[置顶] Linux 设备驱动篇之I2c设备驱动
2013-06-02 20:24
549 查看
Linux 设备驱动篇之I2c设备驱动fulinux一、I2C驱动体系虽然I2C硬件体系结构和协议都很容易理解,但是Linux I2C驱动体系结构却有相当的复杂度,它主要由3部分组成,即I2C设备驱动、I2C总线驱动和I2C核心。
1.I2C核心I2C核心是I2c总线和I2c设备驱动的中间枢纽,它以通用的、与平台无关的接口实现了I2C中设备与适配器的沟通,提供了I2C总线驱动和设备驱动的注册、注销方法,I2C通信方法(即“algorithm”)上层的、与具体适配器无关的代码以及探测设备、检测设备的地址的上层代码等。I2c总线驱动填充I2c_adapter和I2c_algorithm结构体,I2c设备驱动填充I2c_driver和i2c_client结构体并实现其本身所对应设备类型的驱动。
2.I2C总线驱动I2C总线驱动是对I2C硬件体系结构中适配器的实现,适配器可由CPU控制,甚至可以直接集成在CPU内部。
I2C总线驱动主要包含了I2C适配器数据结构i2c_adapter、I2C适配器的algorithm数据结构i2c_algorithm和控制I2C适配器产生通信信号的函数。
经由I2C总线驱动的代码,我们可以控制I2C适配器以主控制方式产生开始、停止位、读写周期,以及以从设备方式读写、产生ACK等。
3.I2C设备驱动I2C设备驱动(也称为客户端驱动)是对I2C硬件体系结构中设备端的实现,设备一般挂接在受CPU控制的I2C适配器上,通过I2C适配器与CPU交换数据。
I2C设备驱动主要包含了数据结构体i2c_driver和i2c_client,我们需要具体设备实现其中的成员函数。
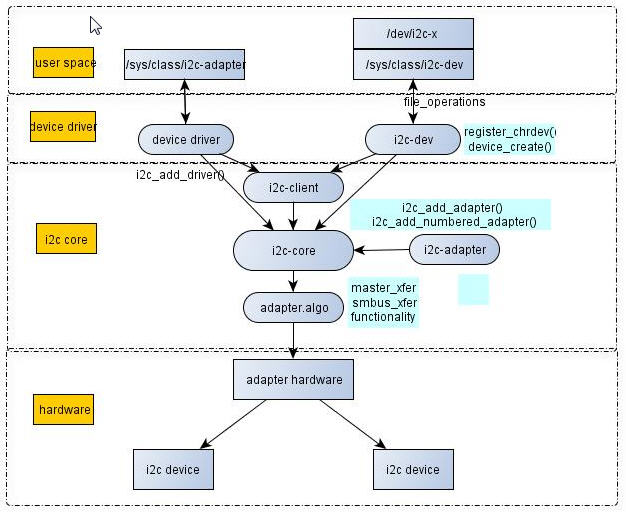
[align=left] [/align]
图1 I2C驱动体系结构图1
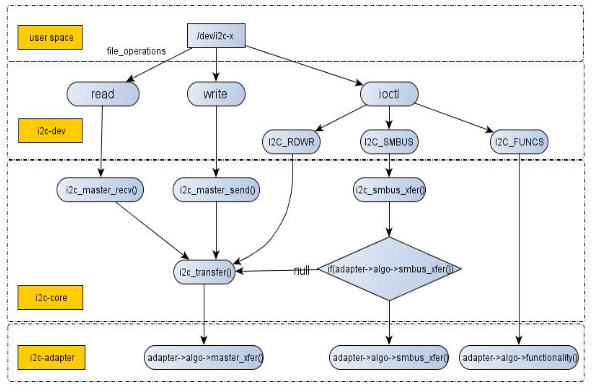
[align=left] [/align]
图2 I2C驱动体系结构图2
另外,系统中i2c-dev.c文件定义的主设备号为89的设备可以方便地给应用程序提供读写I2c设备寄存器的能力,使得工程师大多数时候并不需要为具体的I2c设备驱动定义文件操作接口。
如何理解adapter和client呢?它在s3c2440中对应的是什么?Adapter和client都是linux驱动软件抽象出来的东西,Linux I2C框架搞那么复杂是为了通用性及为了符合Linux内核驱动模式而制定的。简单的说,你的开发板上有几个I2C接口,就有几个adapter , 也就是有几条I2C bus , I2C client对应的就是你的外围I2C 设备,有几个就有几个client , 把这些设备插入开发板, 对应其中的一条bus, 那么相应的就对应了其中的一个adapter , 接下来的就是I2c核心部分使client与 adapter匹配成对。
在linux内核中,所有的I2C设备都在sysfs文件系统中显示,存在于/sys/bus/i2c/目录下,适配器地址和芯片地址的形式列出,例如:1. [fulinux@ubuntu linux-3.0]$ tree /sys/bus/i2c/ 2. /sys/bus/i2c/3. |-- devices4. | |-- i2c-0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-05. | |-- i2c-1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-16. | |-- i2c-2 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-27. | |-- i2c-3 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-38. | |-- i2c-4 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-49. | |-- i2c-5 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-510. | |-- i2c-6 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/drm/card0/card0-DP-1/i2c-611. | `-- i2c-7 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/drm/card0/card0-DP-2/i2c-712. |-- drivers13. | |-- 88PM860x14. | | |-- bind15. | | |-- uevent16. | | `-- unbind17. | |-- aat287018. | | |-- bind19. | | |-- uevent20. | | `-- unbind21. | |-- ab310022. | | |-- bind23. | | |-- uevent24. | | `-- unbind25. | |-- adp5520
下面我以s3c2440开发板及其之上的EEPROM芯片AT24C02和linux-3.0内核平台讲解I2c的三个部分。
********************************************************************************************转载声明:希望大家能转载此文谢谢 原文链接
********************************************************************************************
4.s3c2440和at24c02硬件特性请看s3c2440.pdf
芯片AT24C02的电气特性:• Low-voltage and Standard-voltage Operation– 2.7 (VCC= 2.7V to 5.5V)– 1.8 (VCC= 1.8V to 5.5V)• Internally Organized 128 x 8 (1K), 256 x 8 (2K), 512 x 8 (4K),1024 x 8 (8K) or 2048 x 8 (16K)• Two-wire Serial Interface• Schmitt Trigger, Filtered Inputs for Noise Suppression• Bidirectional Data Transfer Protocol• 100 kHz (1.8V) and 400 kHz (2.7V, 5V) Compatibility• Write Protect Pin for Hardware Data Protection• 8-byte Page (1K, 2K), 16-byte Page (4K, 8K, 16K) Write Modes• Partial Page Writes Allowed• Self-timed Write Cycle (5 ms max)• High-reliability– Endurance: 1 Million Write Cycles– Data Retention: 100 Years• Automotive Grade and Lead-free/Halogen-free Devices Available• 8-lead PDIP, 8-lead JEDEC SOIC, 8-lead MAP, 5-lead SOT23,8-lead TSSOP and 8-ball dBGA2 Packages• Die Sales: Wafer Form, Waffle Pack and Bumped Wafers
主要是看AT24C02.pdf
图3 S3c244开发板核心板电路图
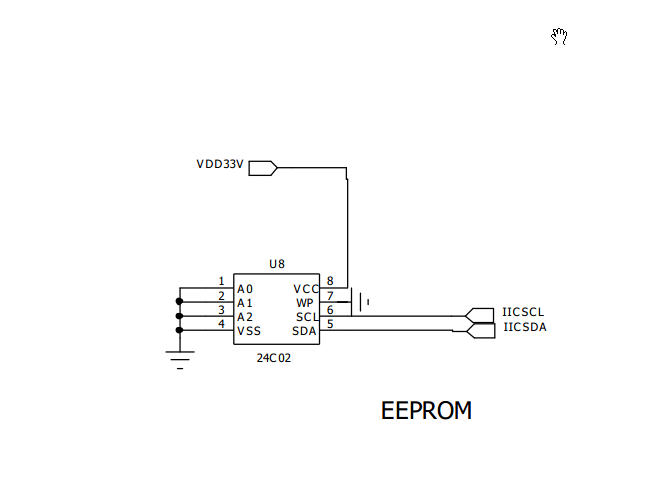
图4 AT24C02电路图
5.i2c.h头文件内核中i2c.h这个头文件对i2c_driver、i2c_client、i2c_adapter和i2c_algorithm着4个数据结构进行了定义。理解这4个结构的作用十分关键,代码清单1、2、3、4分别给出了它们的定义。
代码清单1 i2c_adapter结构体
1. /*2. * i2c_adapter is the structure used to identify a physical i2c bus along3. * with the access algorithms necessary to access it.4. */5. struct i2c_adapter {6. struct module *owner;7. unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */8. const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */9. void *algo_data;10. /* data fields that are valid for all devices */11. struct rt_mutex bus_lock;12. int timeout; /* in jiffies */13. int retries;14. struct device dev; /* the adapter device */15. int nr;16. char name[48];17. struct completion dev_released;18. struct mutex userspace_clients_lock;19. struct list_head userspace_clients;20. };
代码清单2 i2c_algorithm结构体1. /*2. * The following structs are for those who like to implement new bus drivers:3. * i2c_algorithm is the interface to a class of hardware solutions which can4. * be addressed using the same bus algorithms - i.e. bit-banging or the PCF85845. * to name two of the most common.6. */7. struct i2c_algorithm {8. /* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer9. to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set10. smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated11. using common I2C messages */12. /* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully13. processed, or a negative value on error */14. int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs,15. int num);16. int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,17. unsigned short flags, char read_write,18. u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);19. /* To determine what the adapter supports */20. u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adapter *);21. };
上述代码第4行对应为SMBus传输函数指针,SMBus大部分基于I2C总线规范,SMBus不需要增加额外引脚。与I2C总线相比,SMBus增加了一些新的功能特性,在访问时序也有一定的差异。
代码清单3 i2c_driver结构体1. /*2. * struct i2c_driver - represent an I2C device driver3. * @class: What kind of i2c device we instantiate (for detect)4. * @attach_adapter: Callback for bus addition (deprecated)5. * @detach_adapter: Callback for bus removal (deprecated)6. * @probe: Callback for device binding7. * @remove: Callback for device unbinding8. * @shutdown: Callback for device shutdown9. * @suspend: Callback for device suspend10. * @resume: Callback for device resume11. * @alert: Alert callback, for example for the SMBus alert protocol12. * @command: Callback for bus-wide signaling (optional)13. * @driver: Device driver model driver14. * @id_table: List of I2C devices supported by this driver15. * @detect: Callback for device detection16. * @address_list: The I2C addresses to probe (for detect)17. * @clients: List of detected clients we created (for i2c-core use only)18. *19. * The driver.owner field should be set to the module owner of this driver.20. * The driver.name field should be set to the name of this driver.21. *22. * For automatic device detection, both @detect and @address_data must23. * be defined. @class should also be set, otherwise only devices forced24. * with module parameters will be created. The detect function must25. * fill at least the name field of the i2c_board_info structure it is26. * handed upon successful detection, and possibly also the flags field.27. *28. * If @detect is missing, the driver will still work fine for enumerated29. * devices. Detected devices simply won't be supported. This is expected30. * for the many I2C/SMBus devices which can't be detected reliably, and31. * the ones which can always be enumerated in practice.32. *33. * The i2c_client structure which is handed to the @detect callback is34. * not a real i2c_client. It is initialized just enough so that you can35. * call i2c_smbus_read_byte_data and friends on it. Don't do anything36. * else with it. In particular, calling dev_dbg and friends on it is37. * not allowed.38. */39. struct i2c_driver {40. unsigned int class;41. /* Notifies the driver that a new bus has appeared or is about to be42. * removed. You should avoid using this, it will be removed in a43. * near future.44. */45. int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated;46. int (*detach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated;47. /* Standard driver model interfaces */48. int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);49. int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);50. /* driver model interfaces that don't relate to enumeration */51. void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);52. int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_message_t mesg);53. int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *);54. /* Alert callback, for example for the SMBus alert protocol.55. * The format and meaning of the data value depends on the protocol.56. * For the SMBus alert protocol, there is a single bit of data passed57. * as the alert response's low bit ("event flag").58. */59. void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, unsigned int data);60. /* a ioctl like command that can be used to perform specific functions61. * with the device.62. */63. int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);64. struct device_driver driver;65. const struct i2c_device_id *id_table;66. /* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */67. int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *);68. const unsigned short *address_list;69. struct list_head clients;70. };
