Thrift
2013-10-31 23:04
399 查看
[原创](翻译)Java版的各种Thrift server实现的比较
转载请注明出处:http://www.codelast.com/本文是我对这篇文章的翻译:Thrift
Java Servers Compared,为了便于阅读,我将原文附于此处,翻译穿插在其中。此外,为了防止原链接在未来某一天失效后,文中的图片再也看不到的问题,我将原文中的图片也保存到了本站的服务器上,我不知道github或原作者是否允许这样做,但我翻译本文仅在于传播知识的目的,在此向原作者和github表示深深的感谢:感谢你们分享了这样好的文章。
Thrift
Java Servers Compared
This article talks only about Java servers. See this
page if you are interested in C++ servers.
本文仅讨论Java版的Thrift server.如果你对C++版的感兴趣,请参考 这个 页面。
Thrift is
a cross-language serialization/RPC framework with three major components, protocol, transport, and server. Protocol defines how messages are serialized. Transport defines how messages are communicated between client and server. Server receives serialized messages
from the transport, deserializes them according to the protocol and invokes user-defined message handlers, and serializes the responses from the handlers and writes them back to the transport. The modular architecture of Thrift allows it to offer various choices
of servers. Here are the list of server available for Java:
Thrift 是一个跨语言的序列化/RPC框架,它含有三个主要的组件:protocol,transport和server,其中,protocol定义了消息是怎样序列化的,transport定义了消息是怎样在客户端和服务器端之间通信的,server用于从transport接收序列化的消息,根据protocol反序列化之,调用用户定义的消息处理器,并序列化消息处理器的响应,然后再将它们写回transport。Thrift模块化的结构使得它能提供各种server实现。下面列出了Java中可用的server实现:
· TSimpleServer
· TNonblockingServer
· THsHaServer
· TThreadedSelectorServer
· TThreadPoolServer
Having choices is great, but which server is right for you? In this article, I'll describe the differences among all those servers and show benchmark results to illustrate performance characteristics (the details of the benchmark is explained in Appendix B).
Let's start with the simplest one: TSimpleServer.
有多个选择很好,但是哪个适合你呢?在本文中,我将描述这些server之间的区别,并展示测试结果,以说明它们的性能特点(测试的细节在附录B中)。下面,我们就从最简单的开始:TSimpleServer。
文章来源:http://www.codelast.com/
TSimpleServer
TSimpleServer accepts a connection, processes requests from the connection until the client closes the connection, and goes back to accept a new connection. Since it
is all done in a single thread with blocking I/O, it can only serve one client connection, and all the other clients will have to wait until they get accepted. TSimpleServer is mainly used for testing purpose. Don't use it in production!
TSimplerServer接受一个连接,处理连接请求,直到客户端关闭了连接,它才回去接受一个新的连接。正因为它只在一个单独的线程中以阻塞I/O的方式完成这些工作,所以它只能服务一个客户端连接,其他所有客户端在被服务器端接受之前都只能等待。TSimpleServer主要用于测试目的,不要在生产环境中使用它!
文章来源:http://www.codelast.com/
TNonblockingServer vs. THsHaServer
TNonblockingServer solves the problem with TSimpleServer of one client blocking all the other clients by using non-blocking I/O. It usesjava.nio.channels.Selector,
which allows you to get blocked on multiple connections instead of a single connection by calling select().
The select() call returns when one ore more connections are ready to be accepted/read/written. TNonblockingServer handles those connections either by accepting it, reading data from it, or writing data to it, and calls select() again to wait for the next available
connections. This way, multiple clients can be served without one client starving others.
TNonblockingServer使用非阻塞的I/O解决了TSimpleServer一个客户端阻塞其他所有客户端的问题。它使用了java.nio.channels.Selector,通过调用select(),它使得你阻塞在多个连接上,而不是阻塞在单一的连接上。当一或多个连接准备好被接受/读/写时,select()调用便会返回。TNonblockingServer处理这些连接的时候,要么接受它,要么从它那读数据,要么把数据写到它那里,然后再次调用select()来等待下一个可用的连接。通用这种方式,server可同时服务多个客户端,而不会出现一个客户端把其他客户端全部“饿死”的情况。
There is a catch, however. Messages are processed by the same thread that calls select().
