设计模式:如何使用观测者模式实现监控和推送
2013-09-05 23:16
791 查看
观测者模式已在博客"设计模式之观测者模式"中介绍,下面说下如何将观察者模式应用在实际工作中。
这里很适合用观测者模式来解决,其中subject的功能是监控目录变化,和通知观测者变化的数据。观测者的功能是上传新的数据到FTP服务器,这里有多个观测者,而且虽这业务的发展,观察者的数目是变化的。
采用观测者模式,可以在不修改代码的情况下,很容易的添加观测者。
观测者类:上传数据到服务器
现在看下如何使用
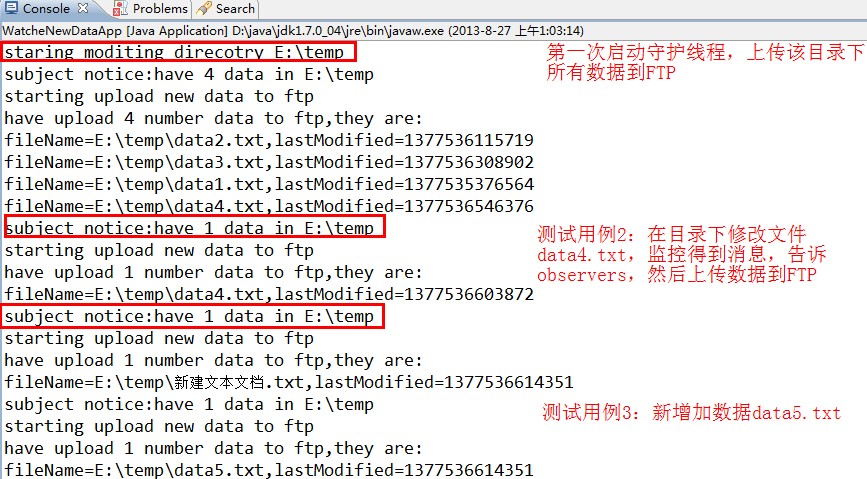
运行main函数,结果如下
sunbject类:只需要修改logicMethod方法中的业务逻辑即可。
observer类:只需要在update方法中写入你的业务逻辑即可
如何使用呢?见代码
上面的例子和模版已共享,点击下载。


问题描述
某业务系统会定期接收到传回来的数据,数据放在一个目录下。由于业务的需要,当有新的数据产生时,需要将数据上传到多台机器上。你如何设计这个业务逻辑呢?功能设计
放在目录下的数据时不断更新的,我们需要一个守护线程来监控目录下数据的变化,当有新数据时就通知观测者observers。这里的观测者是需要将数据上传到FTP服务器的对象,当有新数据产生时,就上传数据到FTP服务器。这里很适合用观测者模式来解决,其中subject的功能是监控目录变化,和通知观测者变化的数据。观测者的功能是上传新的数据到FTP服务器,这里有多个观测者,而且虽这业务的发展,观察者的数目是变化的。
采用观测者模式,可以在不修改代码的情况下,很容易的添加观测者。
详细设计
监控目录变化的subject:import java.io.File;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Observable;
import zyang.designPattern.observerPattern.Observer;
import zyang.designPattern.observerPattern.Subject;
/**
* Fuction:
* 一个守护线程,用户监控目录下是否有新数据
* 如果有新数据,通知监听对象observers
* @author zhonghua
* @version 2013-3-20 下午9:25:56
* @since 1.0
*/
public class DirectoryMonitorSubject extends Observable implements Runnable {
// -------------------------------------------------
// properties
// -------------------------------------------------
/**
* Whether or not this thread is active.
*/
private boolean active = false;
/**
* The interval in seconds to run this thread
*/
private int interval = -1;
/**
* The name of this thread
*/
private String threadName;
/**
* This instance's thread
*/
private Thread runner;
/**
* 监控目录
*/
private String directoryFullPath;
/**
* The map of last recorded files and their timestamps (String fileName => Long lastMod)
*/
private Map prevDatas=new HashMap<String, Long>();
/**
* The map of current files and their timestamps (String fileName => Long lastMod)
*/
private Map currentDatas=new HashMap<String, Long>();
/**
* The map of new files and their timestamps (String fileName => Long lastMod)
*/
private Map newDatas=new HashMap<String, Long>();
// -------------------------------------------------
// constructor
// -------------------------------------------------
/**
* Construct a new interval thread that will run on the given interval
* with the given name.
