hdu 4288 Coder(线段树)
2013-08-18 23:24
471 查看
Coder
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2165 Accepted Submission(s): 882
Problem Description
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm describes a set of procedures or instructions that define a procedure. The term has become increasing popular since the advent of cheap and reliable computers. Many companies now employ a single coder to write
an algorithm that will replace many other employees. An added benefit to the employer is that the coder will also become redundant once their work is done. 1
You are now the signle coder, and have been assigned a new task writing code, since your boss would like to replace many other employees (and you when you become redundant once your task is complete).
Your code should be able to complete a task to replace these employees who do nothing all day but eating: make the digest sum.
By saying “digest sum” we study some properties of data. For the sake of simplicity, our data is a set of integers. Your code should give response to following operations:
1. add x – add the element x to the set;
2. del x – remove the element x from the set;
3. sum – find the digest sum of the set. The digest sum should be understood by
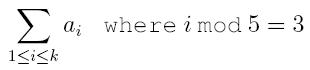
where the set S is written as {a1, a2, ... , ak} satisfying a1 < a2 < a3 < ... < ak
Can you complete this task (and be then fired)?
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 See http://uncyclopedia.wikia.com/wiki/Algorithm
Input
There’re several test cases.
In each test case, the first line contains one integer N ( 1 <= N <= 105 ), the number of operations to process.
Then following is n lines, each one containing one of three operations: “add x” or “del x” or “sum”.
You may assume that 1 <= x <= 109.
Please see the sample for detailed format.
For any “add x” it is guaranteed that x is not currently in the set just before this operation.
For any “del x” it is guaranteed that x must currently be in the set just before this operation.
Please process until EOF (End Of File).
Output
For each operation “sum” please print one line containing exactly one integer denoting the digest sum of the current set. Print 0 if the set is empty.
Sample Input
9 add 1 add 2 add 3 add 4 add 5 sum add 6 del 3 sum 6 add 1 add 3 add 5 add 7 add 9 sum
Sample Output
3 4 5 HintC++ maybe run faster than G++ in this problem.
Source
2012 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Chengdu Online
Recommend
liuyiding
题意:插入或删除一个数,并维护其序列升序,询问为对序列的下标mod 5 余数为3的数求和
题解:离线操作,先读入所有数据,离散化构建线段树,线段树维护该区间个数,和mod 5 余数为0~4的求和,更新父节点sum值的时候偏转一下就好了
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,a[100008],has[100008];
char s[100008][5];
struct node{
__int64 sum[5],cou;
}t[400008];
void build(int l,int r,int pos)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
memset(t[pos].sum,0,sizeof(t[pos].sum));
t[pos].cou=0;
if(l==r) return;
build(l,mid,pos<<1);
build(mid+1,r,pos<<1|1);
}
void updata(int l,int r,int pos,int tag,int val)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1,temp,i;
t[pos].cou+=val;
if(l==r)
{
t[pos].sum[1]=(val==1?has[l]:0);
return;
}
if(tag<=mid) updata(l,mid,pos<<1,tag,val);
else updata(mid+1,r,pos<<1|1,tag,val);
temp=t[pos<<1].cou;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
t[pos].sum[i]=t[pos<<1].sum[i]+t[pos<<1|1].sum[((i-temp)%5+5)%5];
}
int main()
{
int temp,all;
while(scanf("%d",&n)>0)
{
all=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s",s[i]);
if(s[i][0]=='a'||s[i][0]=='d')
{
scanf("%d",a+i);
has[all++]=a[i];
}
}
sort(has,has+all);
all=unique(has,has+all)-has;
build(0,all-1,1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(s[i][0]!='s') temp=lower_bound(has,has+all,a[i])-has;
if(s[i][0]=='a') updata(0,all-1,1,temp,1);
else if(s[i][0]=='d') updata(0,all-1,1,temp,-1);
else printf("%I64d\n",t[1].sum[3]);
}
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- HDU 4288 Coder [线段树]
- HDU 4288 Coder ( 离散化 + 离线 + 线段树 )
- HDU 4288 Coder 线段树
- HDU 4288 Coder 线段树||暴力
- HDU 4288 Coder (线段树)
- HDU 4288 Coder(线段树)
- HDU-4288 Coder 线段树
- hdu 4288(线段树) Coder
- HDU 4288 Coder 【线段树+离线处理+离散化】
- HDU 4288 Coder(12年成都 线段树)
- HDU-4288 Coder 线段树
- HDU 4288 Coder(线段树或者暴力vector)#by zh
- HDU 4288 Coder 线段树维护区间%5的和
- HDU 4288 Coder(线段树)
- hdu-4288-Coder-线段树
- HDU 4288 Coder 【线段树+离线处理+离散化】
- hdu 4288 Coder(树形结构-线段树)
- hdu 4288 Coder(线段树)
- HDU 4288 Coder 线段树
- HDU-4288-Coder(线段树)
