector Redraws the Map
- Mobile Web事件(三)
- hdu1520之树形dp
- L/SQL DEVELOPER执行计划的查看
- 如何下载Chrome离线版EXE安装文件和MSI版安装文件
- 不固定列的报表存储过程
- AWS java+play framework2.1
- slf4j-api、slf4j-log4j12以及log4j之间什么关系?
- C++异常处理解析3: 错误处理(返回值, 错误标志变量, 异常)各有千秋
- centos 6.3挂载ntfs格式系统
- VC2005-应用程序正常初始化失败-0xc0150002
- 函数节流2
- 什么是P2P路由模式,有什么优势?
- iOS 中contraints居中对齐的一点心得
- 网页中嵌入播放器embed元素autostart false失效
- CenOS6.5安全加固及性能优化(脚本)
- [Linux] Bash的环境配置文件
- slf4j-api 1.6.x (or later) is incompatible with this binding.解决方案及原理