Let's say there are 10 clients, and each message takes 100 ms to process. What would be the latency and throughput? While a message is being processed, 9 clients are waiting to be selected, so it takes 1 second for the clients to get the response back from
the server, and throughput will be 10 requests / second. Wouldn't it be great if multiple messages can be processed simultaneously?
然而,还有个棘手的问题:所有消息是被调用select()方法的同一个线程处理的。假设有10个客户端,处理每条消息所需时间为100毫秒,那么,latency和吞吐量分别是多少?当一条消息被处理的时候,其他9个客户端就等着被select,所以客户端需要等待1秒钟才能从服务器端得到回应,吞吐量就是10个请求/秒。如果可以同时处理多条消息的话,会很不错吧?
This is where THsHaServer (Half-Sync/Half-Async server) comes into picture. It uses a single thread for network I/O, and a separate pool of worker threads
to handle message processing. This way messages will get processed immediately if there is an idle worker threads, and multiple messages can be processed concurrently. Using the example above, now the latency is 100 ms and throughput will be 100 requests /
sec.
因此,THsHaServer(半同步/半异步的server)就应运而生了。它使用一个单独的线程来处理网络I/O,一个独立的worker线程池来处理消息。这样,只要有空闲的worker线程,消息就会被立即处理,因此多条消息能被并行处理。用上面的例子来说,现在的latency就是100毫秒,而吞吐量就是100个请求/秒。
To demonstrate this, I ran a benchmark with 10 clients and a modified message handler that simply sleeps for 100 ms before returning. I used THsHaServer with 10 worker threads. The handler looks something like this:
为了演示,我做了一个测试,有10客户端和一个修改过的消息处理器——它的功能仅仅是在返回之前简单地sleep 100毫秒。我使用的是有10个worker线程的THsHaServer。消息处理器的代码看上去就像下面这样:
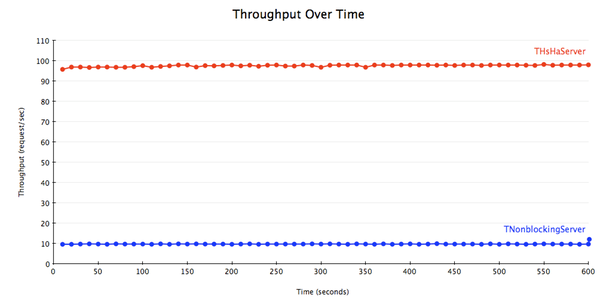
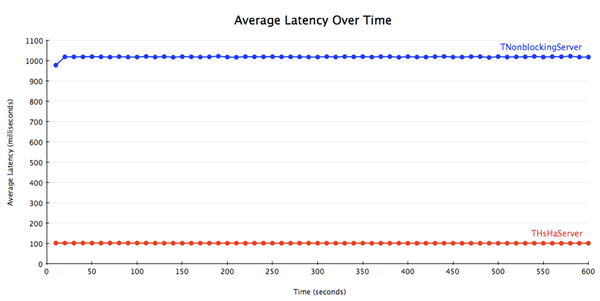
The results are as expected. THsHaServer is able to process all the requests concurrently, while TNonblockingServer processes requests one at a time.
结果正如我们想像的那样,THsHaServer能够并行处理所有请求,而TNonblockingServer只能一次处理一个请求。
文章来源:http://www.codelast.com/
THsHaServer vs. TThreadedSelectorServer
Thrift 0.8 introduced yet another server, TThreadedSelectorServer. The main difference between TThreadedSelectorServer and THsHaServer is that TThreadedSelectorServer
allows you to have multiple threads for network I/O. It maintains 2 thread pools, one for handling network I/O, and one for handling request processing. TThreadedSelectorServer performs better than THsHaServer when the network io is the bottleneck.