代码清单4 i2c_client结构体1. /*2. * struct i2c_client - represent an I2C slave device3. * @flags: I2C_CLIENT_TEN indicates the device uses a ten bit chip address;4. * I2C_CLIENT_PEC indicates it uses SMBus Packet Error Checking5. * @addr: Address used on the I2C bus connected to the parent adapter.6. * @name: Indicates the type of the device, usually a chip name that's7. * generic enough to hide second-sourcing and compatible revisions.8. * @adapter: manages the bus segment hosting this I2C device9. * @driver: device's driver, hence pointer to access routines10. * @dev: Driver model device node for the slave.11. * @irq: indicates the IRQ generated by this device (if any)12. * @detected: member of an i2c_driver.clients list or i2c-core's13. * userspace_devices list14. *15. * An i2c_client identifies a single device (i.e. chip) connected to an16. * i2c bus. The behaviour exposed to Linux is defined by the driver17. * managing the device.18. */19. struct i2c_client {20. unsigned short flags; /* div., see below */21. unsigned short addr; /* chip address - NOTE: 7bit */22. /* addresses are stored in the */23. /* _LOWER_ 7 bits */24. char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE];25. struct i2c_adapter *adapter; /* the adapter we sit on */26. struct i2c_driver *driver; /* and our access routines */27. struct device dev; /* the device structure */28. int irq; /* irq issued by device */29. struct list_head detected;30. };
下面分析i2c_driver、i2c_client、i2c_adapter和i2c_algorithm这4个数据结构的作用及盘根错节的关系。
(1)2c_adapter与i2c_algorithmi2c_adapter对应于物理上的一个适配器,而i2c_algorithm对应一套通信方法。一个I2C适配器需要i2c_algorithm中提供的通信函数来控制适配器上产生特定的访问周期。缺少i2c_algorithm的i2c_adapter什么也做不了,因此i2c_adapter中包含其使用的i2c_algorithm的指针。
I2c_algorithm中关键函数master_xfer用于产生I2C访问周期需要的信号,以i2c_msg(即I2C消息)为单位。I2c_msg结构体非常关键,代码清单5给出了它的定义。
代码清单5 i2c_msg结构体/** * struct i2c_msg - an I2C transaction segment beginning with START * @addr: Slave address, either seven or ten bits. When this is a ten * bit address, I2C_M_TEN must be set in @flags and the adapter * must support I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR. * @flags: I2C_M_RD is handled by all adapters. No other flags may be * provided unless the adapter exported the relevant I2C_FUNC_* * flags through i2c_check_functionality(). * @len: Number of data bytes in @buf being read from or written to the * I2C slave address. For read transactions where I2C_M_RECV_LEN * is set, the caller guarantees that this buffer can hold up to * 32 bytes in addition to the initial length byte sent by the * slave (plus, if used, the SMBus PEC); and this value will be * incremented by the number of block data bytes received. * @buf: The buffer into which data is read, or from which it's written. * * An i2c_msg is the low level representation of one segment of an I2C * transaction. It is visible to drivers in the @i2c_transfer() procedure, * to userspace from i2c-dev, and to I2C adapter drivers through the * @i2c_adapter.@master_xfer() method. * * Except when I2C "protocol mangling" is used, all I2C adapters implement * the standard rules for I2C transactions. Each transaction begins with a * START. That is followed by the slave address, and a bit encoding read * versus write. Then follow all the data bytes, possibly including a byte * with SMBus PEC. The transfer terminates with a NAK, or when all those * bytes have been transferred and ACKed. If this is the last message in a * group, it is followed by a STOP. Otherwise it is followed by the next * @i2c_msg transaction segment, beginning with a (repeated) START. * * Alternatively, when the adapter supports I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING then * passing certain @flags may have changed those standard protocol behaviors. * Those flags are only for use with broken/nonconforming slaves, and with * adapters which are known to support the specific mangling options they * need (one or more of IGNORE_NAK, NO_RD_ACK, NOSTART, and REV_DIR_ADDR). */struct i2c_msg { __u16 addr; /* slave address */ __u16 flags;#define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */#define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */#define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */#define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */#define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */#define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */#define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */ __u16 len; /* msg length */ __u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */};
(2)i2c_driver与i2c_clienti2c_driver对应一套驱动方法,其主要成员函数是probe()、remove()、suspend()、resume()等,另外id_table是该驱动所支持的I2C设备的ID表。i2c_client对应于真实的物理设备,每个I2C设备都需要一个i2c_client来描述。I2c_driver和i2c_client的关系是一对多,一个i2c_driver上可以支持多个同类型的i2c_client。
I2c_client信息通常在BSP的板文件中通过i2c_board_info填充,如下面代码就定义了一个I2C设备ID为“24c02”、地址为0x50的i2c_client:
代码清单6 i2c_board_info结构体定义1. static struct i2c_board_info __initdata smdk2440_i2c_devs[] = {2. {3. I2C_BOARD_INFO("24c02", 0x50),4. .platform_data = &at24c02,5. },6. /* more devices can be added using expansion connectors */7. };
在I2C总线驱动i2c_bus_type的match()函数i2c_device_match()中,会调用i2c_match_id()函数匹配板文件中定义的ID和i2c_driver所支持的ID表。
代码清单7 i2c_device_match函数在linux-3.0/drivers/i2c/i2c-core.c1. static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)2. {3. struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);4. struct i2c_driver *driver;5. if (!client)6. return 0;7. /* Attempt an OF style match */8. if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))9. return 1;10. driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);11. /* match on an id table if there is one */12. if (driver->id_table)13. return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL;14. return 0;15. }
(3)i2c_adpater与i2c_clienti2c_adapter与i2c_client的关系与I2C硬件体系中适配器和设备的关系一致,即i2c_client依附于i2c_adapter。由于一个适配器上可以连接多个I2C设备,所以一个i2c_adapter也可以被多个i2c_client依附,i2c_adapter中包含依附于它的i2c_client的链表。
代码清单8 i2c_client的链表1. struct list_head userspace_clients;
假设I2C总线适配器xxx上有两个使用相同驱动程序的yyyI2C设备,在打开I2C总线的设备节点后相关数据结构之间的逻辑组织关系将如下图所示:
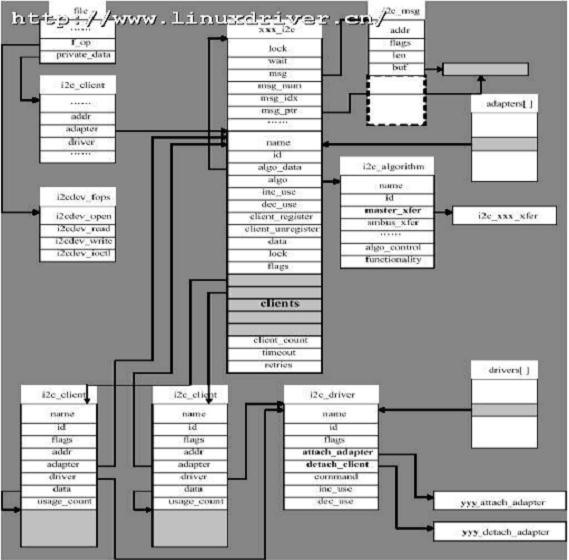
[align=left] [/align]
图5 I2C总线的设备节点后相关数据结构之间的逻辑组织关系图
从上面的分析可知,虽然I2C硬件体系结构简单,但是I2C体系结构在linux中的实现却相当复杂。当工程师拿到实际的电路板,面对复杂的linux I2C子系统,应该如何下手写驱动呢?究竟要哪些是需要亲自做的,哪些是内核已经提供的呢?理清这个问题非常有意义,可以使我们面对具体问题时迅速地抓住重点。
一方面,适配器驱动可能是linux内核本身还不包含的;另一方面,挂接在适配器上的就提设备可能也是linux内核还不包含的。因此,工程师要实现的主要工作如下。
提供I2C适配器的硬件驱动,探测、初始化I2C适配器(如申请I2C的I/O地址和中断号)、驱动CPU控制的I2C适配器从硬件上产生各种信号以及处理I2C中断等。
提供I2C适配器的algorithm,具体适配器的xxx_xfer()函数填充i2c_algorithm的master_xfer指针,并把i2c_algorithm指针赋值给i2c_adapter的algo指针。
实现I2C设备驱动中的i2c_driver接口,具体设备yyy_probe()、yyy_remove()、yyy_suspend()、yyy_resume()函数指针和i2c_device_id设备ID表赋值给i2c_driver的probe、remove、suspend、resume和id_table指针。
实现I2C设备所对应类型的具体驱动,i2c_driver只是实现设备与总线的挂接,而挂接在总线上的设备则是千差万别的。例如,如果字符设备,就实现文件操作接口,即实现具体yyy的yyy_read()、yyy_write()和yyy_ioctl()函数等;如果是声卡,就实现ALSA驱动。
二、I2C的第一部分1.Linux I2C核心I2C核心(driver/i2c/i2c-core.c)文件中提供了一组不依赖与硬件平台的接口函数,这个文件一般不需要被工程师修改,但是理解其中的主要函数非常关键,因为I2C总线驱动和设备驱动之间依赖于I2C核心作为纽带I2C核心中的主要函数如下。
2.增加/删除i2c_adapter代码清单9 i2c_add_adapter函数:1. /**2. * i2c_add_adapter - declare i2c adapter, use dynamic bus number3. * @adapter: the adapter to add4. * Context: can sleep5. *6. * This routine is used to declare an I2C adapter when its bus number7. * doesn't matter. Examples: for I2C adapters dynamically added by8. * USB links or PCI plugin cards.9. *10. * When this returns zero, a new bus number was allocated and stored11. * in adap->nr, and the specified adapter became available for clients.12. * Otherwise, a negative errno value is returned.13. */14. int i2c_add_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adapter)15. {16. int id, res = 0;17. retry:18. if (idr_pre_get(&i2c_adapter_idr, GFP_KERNEL) == 0)19. return -ENOMEM;20. mutex_lock(&core_lock);21. /* "above" here means "above or equal to", sigh */22. res = idr_get_new_above(&i2c_adapter_idr, adapter,23. __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num, &id);24. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);25. if (res < 0) {26. if (res == -EAGAIN)27. goto retry;28. return res;29. }30. adapter->nr = id;31. return i2c_register_adapter(adapter);32. }33. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_add_adapter);
代码清单10 I2c_del_adapter函数:1. /**2. * i2c_del_adapter - unregister I2C adapter3. * @adap: the adapter being unregistered4. * Context: can sleep5. *6. * This unregisters an I2C adapter which was previously registered7. * by @i2c_add_adapter or @i2c_add_numbered_adapter.8. */9. int i2c_del_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)10. {11. int res = 0;12. struct i2c_adapter *found;13. struct i2c_client *client, *next;14. /* First make sure that this adapter was ever added */15. mutex_lock(&core_lock);16. found = idr_find(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap->nr);17. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);18. if (found != adap) {19. pr_debug("i2c-core: attempting to delete unregistered "20. "adapter [%s]\n", adap->name);21. return -EINVAL;22. }23. /* Tell drivers about this removal */24. mutex_lock(&core_lock);25. res = bus_for_each_drv(&i2c_bus_type, NULL, adap,26. __process_removed_adapter);27. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);28. if (res)29. return res;30. /* Remove devices instantiated from sysfs */31. mutex_lock(&adap->userspace_clients_lock);32. list_for_each_entry_safe(client, next, &adap->userspace_clients,33. detected) {34. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "Removing %s at 0x%x\n", client->name,35. client->addr);36. list_del(&client->detected);37. i2c_unregister_device(client);38. }39. mutex_unlock(&adap->userspace_clients_lock);40. 41. /* Detach any active clients. This can't fail, thus we do not42. * check the returned value. This is a two-pass process, because43. * we can't remove the dummy devices during the first pass: they44. * could have been instantiated by real devices wishing to clean45. * them up properly, so we give them a chance to do that first. */46. res = device_for_each_child(&adap->dev, NULL, __unregister_client);47. res = device_for_each_child(&adap->dev, NULL, __unregister_dummy);48. 49. #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT50. class_compat_remove_link(i2c_adapter_compat_class, &adap->dev,51. adap->dev.parent);52. #endif53. 54. /* device name is gone after device_unregister */55. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "adapter [%s] unregistered\n", adap->name);56. 57. /* clean up the sysfs representation */58. init_completion(&adap->dev_released);59. device_unregister(&adap->dev);60. 61. /* wait for sysfs to drop all references */62. wait_for_completion(&adap->dev_released);63. 64. /* free bus id */65. mutex_lock(&core_lock);66. idr_remove(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap->nr);67. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);68. 69. /* Clear the device structure in case this adapter is ever going to be70. added again */71. memset(&adap->dev, 0, sizeof(adap->dev));72. 73. return 0;74. }75. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_del_adapter);