* @param threadName the name of the thread
* @param directoryFullPath
* @param interval the number of seconds to run the thread on
*/
public DirectoryMonitorSubject(String threadName,String directoryFullPath, int interval) {
this.threadName=threadName;
this.directoryFullPath=directoryFullPath;
this.interval=interval;
System.out.println("staring moditing direcotry "+directoryFullPath);
}
// -------------------------------------------------
// public method
// -------------------------------------------------
/**
* Start the thread on the specified interval.
*/
public void start() {
active = true;
//If we don't have a thread yet, make one and start it.
if (runner == null && interval > 0) {
runner = new Thread(this);
runner.start();
}
}//end start()
/**
* Stop the interval thread.
*/
public void stop() {
active = false;
} //end stop()
public void run() {
//Make this a relatively low level thread
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
//Pause this thread for the amount of the interval
while(active){
try {
setNewDatas();
Thread.sleep(interval); //监控时间间隔
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}//end while
}//end run
public void direcotryChanged(){
setChanged();
notifyObservers(newDatas); //将新增加的数据传给observers
} //end temperatureChanged()
//监控目录下是否有新数据,如果有新数据就传给observers
public void setNewDatas(){
if(checkNewDatas()){ //目录下有新数据
System.out.println("subject notice:have "+newDatas.size()+" data in "+directoryFullPath);
direcotryChanged();
}//end if
} //end setNewDatas()
// -------------------------------------------------
// private method
// -------------------------------------------------
/**
* 检查目录下是否有新的数据(线程会反复调用该方法),并将新数据放入newDatas
* @return 如果有新的数据返回ture,否则返回false
*/
private boolean checkNewDatas(){
boolean isHaveNewData=false;
//清空先前的数据
prevDatas.clear();
newDatas.clear();
//将上次的数据先保存在 prevDatas
prevDatas.putAll(currentDatas);
currentDatas.clear(); //清空数据
//添加当前目录下的数据到currentDatas
File direcotryFile=new File(directoryFullPath);
File[] filesList=direcotryFile.listFiles();
for(File file:filesList){
currentDatas.put(file.getAbsolutePath(), new Long(file.lastModified()));
}//end for
//将当前目录下数据与先前目录下数据进行比较
Iterator currentIt=currentDatas.keySet().iterator();
while(currentIt.hasNext()){
String fileName=(String)currentIt.next();
Long lastModified = (Long) currentDatas.get(fileName);
if(!prevDatas.containsKey(fileName)){
newDatas.put(fileName, lastModified);
}//end if
else if(prevDatas.containsKey(fileName)){
Long prevModified = (Long) prevDatas.get(fileName);
if (prevModified.compareTo(lastModified) != 0){
newDatas.put(fileName, lastModified);
}//end if
}//end if
}//end while
if(newDatas.size()>0)
isHaveNewData=true;
return isHaveNewData;
}//end checkNewDatas()
}//end DirectoryWatcher观测者类:上传数据到服务器
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Observable;
import java.util.Observer;
/**
* Fuction:
*
* @author zhonghua
* @version 2013-3-20 下午9:38:54
* @since 1.0
*/
public class DataObserver implements Observer {
private Observable observable;
private Map newDatas=new HashMap<String, Long>(); //新增加的数据
// -------------------------------------------------
public DataObserver(Observable observable){
this.observable=observable;
observable.addObserver(this);
}
// -------------------------------------------------
//当得到subject的通知,做something,上传数据到FTP
public void update(Observable obs, Object dataFromSubject) {
if(obs instanceof DirectoryMonitorSubject){
DirectoryMonitorSubject dw=(DirectoryMonitorSubject)obs;
newDatas.clear(); //先清空数据
newDatas.putAll((Map)dataFromSubject);
uploadData();
}//end if
}//end update()
/**
* 上传新数据到FTP
*/
private void uploadData(){
System.out.println("starting upload new data to ftp");
//这里就不写真正上传的代码了,直接输出
System.out.println("have upload "+newDatas.size()+" number data to ftp,they are:");
Iterator newDatasIt=newDatas.keySet().iterator();
while(newDatasIt.hasNext()){
String fileName=(String)newDatasIt.next();
Long lastModified=(Long)newDatas.get(fileName);
System.out.println("fileName="+fileName+",lastModified="+lastModified.toString());
}//end while
}//end loadNewData()
} //end class FileListener现在看下如何使用
import zyang.DirectoryMonitor.DataObserver;
import zyang.DirectoryMonitor.DirectoryMonitorSubject;
/**
* Fuction:
* How to use subject and observers
* @author zhonghua
* @since 1.0
*/
public class WatcheNewDataApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//subject
DirectoryMonitorSubject wp=new DirectoryMonitorSubject("moniteDirectory","E:\\temp", 2000);
//observers
DataObserver fl=new DataObserver(wp);
wp.start(); //开启监控守护线程
}//end main()
}//end class WatcheNewDataApp运行main函数,结果如下

观测者模式模版
下面写了一个通用的观测者模式模版代码,用户只需要在对应地方加入自己的业务逻辑即可sunbject类:只需要修改logicMethod方法中的业务逻辑即可。
public class YourSubject extends Observable {
// -------------------------------------------------
// constructor
// -------------------------------------------------
public YourSubject() {
}
/**
* Must have this method's content, this method is called by the logicMethod.
