Java Collection 接口描述(一)
2013-06-04 15:31
351 查看
物件容器(container)
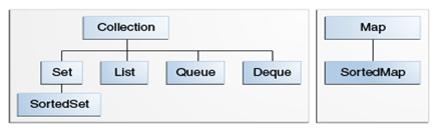
Collection接口分装了不同类型的容器,可以看上图所示。
物件容器可以帮你持有对象。在Java中分作两大类: Collection和Map。前者可持有各自独立的物件,后者持有承兑的key-value物件。
注意所有的核心collection接口是通用的,如何申明一个Collection接口:
Iterator<LinkedList> iterator=collections.iterator();
Collection类包括了List类与Set类,List以放置物件至容器中的顺序来排列物件,Set类不接受重复的物件,并有自己的一套排序规则。
ArrayList:
动态数组,Array的复杂版本,好处在于动态的增加和减少元素;实现了ICollection和IList接口;灵活的设置数组的大小。
ArrayList list1=new
ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
list1.add(i);
}
list1.remove(5);
list1.add(10);
for(int i=0;i<list1.size();i++){
System.out.println(list1.get(i));
}
Output:
0
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10
LinkedList:
HashSet:
SortedSet:
LinkedHashSet:
TreeSet:
EnumSet:
Map类:在将物件存入Map类时,需要配合一把key,要取回物件时就是根据这把key,Map中的key是唯一的,Map拥有自己的排序机制。
HashMap:
TreeMap:
EnumMap:
LinkedHashMap:
算法
1. Sorting:对容器内的元素进行排序
List<String> list =
Arrays.asList(args);
java.util.Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
Argument: I like hangzhou forever
Output: [Hangzhou, I, forever, like]
2. Iterator循环
HashSet collections =
new
HashSet();
String str1="red";
String str2="blue";
String str3="yellow";
String str4="White";
collections.add(str1);
collections.add(str2);
collections.add(str3);
collections.add(str4);
Iterator iterator=collections.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
Output: White
red
blue
yellow

Collection接口分装了不同类型的容器,可以看上图所示。
物件容器可以帮你持有对象。在Java中分作两大类: Collection和Map。前者可持有各自独立的物件,后者持有承兑的key-value物件。
注意所有的核心collection接口是通用的,如何申明一个Collection接口:
Iterator<LinkedList> iterator=collections.iterator();
Collection类包括了List类与Set类,List以放置物件至容器中的顺序来排列物件,Set类不接受重复的物件,并有自己的一套排序规则。
ArrayList:
动态数组,Array的复杂版本,好处在于动态的增加和减少元素;实现了ICollection和IList接口;灵活的设置数组的大小。
ArrayList list1=new
ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
list1.add(i);
}
list1.remove(5);
list1.add(10);
for(int i=0;i<list1.size();i++){
System.out.println(list1.get(i));
}
Output:
0
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10
LinkedList:
HashSet:
SortedSet:
LinkedHashSet:
TreeSet:
EnumSet:
Map类:在将物件存入Map类时,需要配合一把key,要取回物件时就是根据这把key,Map中的key是唯一的,Map拥有自己的排序机制。
HashMap:
TreeMap:
EnumMap:
LinkedHashMap:
算法
1. Sorting:对容器内的元素进行排序
List<String> list =
Arrays.asList(args);
java.util.Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
Argument: I like hangzhou forever
Output: [Hangzhou, I, forever, like]
2. Iterator循环
HashSet collections =
new
HashSet();
String str1="red";
String str2="blue";
String str3="yellow";
String str4="White";
collections.add(str1);
collections.add(str2);
collections.add(str3);
collections.add(str4);
Iterator iterator=collections.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
Output: White
red
blue
yellow
相关文章推荐
- Java Collection Framework : Collection 接口
- 疯狂java学习笔记1030---Collection、Iterator接口和Set接口
- 黑马程序员_Java集合-Collection<T>接口
- Java集合之Collection接口
- java之Collection接口讲解
- 黑马程序员--Java学习日记之集合(collection类与list接口)及泛型概述
- Java中Collection和Iterator接口
- Java集合概述集Collection 和 Iterator 接口用法详解
- 【java读书笔记】——Collection集合之六大接口(Collection、Set、List、Map、Iterator和Comparable)
- 【java集合一】根接口Collection、Map
- Java基础-集合框架2 Collection和Iterator接口
- JAVA中的集合类接口——Collection
- java Collection接口
- java_集合体系之Collection框架相关抽象类接口详解、源码——02
- Java容器深入浅出之Collection与Iterator接口
- Java API ——Collection集合类 & Iterator接口
- java——深入java.util包(collection接口之AbstractList)
- Java中Collection子接口(1)——List接口(传智播客毕老师视频讲解)
- 关于java的collection框架我们最应该知道的两个接口和四个实现类
- java中的集合的根接口Collection以及迭代器