3.增加/删除i2c_driver代码清单11 I2c_register_driver函数:1. static int i2c_register_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)2. {3. int res = 0;4. 5. /* Can't register until after driver model init */6. if (unlikely(WARN_ON(!i2c_bus_type.p))) {7. res = -EAGAIN;8. goto out_list;9. } 10. 11. /* Sanity checks */12. if (unlikely(adap->name[0] == '\0')) { 13. pr_err("i2c-core: Attempt to register an adapter with "14. "no name!\n");15. return -EINVAL;16. } 17. if (unlikely(!adap->algo)) { 18. pr_err("i2c-core: Attempt to register adapter '%s' with "19. "no algo!\n", adap->name); 20. return -EINVAL;21. } 22. 23. rt_mutex_init(&adap->bus_lock); 24. mutex_init(&adap->userspace_clients_lock);25. INIT_LIST_HEAD(&adap->userspace_clients);26. 27. /* Set default timeout to 1 second if not already set */28. if (adap->timeout == 0)29. adap->timeout = HZ; 30. 31. dev_set_name(&adap->dev, "i2c-%d", adap->nr);32. adap->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;33. adap->dev.type = &i2c_adapter_type;34. res = device_register(&adap->dev);35. if (res)36. goto out_list;37. 38. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "adapter [%s] registered\n", adap->name);39. 40. #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT41. res = class_compat_create_link(i2c_adapter_compat_class, &adap->dev,42. adap->dev.parent);43. if (res)44. dev_warn(&adap->dev,45. "Failed to create compatibility class link\n");46. #endif47. 48. /* create pre-declared device nodes */49. if (adap->nr < __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num)50. i2c_scan_static_board_info(adap);51. 52. /* Notify drivers */53. mutex_lock(&core_lock);54. bus_for_each_drv(&i2c_bus_type, NULL, adap, __process_new_adapter);55. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);56. 57. return 0;58. 59. out_list:60. mutex_lock(&core_lock);61. idr_remove(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap->nr);62. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);63. return res;64. }
代码清单12 i2c_del_driver函数:1. /*2. * i2c_del_driver - unregister I2C driver3. * @driver: the driver being unregistered4. * Context: can sleep5. */6. void i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver)7. {8. i2c_for_each_dev(driver, __process_removed_driver);9. 10. driver_unregister(&driver->driver);11. pr_debug("i2c-core: driver [%s] unregistered\n", driver->driver.name);12. }13. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_del_driver);
4.i2c_client依附/脱离当一个具体的client被侦测到并被关联的时候,设备和使用爽肤水文件件被注册。相反地,在client杯取消关联的时候,sysfs文件和设备也被注销。如下代码清单13。
代码清单13 i2c_new_device函数:1. /**2. * i2c_new_device - instantiate an i2c device3. * @adap: the adapter managing the device4. * @info: describes one I2C device; bus_num is ignored5. * Context: can sleep6. *7. * Create an i2c device. Binding is handled through driver model8. * probe()/remove() methods. A driver may be bound to this device when we9. * return from this function, or any later moment (e.g. maybe hotplugging will10. * load the driver module). This call is not appropriate for use by mainboard11. * initialization logic, which usually runs during an arch_initcall() long12. * before any i2c_adapter could exist.13. *14. * This returns the new i2c client, which may be saved for later use with15. * i2c_unregister_device(); or NULL to indicate an error.16. */17. struct i2c_client *18. i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_board_info const *info)19. {20. struct i2c_client *client;21. int status;22. 23. client = kzalloc(sizeof *client, GFP_KERNEL);24. if (!client)25. return NULL;26. 27. client->adapter = adap;28. 29. client->dev.platform_data = info->platform_data;30. 31. if (info->archdata)32. client->dev.archdata = *info->archdata;33. 34. client->flags = info->flags;35. client->addr = info->addr;36. client->irq = info->irq;37. 38. strlcpy(client->name, info->type, sizeof(client->name));39. 40. /* Check for address validity */41. status = i2c_check_client_addr_validity(client);42. if (status) {43. dev_err(&adap->dev, "Invalid %d-bit I2C address 0x%02hx\n",44. client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_TEN ? 10 : 7, client->addr);45. goto out_err_silent;46. }47. 48. /* Check for address business */49. status = i2c_check_addr_busy(adap, client->addr);50. if (status)51. goto out_err;52. 53. client->dev.parent = &client->adapter->dev;54. client->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;55. client->dev.type = &i2c_client_type;56. client->dev.of_node = info->of_node;57. 58. dev_set_name(&client->dev, "%d-%04x", i2c_adapter_id(adap),59. client->addr);60. status = device_register(&client->dev);61. if (status)62. goto out_err;63. 64. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "client [%s] registered with bus id %s\n",65. client->name, dev_name(&client->dev));66. 67. return client;68. 69. out_err:70. dev_err(&adap->dev, "Failed to register i2c client %s at 0x%02x "71. "(%d)\n", client->name, client->addr, status);72. out_err_silent:73. kfree(client);74. return NULL;75. }76. EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_new_device);77. 78. 代码清单14 i2c_unregister_device函数79. /**80. * i2c_unregister_device - reverse effect of i2c_new_device()81. * @client: value returned from i2c_new_device()82. * Context: can sleep83. */84. void i2c_unregister_device(struct i2c_client *client)85. {86. device_unregister(&client->dev);87. }88. EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_unregister_device);
5.I2C传输、发送和接收I2c_transfer()函数本身不具备驱动适配器物理硬件完成消息交互的能力,它只是寻找到i2c_adapter对应的i2c_algorithm,并使用i2c_algorithm的master_xfer()函数真正驱动硬件流程。
代码清单15 i2c_transfer函数1. /* ----------------------------------------------------2. * the functional interface to the i2c busses.3. * ----------------------------------------------------4. */5. 6. /**7. * i2c_transfer - execute a single or combined I2C message8. * @adap: Handle to I2C bus9. * @msgs: One or more messages to execute before STOP is issued to10. * terminate the operation; each message begins with a START.11. * @num: Number of messages to be executed.12. *13. * Returns negative errno, else the number of messages executed.14. *15. * Note that there is no requirement that each message be sent to16. * the same slave address, although that is the most common model.17. */18. int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)19. {20. unsigned long orig_jiffies;21. int ret, try;22. 23. /* REVISIT the fault reporting model here is weak:24. *25. * - When we get an error after receiving N bytes from a slave,26. * there is no way to report "N".27. *28. * - When we get a NAK after transmitting N bytes to a slave,29. * there is no way to report "N" ... or to let the master30. * continue executing the rest of this combined message, if31. * that's the appropriate response.32. *33. * - When for example "num" is two and we successfully complete34. * the first message but get an error part way through the35. * second, it's unclear whether that should be reported as36. * one (discarding status on the second message) or errno37. * (discarding status on the first one).38. */39. 40. if (adap->algo->master_xfer) {41. #ifdef DEBUG42. for (ret = 0; ret < num; ret++) {43. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "master_xfer[%d] %c, addr=0x%02x, "44. "len=%d%s\n", ret, (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RD)45. ? 'R' : 'W', msgs[ret].addr, msgs[ret].len,46. (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RECV_LEN) ? "+" : "");47. }48. #endif49. 50. if (in_atomic() || irqs_disabled()) {51. ret = i2c_trylock_adapter(adap);52. if (!ret)53. /* I2C activity is ongoing. */54. return -EAGAIN;55. } else {56. i2c_lock_adapter(adap);57. }58. 59. /* Retry automatically on arbitration loss */60. orig_jiffies = jiffies;61. for (ret = 0, try = 0; try <= adap->retries; try++) {62. ret = adap->algo->master_xfer(adap, msgs, num);63. if (ret != -EAGAIN)64. break;65. if (time_after(jiffies, orig_jiffies + adap->timeout))66. break;67. }68. i2c_unlock_adapter(adap);69. 70. return ret;71. } else {72. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "I2C level transfers not supported\n");73. return -EOPNOTSUPP;74. }75. }76. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_transfer);