To show the difference, I ran a benchmark with a handler that returns immediately without doing anything, and measured the average latency and throughput with varying number of clients. I used 32 worker threads for THsHaServer, and 16 worker threads/16 selector
threads for TThreadedSelectorServer.
Thrift 0.8引入了另一种server实现,即TThreadedSelectorServer。它与THsHaServer的主要区别在于,TThreadedSelectorServer允许你用多个线程来处理网络I/O。它维护了两个线程池,一个用来处理网络I/O,另一个用来进行请求的处理。当网络I/O是瓶颈的时候,TThreadedSelectorServer比THsHaServer的表现要好。为了展现它们的区别,我进行了一个测试,令其消息处理器在不做任何工作的情况下立即返回,以衡量在不同客户端数量的情况下的平均latency和吞吐量。对THsHaServer,我使用32个worker线程;对TThreadedSelectorServer,我使用16个worker线程和16个selector线程。
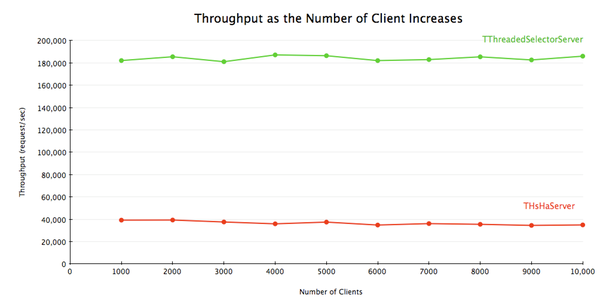
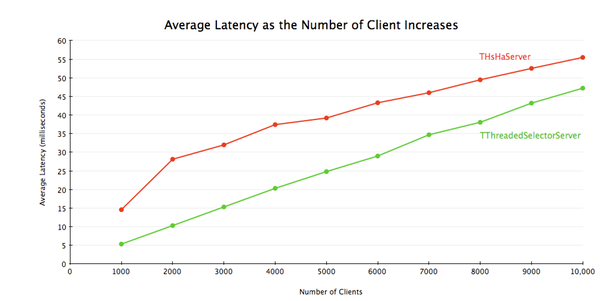
The result shows that TThreadedSelectorServer has much higher throughput than THsHaServer while maintaining lower latency.
结果显示,TThreadedSelectorServer比THsHaServer的吞吐量高得多,并且维持在一个更低的latency上。
文章来源:http://www.codelast.com/
TThreadedSelectorServer vs. TThreadPoolServer
Finally, there is TThreadPoolServer. TThreadPoolServer is different from the other 3 servers in that:
最后,还剩下 TThreadPoolServer。TThreadPoolServer与其他三种server不同的是:
· There is a dedicated thread for accepting connections.
· 有一个专用的线程用来接受连接。
· Once a connection is accepted, it gets scheduled to be processed by a worker thread in ThreadPoolExecutor.
· 一旦接受了一个连接,它就会被放入ThreadPoolExecutor中的一个worker线程里处理。
· The worker thread is tied to the specific client connection until it's
closed. Once the connection is closed, the worker thread goes back to the thread pool.
· worker线程被绑定到特定的客户端连接上,直到它关闭。一旦连接关闭,该worker线程就又回到了线程池中。
· You can configure both minimum and maximum number of threads in the thread pool. Default values are 5 and Integer.MAX_VALUE, respectively.
· 你可以配置线程池的最小、最大线程数,默认值分别是5(最小)和Integer.MAX_VALUE(最大)。
This means that if there are 10000 concurrent client connections, you need to run 10000 threads. As such, it is not as resource friendly as other servers. Also, if the number of clients exceeds the maximum number of threads in the thread pool, requests will
be blocked until a worker thread becomes available.