* of course,you can change this method's name
*/
public void informationChanged(){
setChanged();
notifyObservers();
//该方法的参数用于subject和observers传递数据,向observers传递数据,observers在其update方法中使用传过来的数据
// notifyObservers(dataSendToObservers)
} //end informationChanged()
/**
* the subject only need do one thing: write your logic in this method
*/
public void logicMethod(){
//write your logic code here
//TODO
System.out.println("subject notice:monitor information has changed, observers can do their things now."); //for example
//end TODO
informationChanged();
} //end logicMethod()
} //end class YourSubjectobserver类:只需要在update方法中写入你的业务逻辑即可
public class OneObserver implements Observer {
private Observable observable;
// -------------------------------------------------
// constructor
// -------------------------------------------------
public OneObserver(Observable observable){
this.observable=observable;
observable.addObserver(this);
}
/**
* the observer only need do one thing: write your logic in this method
*/
public void update(Observable obs, Object dataFromSubject) {
if(obs instanceof YourSubject){
YourSubject yourSubject=(YourSubject)obs;
//write your logic code here
//TODO
System.out.println("observer:have upload to ftp"); //for example
}//end if
}//end update
}//end class OneObserver如何使用呢?见代码
/**
* Fuction:
* the example shows how to use subject object and observers objects
* @author zhonghua
* @version 2013-8-26 下午9:25:56
* @since 1.0
*/
public class UseApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//subject
YourSubject wp=new YourSubject();
//observers
OneObserver clientA=new OneObserver(wp);
//notify observers,and observers do their things after have the notice
wp.logicMethod();
}//end main()
}上面的例子和模版已共享,点击下载。
推送功能
现在很多手机软件的推送功能,比如百度新闻,微信公众平台,其实很适合用观测者模式。发消息的服务端即时subject,接收消息的观测者observers即手机软件使用者。服务端监控消息,当有消息时通知多个观测者,并发送消息给观测者。

相关文章推荐
- 如何使用观测者模式实现监控和推送
- 项目开发中的一些注意事项以及技巧总结 基于Repository模式设计项目架构—你可以参考的项目架构设计 Asp.Net Core中使用RSA加密 EF Core中的多对多映射如何实现? asp.net core下的如何给网站做安全设置 获取服务端https证书 Js异常捕获
- 如何使用三层架构设计模式去完整的实现一个功能?
- 设计模式-观察者模式,以及如何使用观察者来为app实现即时通讯功能
- 如何使用Spring Cloud实现高并发微服务设计 - PaaS云
- DAO设计模式 -- 使用数据库连接类连接MySql数据库并实现添加用户
- 如何使用 Cloud Insight SDK 实现 Druid 监控?
- 实例讲解如何在iOS应用开发中使用设计模式中的代理模式
- 第6章 使用一等函数实现设计模式
- 如何使用设计模式系列
- 求助:TelephonyManager.listen 监听使用的问题--如何实现TM同时监控多个状态的改变
- 使用C++实现设计模式(连载): 第一回 Singleton 单例模式
- 如果设计中使用了非标准的字体,你该如何去实现?
- 设计模式应用之使用COMPOSITE模式实现流程(四)
- 使用 IBM 中间件实现 SaaS 解决方案,第 4 部分: 单一实例多租户应用程序中资源共享的设计模式
- 设计模式应用之使用COMPOSITE模式实现流程(三)
- 如何使用设计模式来构造系统--(4)
- 如何使用 Java8 实现观察者模式?(上)
- 使用单例和工厂设计模式实现dao实现层的解耦
- (转载)如何将多种设计模式结合使用(有原代码)