代码清单16 i2c_master_send函数1. /**2. * i2c_master_send - issue a single I2C message in master transmit mode3. * @client: Handle to slave device4. * @buf: Data that will be written to the slave5. * @count: How many bytes to write, must be less than 64k since msg.len is u166. *7. * Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes written.8. */9. int i2c_master_send(const struct i2c_client *client, const char *buf, int count)10. {11. int ret;12. struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter;13. struct i2c_msg msg;14. 15. msg.addr = client->addr;16. msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN;17. msg.len = count;18. msg.buf = (char *)buf;19. 20. ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1);21. 22. /* If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg transmitted), return #bytes23. transmitted, else error code. */24. return (ret == 1) ? count : ret;25. }26. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_master_send);
代码清单17 i2c_master_recv函数1. /**2. * i2c_master_recv - issue a single I2C message in master receive mode3. * @client: Handle to slave device4. * @buf: Where to store data read from slave5. * @count: How many bytes to read, must be less than 64k since msg.len is u166. *7. * Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes read.8. */9. int i2c_master_recv(const struct i2c_client *client, char *buf, int count)10. {11. struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter;12. struct i2c_msg msg;13. int ret;14. 15. msg.addr = client->addr;16. msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN;17. msg.flags |= I2C_M_RD;18. msg.len = count;19. msg.buf = buf;20. 21. ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1);22. 23. /* If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg transmitted), return #bytes24. transmitted, else error code. */25. return (ret == 1) ? count : ret;26. }27. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_master_recv);
i2c_transfer()函数用于进行I2C适配器和I2C设备之间的一组消息交互,i2c_master_send()函数和i2c_master_recv()函数内部会调用i2c_transfer函数分别完成一条写消息和一条读消息。
三、I2c的第二部分1.2C总线驱动(1)I2c总线驱动模块的加载函数要完成两个工作。
l 第一个是初始化i2c适配器所使用的硬件资源,如申请I/O地址、中断号等。
l 第二个是通过i2c_add_adapter()添加i2c_adapter的数据结构,当然这个i2c_adapter数据结构的成员已经被xxx适配器的相应的函数指针所初始化。
(2)I2C总线驱动模块的卸载函数要完成的工作与加载函数相反。
l 释放I2C适配器所使用的硬件资源,如释放I/O地址,中断号等。
l 通过i2c_del_adapter()删除i2c_adapter的函数数据结构。
代码清单18所示为I2C适配器驱动的模块加载和卸载函数的模板。
代码清单18 I2C总线驱动的模板加载和卸载函数模板1. static int __init i2c_adap_xxx_init(void)2. {3. xxx_adapter_hw_init();4. I2c_add_adapter(&xxx_adapter);5. }6. subsys_initcall(i2c_adap_xxx_init);7. 8. static void __exit i2c_adap_xxx_exit(void)9. {10. xxx_adapter_hw_free();11. i2c_del_adapter(&xxx_adapter);12. }13. module_exit(i2c_adap_xxx_exit);
上述代码中xxx_adapter_hw_init()和xxx_adapter_hw_free()函数的实现都与具体的CPU和I2C适配器硬件直接相关。
2.I2C总线通信方法我们需要为特定的I2C适配器实现其通信方法,主要实现i2c_algorithm的master_xfer()函数和functionality()函数。
Functionality()函数非常简单,用于返回algorithm所支持的通信协议,如I2C_FUNC_I2C、I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR、I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE、I2C_FUNC_SUMBUS_WRITE_BYTE等。
Master_xfer()函数在I2C适配器上完成传递给它的i2c_msg数组中每个I2C消息,代码清单19所示为xxx设备的master_xfer()函数模板。
代码清单19 I2C总线驱动master_xfer()函数模板1. static int i2c_adapter_xxx_xfer(structi2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num) 2. { 3. ...... 4. for (i = 0; i < num; i++) { 5. i2c_adapter_xxx_start(); /*产生起始位*/ 6. if (msgs[i]->flags & I2C_M_RD) { /*读取*/ 7. i2c_adapter_xxx_setaddr((msg->addr << 1) | 1); /*发送从设备地址*/ 8. i2c_adapter_xxx_wait_ack(); /*获得从设备的ACK*/ 9. i2c_adapter_xxx_readbytes(msgs[i]->buf,msgs[i]->len); /*读取len长度的数据到buf中*/ 10. } else { 11. i2c_adapter_xxx_setaddr(msg->addr << 1); 12. i2c_adapter_xxx_wait_ack(); 13. i2c_adapter_xxx_writebytes(msgs[i]->buf, msgs[i]->len); 14. } 15. } 16. i2c_adapter_xxx_stop(); /*产生停止位*/ 17. }
上述代码实际上给出了一个master_xfer()函数处理I2C消息数组的流程,对于数组中的每个消息,判断消息类型,若为读消息,则赋从设备地址为(msg->addr<<1)|1,否则为msg->addr<<1,对每个消息产生一个开始位,紧接着传送从设备的地址,然后开始数据的发送或接收,队最后的消息还需产生一个停止位。
master_xfer()函数模板中i2c_adapter_xxx_start()、i2c_adapter_xxx_setaddr()、i2c_adapter_xxx_wait_ack()、i2c_adapter_xxx_readbytes()、i2c_adapter_xxx_stop()函数用于完成适配器底层硬件操作,与I2C适配器和CPU的具体硬件直接相关,需要由工程师根据芯片的数据手册来实现。
I2c_adapter_xxx_readbytes()用于从设备上接收一串数据,i2c_adapter_xxx_writebytes()用于向从设备写入一串数据,这两个函数的内部也会涉及I2C总线协议中的ACK应答。
master_xfer()函数的实现在形式上会有很多样,即便是linux内核源代码中已经给出了一些I2C总线驱动的master_xfer()函数,由于由不同的组织或个人完成,风格上的差别也非常大,不一定能与模板完全对应,如master_xfer()函数模板给出的消息处理顺序进行的,而有的驱动以中断方式来完成这个流程。不管具体怎么实施,流程的本质都是不变的。因为这个流程不以驱动工程师的意志为转移,最终由I2C总线硬件上的通信协议决定。
多数I2C总线驱动会定义一个xxx_i2c结构体,作为i2c_adapter的algo_data(类似“是有数据”),其中包含I2C消息数组指针、数组索引及I2C适配器algorithm访问控制用的自旋锁、等待队列等,而master_xfer()函数完成消息数组中消息的处理也可通过对xxx_i2c结构体相关成员的访问来控制。代码清单20所示为xxx_i2c结构体的定义。
代码清单20 xxx_i2c结构体模板1. struct xxx_i2c {2. spinlock_t lock;3. wait_queue_head_t wait;4. struct i2c_msg *msg;5. unsigned int msg_num;6. unsigned int msg_idx;7. unsigned int msg_ptr;8. struct i2c_adapter adap;9. };
对于s3c2440的i2c模块而言内核中做了如下的工作:
S3c2440处理器内部集成了一个I2C控制器,通过4个寄存器就可以方便地对其进行控制,这4个寄存器如下:
l IICCON:I2C控制寄存器。
l IICSTAT:I2C状态寄存器。
l IICDS:I2C收发数据移位寄存器。
l IICADD:I2C地址寄存器。
S3c2440处理器内部集成的I2C控制器可支持主、从两种模式,我们主要使用其主模式。通过对IICCON、IICDS和IICADD寄存器的操作,可
在I2C总线上产生开始位、停止位、数据和地址,而传输的状态则通过IICSTAT寄存器获取。
3.s3c2440 I2C 总线驱动总体分析s3c_2440的I2C总线驱动driver/i2c/busses/i2c-s3c2410.c支持s3c24xx、s3c64xx、s5pc1xx和s5p64xx处理器,在我们使用的3.0内核版本中,其名称任然叫2410,显然是历史原因引起的。它主要完成以下工作。
设计对应于i2c_adapter_xxx_init()模板的s3c_2440的模块加载函数和对应于i2c_adapter_xxx_exit()函数模板的模块卸载函数。
设计对应于i2c_adapter_xxx_xfer()模板的s3c_2440适配器的通信方法函数。
针对s3c24xx、s3c64xx、s5pc1xx和s5p64xx处理器,functionality()函数s3c24xx_i2c_func()只需要简单地返回I2C_FUNC_I2C|I2C_FUNC_SUMBUS_EMUL|I2C_FUNU_PROTOCOL_MANGLING表明其支持的功能。
下图给出了s3c2440驱动中的主要函数与总线模板函数的对应关系,由于实现通信方法的方式不一样,模板的一个函数可能对应于s3c2440 I2C总线驱动的多个函数。

图6 i2c总线驱动模板于s3c2440 I2C总线驱动的映射
4.S3c2440 I2C适配器驱动的模板加载于卸载I2C适配器驱动被作为一个单独的模块加载进内核,在模块的加载和卸载函数中,只需注册和注销一个platform——driver结构体,如代码清单21所示。
代码清单21 S3c2440 I2C1. static int __init i2c_adap_s3c_init(void)2. {3. return platform_driver_register(&s3c24xx_i2c_driver);4. }5. subsys_initcall(i2c_adap_s3c_init);6. 7. static void __exit i2c_adap_s3c_exit(void)8. {9. platform_driver_unregister(&s3c24xx_i2c_driver);10. }11. module_exit(i2c_adap_s3c_exit);
代码清单22 platfrom_driver_register()和platfrom_driver_unregister()函数1. /**2. * platform_driver_register - register a driver for platform-level devices3. * @drv: platform driver structure4. */5. int platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv)6. {7. drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type;8. if (drv->probe)9. drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe;10. if (drv->remove)11. drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove;12. if (drv->shutdown)13. drv->driver.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown;14. 15. return driver_register(&drv->driver);16. }17. EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_driver_register);18. 19. /** 20. * platform_driver_unregister - unregister a driver for platform-level devices21. * @drv: platform driver structure22. */23. void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *drv)24. { 25. driver_unregister(&drv->driver);26. } 27. EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_driver_unregister);
Platfrom_driver结构体包含了具体适配器的probe()函数、remove()函数、resume()函数指针等信息,它需要被定义和赋值,如代码清单23所示。
代码清单23 platfrom_driver结构体1. static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_i2c_driver = {2. .probe = s3c24xx_i2c_probe,3. .remove = s3c24xx_i2c_remove,4. .id_table = s3c24xx_driver_ids,5. .driver = {6. .owner = THIS_MODULE,7. .name = "s3c-i2c",8. .pm = S3C24XX_DEV_PM_OPS,9. },10. };
当通过linux内核源代码/drivers/base/platform.c文件中定义platform_driver_register()函数注册platfrom_driver结构体时,其中probe指针指向s3c24xx_i2c_probe()函数将被调用,以初始化适配器硬件。s3c24xx_i2c_init()函数会调用函数。
代码清单24 s3c24xx_i2c_init()函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_init2. *3. * initialise the controller, set the IO lines and frequency4. */5. 6. static int s3c24xx_i2c_init(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)7. {8. unsigned long iicon = S3C2410_IICCON_IRQEN | S3C2410_IICCON_ACKEN;9. struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata;10. unsigned int freq;11. 12. /* get the plafrom data */13. 14. pdata = i2c->dev->platform_data;15. 16. /* inititalise the gpio */17. 18. if (pdata->cfg_gpio)19. pdata->cfg_gpio(to_platform_device(i2c->dev));20. 21. /* write slave address */22. 23. writeb(pdata->slave_addr, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICADD);24. 25. dev_info(i2c->dev, "slave address 0x%02x\n", pdata->slave_addr);26. 27. writel(iicon, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);28. 29. /* we need to work out the divisors for the clock... */30. 31. if (s3c24xx_i2c_clockrate(i2c, &freq) != 0) {32. writel(0, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);33. dev_err(i2c->dev, "cannot meet bus frequency required\n");34. return -EINVAL;35. }36. 37. /* todo - check that the i2c lines aren't being dragged anywhere */38. 39. dev_info(i2c->dev, "bus frequency set to %d KHz\n", freq);40. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "S3C2410_IICCON=0x%02lx\n", iicon);41. 42. return 0;43. }44.