这意味着,如果有1万个并发的客户端连接,你就需要运行1万个线程。所以它对系统资源的消耗不像其他类型的server一样那么“友好”。此外,如果客户端数量超过了线程池中的最大线程数,在有一个worker线程可用之前,请求将被一直阻塞在那里。
Having said that, TThreadPoolServer performs very well; on the box I'm using it's able to support 10000 concurrent clients without any problem. If you know the number of clients that will be connecting to your server in advance and you don't mind running a
lot of threads, TThreadPoolServer might be a good choice for you.
我们已经说过,TThreadPoolServer的表现非常优异。在我正在使用的计算机上,它可以支持1万个并发连接而没有任何问题。如果你提前知道了将要连接到你服务器上的客户端数量,并且你不介意运行大量线程的话,TThreadPoolServer对你可能是个很好的选择。
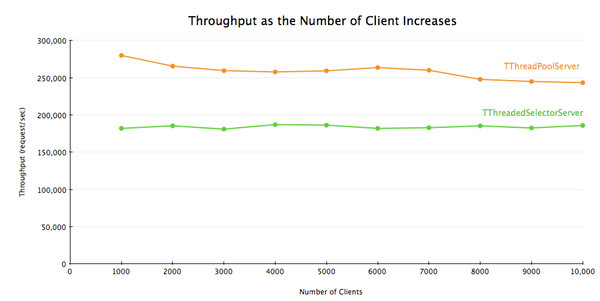
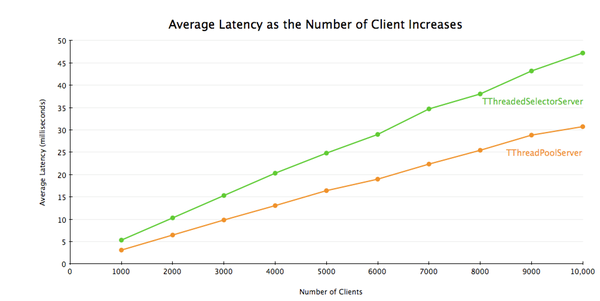
文章来源:http://www.codelast.com/
Conclusion
结论
I hope this article helps you decide which Thrift server is right for you. I think TThreadedSelectorServer would be a safe choice for most of the use cases. You might also want to consider TThreadPoolServer if you can afford to run lots of concurrent threads.
Feel free to send me email atmapkeeper-users@googlegroups.com or post your comments here if
you have any questions/comments.
希望本文能帮你做出决定:哪一种Thrift server适合你。我认为TThreadedSelectorServer对大多数案例来说都是个安全之选。如果你的系统资源允许运行大量并发线程的话,你可能会想考虑使用TThreadPoolServer。(后面的就不翻译了)
Appendix A: Hardware Configuration
It's pretty straightforward to run the benchmark yourself. First clone the MapKeeper repository
and compile the stub java server:
page.
**********************************************************************************************************************************************
设计
Thrift的架构如下:
Thrift采取了很优雅的分层设计,下面简述各层的主要功能:
Ø Transport
负责传输数据的接口,有文件,内存,套接字等实现。
Ø Protocol
负责数据的协议交互接口,有二进制,Json等实现。
Ø Processor
负责输入输出数据处理的接口,其实就是对Protocol的处理。
Ø Server
包括了上面各层的创建和管理,并提供网络服务的功能,网络服务这块目前有四个实现,分别是最简单的单线程阻塞,多线程阻塞,线程池阻塞和基于libevent的非阻塞模式。
http://www.myexception.cn/internet/1179506.html
Thrift的使用与优化
去年一年的时间中,用Thrift提供服务的方式,开发了一个用户中心系统,以便于与其它的各个业务系统进行相应的集成。
在生产环境中,ThriftServer的选择是很重要的。建议在TThreadPoolServer和 TThreadedSelectorServer中进行相应的选择。个人建议选择TThreadedSelectorServer,因为其支持网络NIO,在一个业务的处理过程中,很大一部分时间会阻塞在网络通信上,并且TThreadedSelectorServer能吞吐更多的网络连接,而ThreadPoolServer吞吐的网络连接数和其启动的线程数量有关,如果存在客户端调用代码未正常关闭Transport时,其网络连接只有在时间超时时才会正常释放掉,造成服务的无法正常提供。