代码清单25 s3c24xx_i2c_probe()函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_probe2. *3. * called by the bus driver when a suitable device is found4. */5. 6. static int s3c24xx_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)7. {8. struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c;9. struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata;10. struct resource *res;11. int ret;12. 13. pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data;14. if (!pdata) {15. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "no platform data\n");16. return -EINVAL;17. }18. 19. i2c = kzalloc(sizeof(struct s3c24xx_i2c), GFP_KERNEL);20. if (!i2c) {21. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "no memory for state\n");22. return -ENOMEM;23. }24. 25. strlcpy(i2c->adap.name, "s3c2410-i2c", sizeof(i2c->adap.name));26. i2c->adap.owner = THIS_MODULE;27. i2c->adap.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm;28. i2c->adap.retries = 2;29. i2c->adap.class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON | I2C_CLASS_SPD;30. i2c->tx_setup = 50;31. 32. spin_lock_init(&i2c->lock);33. init_waitqueue_head(&i2c->wait);34. 35. /* find the clock and enable it */36. 37. i2c->dev = &pdev->dev;38. i2c->clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "i2c");39. if (IS_ERR(i2c->clk)) {40. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot get clock\n");41. ret = -ENOENT;42. goto err_noclk;43. }44. 45. dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "clock source %p\n", i2c->clk);46. 47. clk_enable(i2c->clk);48. 49. /* map the registers */50. 51. res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);52. if (res == NULL) {53. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot find IO resource\n");54. ret = -ENOENT;55. goto err_clk;56. }57. 58. i2c->ioarea = request_mem_region(res->start, resource_size(res),59. pdev->name);60. 61. if (i2c->ioarea == NULL) {62. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot request IO\n");63. ret = -ENXIO;64. goto err_clk;65. }66. 67. i2c->regs = ioremap(res->start, resource_size(res));68. 69. if (i2c->regs == NULL) {70. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot map IO\n");71. ret = -ENXIO;72. goto err_ioarea;73. }74. 75. dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "registers %p (%p, %p)\n",76. i2c->regs, i2c->ioarea, res);77. 78. /* setup info block for the i2c core */79. 80. i2c->adap.algo_data = i2c;81. i2c->adap.dev.parent = &pdev->dev;82. 83. /* initialise the i2c controller */84. 85. ret = s3c24xx_i2c_init(i2c);86. if (ret != 0)87. goto err_iomap;88. 89. /* find the IRQ for this unit (note, this relies on the init call to90. * ensure no current IRQs pending91. */92. 93. i2c->irq = ret = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);94. if (ret <= 0) {95. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot find IRQ\n");96. goto err_iomap;97. }98. 99. ret = request_irq(i2c->irq, s3c24xx_i2c_irq, IRQF_DISABLED,100. dev_name(&pdev->dev), i2c);101. 102. if (ret != 0) {103. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot claim IRQ %d\n", i2c->irq);104. goto err_iomap;105. }106. 107. ret = s3c24xx_i2c_register_cpufreq(i2c);108. if (ret < 0) {109. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to register cpufreq notifier\n");110. goto err_irq;111. }112. 113. /* Note, previous versions of the driver used i2c_add_adapter()114. * to add the bus at any number. We now pass the bus number via115. * the platform data, so if unset it will now default to always116. * being bus 0.117. */118. 119. i2c->adap.nr = pdata->bus_num;120. 121. ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&i2c->adap);122. if (ret < 0) {123. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to add bus to i2c core\n");124. goto err_cpufreq;125. }126. 127. platform_set_drvdata(pdev, i2c);128. 129. dev_info(&pdev->dev, "%s: S3C I2C adapter\n", dev_name(&i2c->adap.dev));130. clk_disable(i2c->clk);131. return 0;132. 133. err_cpufreq:134. s3c24xx_i2c_deregister_cpufreq(i2c);135. 136. err_irq:137. free_irq(i2c->irq, i2c);138. 139. err_iomap:140. iounmap(i2c->regs);141. 142. err_ioarea:143. release_resource(i2c->ioarea);144. kfree(i2c->ioarea);145. 146. err_clk:147. clk_disable(i2c->clk);148. clk_put(i2c->clk);149. 150. err_noclk:151. kfree(i2c);152. return ret;153. }
上述代码中的主体工作是使能硬件并且申请I2C适配器使用I/O地址、中断号等,在这些工作都完成无误后,通过I2C核心提供i2c_add_adapter函数添加这个适配器。当处理器包含多个I2C控制器时,我们通过板文件定义的platform数据中bus_num进行区分。
与s3c24xx_i2c_probe()函数完全相反的功能的函数是s3c24xx_i2c_remove()函数,它在适配器模块函数调用platform_driver_unregister函数是通过platfrom_driver的remove指针方式被调用。Xxx_i2c_remove()的设计模块如代码清单26所示。
********************************************************************************************转载声明:希望大家能转载此文谢谢 原文链接
********************************************************************************************
代码清单26 s3c2440 I2C总线驱动中的s3c24xx_i2c_remove函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_remove2. *3. * called when device is removed from the bus4. */5. 6. static int s3c24xx_i2c_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)7. {8. struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);9. 10. s3c24xx_i2c_deregister_cpufreq(i2c);11. 12. i2c_del_adapter(&i2c->adap);13. free_irq(i2c->irq, i2c);14. 15. clk_disable(i2c->clk);16. clk_put(i2c->clk);17. 18. iounmap(i2c->regs);19. 20. release_resource(i2c->ioarea);21. kfree(i2c->ioarea);22. kfree(i2c);23. 24. return 0;25. }
上面的代码清单26中用到了s3c24xx_i2c结构体进行适配器所有信息的封装。类似于私有信息结构体,它与代码清单20所示的xxx_i2c结构体模板对应,代码清单27所示为s3c24xx_i2c结构体的定义。
代码清单27 s3c24xx_i2c结构体1. struct s3c24xx_i2c {2. spinlock_t lock;3. wait_queue_head_t wait;4. unsigned int suspended:1;5. 6. struct i2c_msg *msg;7. unsigned int msg_num;8. unsigned int msg_idx;9. unsigned int msg_ptr;10. 11. unsigned int tx_setup;12. unsigned int irq;13. 14. enum s3c24xx_i2c_state state;15. unsigned long clkrate;16. 17. void __iomem *regs;18. struct clk *clk;19. struct device *dev;20. struct resource *ioarea;21. struct i2c_adapter adap;22. 23. #ifdef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ24. struct notifier_block freq_transition;25. #endif26. };
5.s3c2440 I2C 总线通信方法由代码清单25的23行可以看出,I2C适配器对应的i2c_algorithm结构体实例为s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm,代码清单28所示为s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm的定义。
代码清单28 s3c2440的i2c_algorithm结构体1. /* i2c bus registration info */2. 3. static const struct i2c_algorithm s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm = {4. .master_xfer = s3c24xx_i2c_xfer,5. .functionality = s3c24xx_i2c_func,6. };
上述代码第一行指定了s3c2440 I2C总线通信传输函数s3c24xx_i2c_xfer(),这个函数非常关键,所有I2C总线上对设备的访问最终应该由它来完成,代码清单29所示为这个重要函数以及其依赖的s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()函数和s3c24xx_i2c_message_start()函数的源代码。
代码清单29 s3c2440 I2C总线驱动的master_xfer函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_xfer2. *3. * first port of call from the i2c bus code when an message needs4. * transferring across the i2c bus.5. */6. 7. static int s3c24xx_i2c_xfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap,8. struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)9. {10. struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = (struct s3c24xx_i2c *)adap->algo_data;11. int retry;12. int ret;13. 14. clk_enable(i2c->clk);15. 16. for (retry = 0; retry < adap->retries; retry++) {17. 18. ret = s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer(i2c, msgs, num);19. 20. if (ret != -EAGAIN) {21. clk_disable(i2c->clk);22. return ret;23. }24. 25. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "Retrying transmission (%d)\n", retry);26. 27. udelay(100);28. }29. 30. clk_disable(i2c->clk);31. return -EREMOTEIO;32. }
s3c24xx_i2c_xfer()函数调用s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()函数传输I2C消息,第13行的循环意味着最多可以重试adap->retres次。
代码清单30 s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer2. *3. * this starts an i2c transfer4. */5. 6. static int s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c,7. struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)8. {9. unsigned long iicstat, timeout;10. int spins = 20;11. int ret;12. 13. if (i2c->suspended)14. return -EIO;15. 16. ret = s3c24xx_i2c_set_master(i2c);17. if (ret != 0) {18. dev_err(i2c->dev, "cannot get bus (error %d)\n", ret);19. ret = -EAGAIN;20. goto out;21. }22. 23. spin_lock_irq(&i2c->lock);24. 25. i2c->msg = msgs;26. i2c->msg_num = num;27. i2c->msg_ptr = 0;28. i2c->msg_idx = 0;29. i2c->state = STATE_START;30. 31. s3c24xx_i2c_enable_irq(i2c);32. s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(i2c, msgs);33. spin_unlock_irq(&i2c->lock);34. 35. timeout = wait_event_timeout(i2c->wait, i2c->msg_num == 0, HZ * 5);36. 37. ret = i2c->msg_idx;38. 39. /* having these next two as dev_err() makes life very40. * noisy when doing an i2cdetect */41. 42. if (timeout == 0)43. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "timeout\n");44. else if (ret != num)45. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "incomplete xfer (%d)\n", ret);46. 47. /* ensure the stop has been through the bus */48. 49. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "waiting for bus idle\n");50. 51. /* first, try busy waiting briefly */52. do {53. iicstat = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);54. } while ((iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_START) && --spins);55. 56. /* if that timed out sleep */57. if (!spins) {58. msleep(1);59. iicstat = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);60. }61. 62. if (iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_START)63. dev_warn(i2c->dev, "timeout waiting for bus idle\n");64. 65. out:66. return ret;67. }
s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()首先将s3c2440的I2C适配器设置为I2C主设备,其后初始化s3c24xx_i2c结构体,使能I2C中断,并调用s3c24xx_i2c_message_start()函数启动I2C消息的传输。
代码清单31 s3c24xx_i2c_message_start()函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_message_start2. *3. * put the start of a message onto the bus4. */5. 6. static void s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c,7. struct i2c_msg *msg)8. {9. unsigned int addr = (msg->addr & 0x7f) << 1;10. unsigned long stat;11. unsigned long iiccon;12. 13. stat = 0;14. stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_TXRXEN;15. 16. if (msg->flags & I2C_M_RD) {17. stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_MASTER_RX;18. addr |= 1;19. } else20. stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_MASTER_TX;21. 22. if (msg->flags & I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR)23. addr ^= 1;24. 25. /* todo - check for wether ack wanted or not */26. s3c24xx_i2c_enable_ack(i2c);27. 28. iiccon = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);29. writel(stat, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);30. 31. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "START: %08lx to IICSTAT, %02x to DS\n", stat, addr);32. writeb(addr, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS);33. 34. /* delay here to ensure the data byte has gotten onto the bus35. * before the transaction is started */36. 37. ndelay(i2c->tx_setup);38. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "iiccon, %08lx\n", iiccon);39. writel(iiccon, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);40. 41. stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_START;42. writel(stat, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);43. }
s3c24xx_i2c_message_start()函数写s3c2440适配器对应的控制寄存器,向I2C从设备传递开始位和从设备地址。
上述代码只是启动了I2C消息数组的传输周期,并没有完整实现algorithm master_xfer时序的流程。这个流程的完整实现需要借助I2C适配器上的中断来步步推进。代码清单32所示为s3c2440 I2C适配器中断处理函数以及其依赖的i2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte()函数的源码。
代码清单32 s3c2440 I2C适配器中断处理函数1. /* i2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte2. *3. * process an interrupt and work out what to do4. */5. 6. static int i2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c, unsigned long iicstat)7. {8. unsigned long tmp;9. unsigned char byte;10. int ret = 0;11. 12. switch (i2c->state) {13. 14. case STATE_IDLE:15. dev_err(i2c->dev, "%s: called in STATE_IDLE\n", __func__);16. goto out;17. 18. case STATE_STOP:19. dev_err(i2c->dev, "%s: called in STATE_STOP\n", __func__);20. s3c24xx_i2c_disable_irq(i2c);21. goto out_ack;22. 23. case STATE_START:24. /* last thing we did was send a start condition on the25. * bus, or started a new i2c message26. */27. 28. if (iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_LASTBIT &&29. !(i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK)) {30. /* ack was not received... */31. 32. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "ack was not received\n");33. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -ENXIO);34. goto out_ack;35. }36. 37. if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_RD)38. i2c->state = STATE_READ;39. else40. i2c->state = STATE_WRITE;41. 42. /* terminate the transfer if there is nothing to do43. * as this is used by the i2c probe to find devices. */44. 45. if (is_lastmsg(i2c) && i2c->msg->len == 0) {46. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0);47. goto out_ack;48. }49. 50. if (i2c->state == STATE_READ)51. goto prepare_read;52. 53. /* fall through to the write state, as we will need to54. * send a byte as well */55. 56. case STATE_WRITE:57. /* we are writing data to the device... check for the58. * end of the message, and if so, work out what to do59. */60. 61. if (!(i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK)) {62. if (iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_LASTBIT) {63. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "WRITE: No Ack\n");64. 65. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -ECONNREFUSED);66. goto out_ack;67. }68. }69. 70. retry_write:71. 72. if (!is_msgend(i2c)) {73. byte = i2c->msg->buf[i2c->msg_ptr++];74. writeb(byte, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS);75. 76. /* delay after writing the byte to allow the77. * data setup time on the bus, as writing the78. * data to the register causes the first bit79. * to appear on SDA, and SCL will change as80. * soon as the interrupt is acknowledged */81. 82. ndelay(i2c->tx_setup);83. 84. } else if (!is_lastmsg(i2c)) {85. /* we need to go to the next i2c message */86. 87. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "WRITE: Next Message\n");88. 89. i2c->msg_ptr = 0;90. i2c->msg_idx++;91. i2c->msg++;92. 93. /* check to see if we need to do another message */94. if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_NOSTART) {95. 96. if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_RD) {97. /* cannot do this, the controller98. * forces us to send a new START99. * when we change direction */100. 101. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -EINVAL);102. }103. 104. goto retry_write;105. } else {106. /* send the new start */107. s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(i2c, i2c->msg);108. i2c->state = STATE_START;109. }110. 111. } else {112. /* send stop */113. 114. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0);115. }116. break;117. 118. case STATE_READ:119. /* we have a byte of data in the data register, do120. * something with it, and then work out wether we are121. * going to do any more read/write122. */123. 124. byte = readb(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS);125. i2c->msg->buf[i2c->msg_ptr++] = byte;126. 127. prepare_read:128. if (is_msglast(i2c)) {129. /* last byte of buffer */130. 131. if (is_lastmsg(i2c))132. s3c24xx_i2c_disable_ack(i2c);133. 134. } else if (is_msgend(i2c)) {135. /* ok, we've read the entire buffer, see if there136. * is anything else we need to do */137. 138. if (is_lastmsg(i2c)) {139. /* last message, send stop and complete */140. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "READ: Send Stop\n");141. 142. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0);143. } else {144. /* go to the next transfer */145. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "READ: Next Transfer\n");146. 147. i2c->msg_ptr = 0;148. i2c->msg_idx++;149. i2c->msg++;150. }151. }152. 153. break;154. }155. 156. /* acknowlegde the IRQ and get back on with the work */157. 158. out_ack:159. tmp = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);160. tmp &= ~S3C2410_IICCON_IRQPEND;161. writel(tmp, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);162. out:163. return ret;164. }
中断处理函数s3c24xx_i2c_irq()主要通过调用i2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte()函数进行传输工作的进一步推进。I2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte()函数通过switch(i2c->state)的不同状态进行处理,在每种状态下,先检查i2c->state的状态与硬件寄存器应该处于的状态是否一致,如果不一致,则证明有误,直接返回。当I2C处于读状态STATE_READ或是写状态STATE_WRITE时,通过is_lastmsg()函数判断是否传输的最后一条I2C消息,如果是,则产生停止位,否则通过i2c->msg_idx++、i2c->msg++推进到下一条消息。
四、I2C的第三部分1.Linux I2C 设备驱动I2C设备驱动要使用i2c_driver和i2c_client数据结构并填充i2c_driver中的成员函数。I2c_client一般被包含在设备的私有信息结构体yyy_data中,而i2c_driver则适合被定义为全局变量并初始化,代码清单33所示为已被初始化的i2c_driver。
代码清单33 已被初始化的i2c_driver1. static struct i2c_driver yyy_driver= {2. .driver = {3. .name = “yyy”,4. },5. .probe = yyy_probe,6. .remove = yyy_remove,7. .id_table = yyy_id,8. };
2.Linux I2C 设备驱动的模块加载与卸载I2C设备驱动的模块加载函数通用的方法是在I2C设备驱动模块加载函数进行通过I2C核心的i2c_add_driver()函数添加i2c_driver的工作,而在模块卸载函数中需要做相反的工作:通过I2C核心的i2c_del_driver()函数删除i2c_driver。代码清单34所示为I2C设备驱动的加载与卸载函数模板
代码清单34 I2C设备驱动的加载与卸载函数模板1. Static int __init yyy_init(void)2. {3. return i2c_add_driver(&yyy_driver);4. };5. void __exit yyy_exit(void)6. {7. i2c_del_driver(&yyy_driver);8. }
3.Linux I2C设备驱动的数据传输在I2C设备上读写数据的时序和数据通常通过i2c_msg数组组织,最后i2c_transfer()函数完成,代码清单35所示为一个读取指定偏移offs寄存器的例子。
代码清单35 I2C设备驱动数据传输范例1. struct i2c_msg msg[2];2. /*第一条消息是写消息*/3. msg[0].addr = client->addr;4. msg[0].flags = 0;5. msg[0].len = 1;6. msg[0].buf = &offs;7. /*第二条消息是读消息*/8. msg[1].addr = client->addr;9. msg[1].flags = I2C_M_RD;10. msg[1].len = sizeof(buf);11. msg[1].buf = &buf[0];
i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msg, 2);
4.Linux的i2c-dev.c文件分析I2c_dev.c文件完全可以被看作一个I2C设备驱动,不过,它实现的一个i2c_client是虚拟、临时的、随着设备文件的打开而产生,并随着设备文件的关闭而撤销,并没有被添加到i2c_adapter的client链表中。i2c-dev.c针对每个I2C适配器生成一个主设备号为89的设备文件,实现了i2c_driver的成员函数以及文件操作接口,所以i2c-dev.c的主体是“i2c_driver成员函数+字符设备驱动”。
i2c-dev.c中提供i2cdev_read()、i2cdev_write()函数来对应用户空间要使用的read()和write()文件操作接口,这两个函数分别调用I2C核心的i2c_master_recv()和i2c_master_send()函数来构造一条I2C消息并引发适配器algorithm通信函数的调用,完成消息的传输,对应于图所示的时序。但是很遗憾,大多数稍微复杂一点I2C设备的读写流程并不对应于一条消息,往往需要两条甚至跟多的消息来进行一次读写周期(即如图所示的重复开始位RepStart模式),这种情况下,在应用层仍然调用read()、write()文件API来读写I2C设备,将不能正确地读写。许多工程师碰到过类似的问题,往往经过相当长时间的调试都没法解决I2C设备的读写,连错误的原因也无法找到,显然是对i2cdev_read()和i2cdev_write()函数的作用有所误解。

[align=left] [/align]
图7 i2cdev_read()和i2cdev_write()函数对应的时序

[align=left] [/align]
图8 RepStart模式
鉴于上述的原因,i2c-dev.c中i2cdev_read()和i2cdev_write()函数不具备太强的通用性,没有太大的实用价值,只能实用于非RepStart模式的情况。对于两条以上消息组成的读写,在用户空间需要组织i2c_msg消息数组并调用I2C_RDWRIOCTL命令。代码清单36所示i2cdev_ioctl()函数的框架。