http://demohome.blogspot.com/2013/08/thrift.html
Servers andMultithreading
(服务器和多线程)
为处理来自多个客户机的同时的请求,Thrift服务要求基本的多线程。对Thrift服务器逻辑的Python和Java实现来说,随语言发布的标准线程库提供了足够的支持。对C++实现来说,不存在标准的多线程运行时库。具体说来,不存在健壮的、轻量的和可移植的线程管理器及定时器类。为此,Thrift实现了自己的库,如下所述。
Thread
,Runnable andshared_ptr
贯穿ThreadManager和TimerManager的实现,我们使用boost::shared_ptr来保证可被多个线程接入的已死对象的清理。
线程创建要求调用一个C库。典型地,操作系统几乎不能保证C线程的进入点函数ThreadMain何时会被调用。因此,我们的线程创建调用——ThreadFactory::newThread()可能在操作系统调用ThreadMain之前就返回给调用者。如果调用者在ThreadMain调用之前放弃了对线程的引用,为确保返回的线程对象不会被过早地清理,线程对象在它的start方法中制造了一个指向它自身的弱引用。
有了这个弱引用,ThreadMain函数能够在进入绑定到该线程的Runnable对象的Runnable::run方法之前,尝试获得一个强引用。倘若在离开Thread::start和进入ThreadMain之间,没能获得对该线程的强引用,那么弱引用返回null,函数将立刻退出。
线程制造一个对它自身的弱引用的需求,对API有着重大影响。因为引用是通过boost::shared_ptr模板管理的,线程对象必须有一个返回给调用者的、同样以boost::shared_ptr封装的指向它自身的引用。这需要使用工厂模式。ThreadFactory创建一个原始的线程对象,以及一个boost::shared_ptr包装器,并调用实现了Thread接口的类的一个私有helper方法,以使它能够通过boost::shared_ptr封装制造添加对它自身的弱引用。
Thread和Runnable对象彼此互相引用。一个Runnable对象可能需要知道它在其中执行的线程的信息,而一个Thread显然也需要知道它正在主持什么Runnable对象。这一相关性非常复杂,因为各对象的生命周期与其它对象是不相关的。一个应用可能创建一组Runnable对象,重用在不同线程里,或者它可能创建一个Runnable对象,一旦有一个线程为之创建并启动,它可能会忘记这个Runnable对象。
Thread类在它的构造函数中,使用一个boost::shared_ptr引用它所主持的Runnable对象,而Runnable类有显式的thread方法(ThreadFactory::newThread),允许地显式绑定主持的线程。
ThreadManager
ThreadManager创建一池工作者线程,一旦有空闲的工作者线程,应用就可以调度任务来执行。ThreadManager并未实现动态线程池大小的调整,但提供了原语,以便应用能基于负载添加和移除线程。Thrift把复杂的API抽象留给特定应用,提供原语以制定所期望的政策,并对当前状态进行采样。
相关文章推荐
- C程序的内存分配
- SQL_TRACE及 Tkprof用法以及问题分析
- oracle笔记系列(一)
- 才高行厚的hibernate(4)---hibernate的HQL语言
- IOS越狱开发(三)------DEB生成和apt建立
- IOS越狱开发(三)------DEB生成和apt建立
- Sql Server Job 简单使用
- Linux bridge 网桥模块内部数据包转发流程
- Oracle使用ssh导出库报字符集不正确
- EFCodeFirst安装失败(包括EntityFrameWork安装),这样解决。。。
- 驱动保护中的ObjectType_Callback探索
- 《深入理解Java虚拟机》笔记
- show drop down menu within/from action bar
- java类库的阅读笔记_jdk1.7.0_40_java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport
- 封装DLL
- 【帧中继】帧中继基础配置
- 大数除法
- AsyncTask异步加载图片(显示进度条刻度)
- utf-8和GBK中文字符的长度计算
- oracle数据库查询锁及解锁