代码清单36 i2c-dev.c中的i2cdev_ioctl函数1. static long i2cdev_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)2. {3. struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data;4. unsigned long funcs;5. dev_dbg(&client->adapter->dev, "ioctl, cmd=0x%02x, arg=0x%02lx\n",6. cmd, arg);7. switch (cmd) {8. case I2C_SLAVE:9. case I2C_SLAVE_FORCE:10. /* NOTE: devices set up to work with "new style" drivers11. * can't use I2C_SLAVE, even when the device node is not12. * bound to a driver. Only I2C_SLAVE_FORCE will work.13. *14. * Setting the PEC flag here won't affect kernel drivers,15. * which will be using the i2c_client node registered with16. * the driver model core. Likewise, when that client has17. * the PEC flag already set, the i2c-dev driver won't see18. * (or use) this setting.19. */20. if ((arg > 0x3ff) ||21. (((client->flags & I2C_M_TEN) == 0) && arg > 0x7f))22. return -EINVAL;23. if (cmd == I2C_SLAVE && i2cdev_check_addr(client->adapter, arg))24. return -EBUSY;25. /* REVISIT: address could become busy later */26. client->addr = arg;27. return 0;28. case I2C_TENBIT:29. if (arg)30. client->flags |= I2C_M_TEN;31. else32. client->flags &= ~I2C_M_TEN;33. return 0;34. case I2C_PEC:35. if (arg)36. client->flags |= I2C_CLIENT_PEC;37. else38. client->flags &= ~I2C_CLIENT_PEC;39. return 0;40. case I2C_FUNCS:41. funcs = i2c_get_functionality(client->adapter);42. return put_user(funcs, (unsigned long __user *)arg);43. case I2C_RDWR:44. return i2cdev_ioctl_rdrw(client, arg);45. case I2C_SMBUS:46. return i2cdev_ioctl_smbus(client, arg);47. case I2C_RETRIES:48. client->adapter->retries = arg;49. break;50. case I2C_TIMEOUT:51. /* For historical reasons, user-space sets the timeout52. * value in units of 10 ms.53. */54. client->adapter->timeout = msecs_to_jiffies(arg * 10);55. break;56. default:57. /* NOTE: returning a fault code here could cause trouble58. * in buggy userspace code. Some old kernel bugs returned59. * zero in this case, and userspace code might accidentally60. * have depended on that bug.61. */62. return -ENOTTY;63. }64. return 0;65. }
常用的IOCTL包含I2C_SLAVE(设备从设备地址)、I2C_RETRIES(没有收到设备ACK情况下的重试次数,默认为1)、I2C_TIMEOUT以及I2C_RDWR。
5.AT24C02 EEPROM的I2C设备驱动实例I2c设备驱动(也称为客户驱动)是对I2c硬件体系结构中设备端的实现,我们这里是AT24C02的I2c设备驱动,设备一般挂接在受CPU控制的I2c适配器上,通过I2c适配器与CPU交换数据。
drivers/misc/eeprom/at24.c文件支持大多数I2C接口的EEPROM,正如我们前面所述,一个具体的I2C设备驱动有两部分组成,一部分是i2c_driver,用于将设备挂接于I2C总线,一部分是设备本身的驱动。对于EEPROM而言,设备本身的驱动以bin_attribute二进制sysfs结点形式呈现。代码清单37给出了该驱动的框架。
代码清单37 at24_bin_read()函数1. static ssize_t at24_bin_read(struct file *filp, struct kobject *kobj,2. struct bin_attribute *attr,3. char *buf, loff_t off, size_t count)4. {5. struct at24_data *at24;6. 7. at24 = dev_get_drvdata(container_of(kobj, struct device, kobj));8. return at24_read(at24, buf, off, count);9. }
代码清单38 at24_bin_write()函数1. /*2. * Note that if the hardware write-protect pin is pulled high, the whole3. * chip is normally write protected. But there are plenty of product4. * variants here, including OTP fuses and partial chip protect.5. *6. * We only use page mode writes; the alternative is sloooow. This routine7. * writes at most one page.8. */9. static ssize_t at24_eeprom_write(struct at24_data *at24, const char *buf,10. unsigned offset, size_t count)11. {12. struct i2c_client *client;13. struct i2c_msg msg;14. ssize_t status;15. unsigned long timeout, write_time;16. unsigned next_page;17. 18. /* Get corresponding I2C address and adjust offset */19. client = at24_translate_offset(at24, &offset);20. 21. /* write_max is at most a page */22. if (count > at24->write_max)23. count = at24->write_max;24. 25. /* Never roll over backwards, to the start of this page */26. next_page = roundup(offset + 1, at24->chip.page_size);27. if (offset + count > next_page)28. count = next_page - offset;29. 30. /* If we'll use I2C calls for I/O, set up the message */31. if (!at24->use_smbus) {32. int i = 0;33. 34. msg.addr = client->addr;35. msg.flags = 0;36. 37. /* msg.buf is u8 and casts will mask the values */38. msg.buf = at24->writebuf;39. if (at24->chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_ADDR16)40. msg.buf[i++] = offset >> 8;41. 42. msg.buf[i++] = offset;43. memcpy(&msg.buf[i], buf, count);44. msg.len = i + count;45. }46. 47. /*48. * Writes fail if the previous one didn't complete yet. We may49. * loop a few times until this one succeeds, waiting at least50. * long enough for one entire page write to work.51. */52. timeout = jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(write_timeout);53. do {54. write_time = jiffies;55. if (at24->use_smbus) {56. status = i2c_smbus_write_i2c_block_data(client,57. offset, count, buf);58. if (status == 0)59. status = count;60. } else {61. status = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, &msg, 1);62. if (status == 1)63. status = count;64. }65. dev_dbg(&client->dev, "write %zu@%d --> %zd (%ld)\n",66. count, offset, status, jiffies);67. 68. if (status == count)69. return count;70. 71. /* REVISIT: at HZ=100, this is sloooow */72. msleep(1);73. } while (time_before(write_time, timeout));74. 75. return -ETIMEDOUT;76. }
代码清单39 i2c_device_id结构体1. static const struct i2c_device_id at24_ids[] = {2. /* needs 8 addresses as A0-A2 are ignored */3. { "24c00", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(128 / 8, AT24_FLAG_TAKE8ADDR) },4. /* old variants can't be handled with this generic entry! */5. { "24c01", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(1024 / 8, 0) },6. { "24c02", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(2048 / 8, 0) },7. /* spd is a 24c02 in memory DIMMs */8. { "spd", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(2048 / 8,9. AT24_FLAG_READONLY | AT24_FLAG_IRUGO) },10. { "24c04", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(4096 / 8, 0) },11. /* 24rf08 quirk is handled at i2c-core */12. { "24c08", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(8192 / 8, 0) },13. { "24c16", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(16384 / 8, 0) },14. { "24c32", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(32768 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },15. { "24c64", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(65536 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },16. { "24c128", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(131072 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },17. { "24c256", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(262144 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },18. { "24c512", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(524288 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },19. { "24c1024", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(1048576 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },20. { "at24", 0 },21. { /* END OF LIST */ }22. };23. MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(i2c, at24_ids);
代码清单40 初始化at24xx设备的i2c_driver结构体1. /*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/2. 3. static struct i2c_driver at24_driver = {4. .driver = {5. .name = "at24",6. .owner = THIS_MODULE,7. },8. .probe = at24_probe,9. .remove = __devexit_p(at24_remove),10. .id_table = at24_ids,11. };
代码清单41 at24_probe函数1. static int at24_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id)2. {3. struct at24_platform_data chip;4. bool writable;5. int use_smbus = 0;6. struct at24_data *at24;7. int err;8. unsigned i, num_addresses;9. kernel_ulong_t magic;10. 11. if (client->dev.platform_data) {12. chip = *(struct at24_platform_data *)client->dev.platform_data;13. } else {14. if (!id->driver_data) {15. err = -ENODEV;16. goto err_out;17. }18. magic = id->driver_data;19. chip.byte_len = BIT(magic & AT24_BITMASK(AT24_SIZE_BYTELEN));20. magic >>= AT24_SIZE_BYTELEN;21. chip.flags = magic & AT24_BITMASK(AT24_SIZE_FLAGS);22. /*23. * This is slow, but we can't know all eeproms, so we better24. * play safe. Specifying custom eeprom-types via platform_data25. * is recommended anyhow.26. */27. chip.page_size = 1;28. 29. /* update chipdata if OF is present */30. at24_get_ofdata(client, &chip);31. 32. chip.setup = NULL;33. chip.context = NULL;34. }35. 36. if (!is_power_of_2(chip.byte_len))37. dev_warn(&client->dev,38. "byte_len looks suspicious (no power of 2)!\n");39. if (!chip.page_size) {40. dev_err(&client->dev, "page_size must not be 0!\n");41. err = -EINVAL;42. goto err_out;43. }44. if (!is_power_of_2(chip.page_size))45. dev_warn(&client->dev,46. "page_size looks suspicious (no power of 2)!\n");47. 48. /* Use I2C operations unless we're stuck with SMBus extensions. */49. if (!i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter, I2C_FUNC_I2C)) {50. if (chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) {51. err = -EPFNOSUPPORT;52. goto err_out;53. } 54. if (i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter,55. I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_I2C_BLOCK)) {56. use_smbus = I2C_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK_DATA;57. } else if (i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter,58. I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_WORD_DATA)) {59. use_smbus = I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA;60. } else if (i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter,61. I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE_DATA)) {62. use_smbus = I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA;63. } else {64. err = -EPFNOSUPPORT;65. goto err_out;66. }67. }68. 69. if (chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_TAKE8ADDR)70. num_addresses = 8;71. else72. num_addresses = DIV_ROUND_UP(chip.byte_len,73. (chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) ? 65536 : 256);74. 75. at24 = kzalloc(sizeof(struct at24_data) +76. num_addresses * sizeof(struct i2c_client *), GFP_KERNEL);77. if (!at24) {78. err = -ENOMEM;79. goto err_out;80. }81. 82. mutex_init(&at24->lock);83. at24->use_smbus = use_smbus;84. at24->chip = chip;85. at24->num_addresses = num_addresses;86. 87. /*88. * Export the EEPROM bytes through sysfs, since that's convenient.89. * By default, only root should see the data (maybe passwords etc)90. */91. sysfs_bin_attr_init(&at24->bin);92. at24->bin.attr.name = "eeprom";93. at24->bin.attr.mode = chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_IRUGO ? S_IRUGO : S_IRUSR;94. at24->bin.read = at24_bin_read;95. at24->bin.size = chip.byte_len;96. 97. at24->macc.read = at24_macc_read;98. 99. writable = !(chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_READONLY);100. if (writable) {101. if (!use_smbus || i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter,102. I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_I2C_BLOCK)) {103. 104. unsigned write_max = chip.page_size;105. 106. at24->macc.write = at24_macc_write;107. 108. at24->bin.write = at24_bin_write;109. at24->bin.attr.mode |= S_IWUSR;110. 111. if (write_max > io_limit)112. write_max = io_limit;113. if (use_smbus && write_max > I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_MAX)114. write_max = I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_MAX;115. at24->write_max = write_max;116. 117. /* buffer (data + address at the beginning) */118. at24->writebuf = kmalloc(write_max + 2, GFP_KERNEL);119. if (!at24->writebuf) {120. err = -ENOMEM;121. goto err_struct;122. }123. } else {124. dev_warn(&client->dev,125. "cannot write due to controller restrictions.");126. }127. }128. 129. at24->client[0] = client;130. 131. /* use dummy devices for multiple-address chips */132. for (i = 1; i < num_addresses; i++) {133. at24->client[i] = i2c_new_dummy(client->adapter,134. client->addr + i);135. if (!at24->client[i]) {136. dev_err(&client->dev, "address 0x%02x unavailable\n",137. client->addr + i);138. err = -EADDRINUSE;139. goto err_clients;140. }141. }142. err = sysfs_create_bin_file(&client->dev.kobj, &at24->bin);143. if (err)144. goto err_clients;145. 146. i2c_set_clientdata(client, at24);147. 148. dev_info(&client->dev, "%zu byte %s EEPROM, %s, %u bytes/write\n",149. at24->bin.size, client->name,150. writable ? "writable" : "read-only", at24->write_max);151. if (use_smbus == I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA ||152. use_smbus == I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA) {153. dev_notice(&client->dev, "Falling back to %s reads, "154. "performance will suffer\n", use_smbus ==155. I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA ? "word" : "byte");156. }157. 158. /* export data to kernel code */159. if (chip.setup)160. chip.setup(&at24->macc, chip.context);161. 162. return 0;163. 164. err_clients:165. for (i = 1; i < num_addresses; i++)166. if (at24->client[i])167. i2c_unregister_device(at24->client[i]);168. 169. kfree(at24->writebuf);170. err_struct:171. kfree(at24);172. err_out:173. dev_dbg(&client->dev, "probe error %d\n", err);174. return err;175. }176. 177. 代码清单42 at24_remove函数178. static int __devexit at24_remove(struct i2c_client *client)179. {180. struct at24_data *at24;181. int i;182. 183. at24 = i2c_get_clientdata(client);184. sysfs_remove_bin_file(&client->dev.kobj, &at24->bin);185. 186. for (i = 1; i < at24->num_addresses; i++)187. i2c_unregister_device(at24->client[i]);188. 189. kfree(at24->writebuf);190. kfree(at24);191. return 0;192. }
代码清单43 at24xx设备驱动模块的加载和卸载函数1. static int __init at24_init(void)2. {3. if (!io_limit) {4. pr_err("at24: io_limit must not be 0!\n");5. return -EINVAL;6. } 7. 8. io_limit = rounddown_pow_of_two(io_limit);9. return i2c_add_driver(&at24_driver);10. } 11. module_init(at24_init);12. 13. static void __exit at24_exit(void)14. {15. i2c_del_driver(&at24_driver);16. }17. module_exit(at24_exit);18. 19. MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Driver for most I2C EEPROMs");20. MODULE_AUTHOR("David Brownell and Wolfram Sang");21. MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
At24_bin_read()和at24_bin_write()俩个函数是EEPROM驱动本身的读写实现即bin_attribute驱动,之后一部分是i2c_driver,两者在i2c_driver的probe()、remove函数中建立关联。I2c_driver的probe()函数中的初始化并通过sysfs_create_bin_file()注册了二进制sysfs结点,而remove()函数则通过sysfs_remove_bin_file()注销了sysfs结点。
6.添加板级信息drivers/misc/eeprom/at24.c不依赖于具体的CPU和I2C控制寄存器硬件特性,因此,如果某一电路板包含该外设,只需要在板文件中添加对应的i2c_board_info,如对于s3c2440要使其支持at24c02 eeprom只需要作如下工作:
首先是要在内核中注册板级信息,因为设备和驱动需要匹配,它们是通过设备名和驱动名进行匹配的。因为AT24C02芯片是由2048bits构成,所以有2048 / 8 = 256byte,并将其分成32页每页有8byte大小,是8bits寻址,如果AT24C02芯片的A0,A1,A2,这三个引脚接地,着AT24C02芯片从地址是01010000b(即0x50),如果AT24C02芯片的A0结高电平,A1,A2两个引脚接地,着AT24C02芯片从地址是01010001b(即0x51),这些都是AT24C02的datasheet上有的,不同芯片不同情况。下面在linux-3.0/arch/arm/mach-s3c2440/mach-smdk2440.c添加AT24C02设备的板级信息如下:1. [fulinux@ubuntu linux-3.0]$ vim arch/arm/mach-s3c2440/mach-smdk2440.c 2. #include <linux/i2c.h> 3. #include <linux/i2c/at24.h> 4. 5. static struct at24_platform_data at24c02= {6. .byte_len = SZ_2K / 8,7. .page_size = 8,8. .flags = AT24_FLAG_ADDR8,9. };10. 11. static struct i2c_board_info __initdata smdk2440_i2c_devs[] = {12. {13. I2C_BOARD_INFO("24c02", 0x50),14. .platform_data = &at24c02,15. },16. /* more devices can be added using expansion connectors */17. };
********************************************************************************************装载声明:希望大家能转载此文谢谢:原文链接
********************************************************************************************
1.I2C核心I2C核心是I2c总线和I2c设备驱动的中间枢纽,它以通用的、与平台无关的接口实现了I2C中设备与适配器的沟通,提供了I2C总线驱动和设备驱动的注册、注销方法,I2C通信方法(即“algorithm”)上层的、与具体适配器无关的代码以及探测设备、检测设备的地址的上层代码等。I2c总线驱动填充I2c_adapter和I2c_algorithm结构体,I2c设备驱动填充I2c_driver和i2c_client结构体并实现其本身所对应设备类型的驱动。
2.I2C总线驱动I2C总线驱动是对I2C硬件体系结构中适配器的实现,适配器可由CPU控制,甚至可以直接集成在CPU内部。
I2C总线驱动主要包含了I2C适配器数据结构i2c_adapter、I2C适配器的algorithm数据结构i2c_algorithm和控制I2C适配器产生通信信号的函数。
经由I2C总线驱动的代码,我们可以控制I2C适配器以主控制方式产生开始、停止位、读写周期,以及以从设备方式读写、产生ACK等。
3.I2C设备驱动I2C设备驱动(也称为客户端驱动)是对I2C硬件体系结构中设备端的实现,设备一般挂接在受CPU控制的I2C适配器上,通过I2C适配器与CPU交换数据。
I2C设备驱动主要包含了数据结构体i2c_driver和i2c_client,我们需要具体设备实现其中的成员函数。

[align=left] [/align]
图1 I2C驱动体系结构图1

[align=left] [/align]
图2 I2C驱动体系结构图2
另外,系统中i2c-dev.c文件定义的主设备号为89的设备可以方便地给应用程序提供读写I2c设备寄存器的能力,使得工程师大多数时候并不需要为具体的I2c设备驱动定义文件操作接口。
如何理解adapter和client呢?它在s3c2440中对应的是什么?Adapter和client都是linux驱动软件抽象出来的东西,Linux I2C框架搞那么复杂是为了通用性及为了符合Linux内核驱动模式而制定的。简单的说,你的开发板上有几个I2C接口,就有几个adapter , 也就是有几条I2C bus , I2C client对应的就是你的外围I2C 设备,有几个就有几个client , 把这些设备插入开发板, 对应其中的一条bus, 那么相应的就对应了其中的一个adapter , 接下来的就是I2c核心部分使client与 adapter匹配成对。
在linux内核中,所有的I2C设备都在sysfs文件系统中显示,存在于/sys/bus/i2c/目录下,适配器地址和芯片地址的形式列出,例如:1. [fulinux@ubuntu linux-3.0]$ tree /sys/bus/i2c/ 2. /sys/bus/i2c/3. |-- devices4. | |-- i2c-0 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-05. | |-- i2c-1 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-16. | |-- i2c-2 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-27. | |-- i2c-3 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-38. | |-- i2c-4 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-49. | |-- i2c-5 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/i2c-510. | |-- i2c-6 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/drm/card0/card0-DP-1/i2c-611. | `-- i2c-7 -> ../../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:02.0/drm/card0/card0-DP-2/i2c-712. |-- drivers13. | |-- 88PM860x14. | | |-- bind15. | | |-- uevent16. | | `-- unbind17. | |-- aat287018. | | |-- bind19. | | |-- uevent20. | | `-- unbind21. | |-- ab310022. | | |-- bind23. | | |-- uevent24. | | `-- unbind25. | |-- adp5520
下面我以s3c2440开发板及其之上的EEPROM芯片AT24C02和linux-3.0内核平台讲解I2c的三个部分。
********************************************************************************************转载声明:希望大家能转载此文谢谢 原文链接
********************************************************************************************
4.s3c2440和at24c02硬件特性请看s3c2440.pdf
芯片AT24C02的电气特性:• Low-voltage and Standard-voltage Operation– 2.7 (VCC= 2.7V to 5.5V)– 1.8 (VCC= 1.8V to 5.5V)• Internally Organized 128 x 8 (1K), 256 x 8 (2K), 512 x 8 (4K),1024 x 8 (8K) or 2048 x 8 (16K)• Two-wire Serial Interface• Schmitt Trigger, Filtered Inputs for Noise Suppression• Bidirectional Data Transfer Protocol• 100 kHz (1.8V) and 400 kHz (2.7V, 5V) Compatibility• Write Protect Pin for Hardware Data Protection• 8-byte Page (1K, 2K), 16-byte Page (4K, 8K, 16K) Write Modes• Partial Page Writes Allowed• Self-timed Write Cycle (5 ms max)• High-reliability– Endurance: 1 Million Write Cycles– Data Retention: 100 Years• Automotive Grade and Lead-free/Halogen-free Devices Available• 8-lead PDIP, 8-lead JEDEC SOIC, 8-lead MAP, 5-lead SOT23,8-lead TSSOP and 8-ball dBGA2 Packages• Die Sales: Wafer Form, Waffle Pack and Bumped Wafers
主要是看AT24C02.pdf

图3 S3c244开发板核心板电路图

图4 AT24C02电路图
5.i2c.h头文件内核中i2c.h这个头文件对i2c_driver、i2c_client、i2c_adapter和i2c_algorithm着4个数据结构进行了定义。理解这4个结构的作用十分关键,代码清单1、2、3、4分别给出了它们的定义。
代码清单1 i2c_adapter结构体
1. /*2. * i2c_adapter is the structure used to identify a physical i2c bus along3. * with the access algorithms necessary to access it.4. */5. struct i2c_adapter {6. struct module *owner;7. unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */8. const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */9. void *algo_data;10. /* data fields that are valid for all devices */11. struct rt_mutex bus_lock;12. int timeout; /* in jiffies */13. int retries;14. struct device dev; /* the adapter device */15. int nr;16. char name[48];17. struct completion dev_released;18. struct mutex userspace_clients_lock;19. struct list_head userspace_clients;20. };
代码清单2 i2c_algorithm结构体1. /*2. * The following structs are for those who like to implement new bus drivers:3. * i2c_algorithm is the interface to a class of hardware solutions which can4. * be addressed using the same bus algorithms - i.e. bit-banging or the PCF85845. * to name two of the most common.6. */7. struct i2c_algorithm {8. /* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer9. to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set10. smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated11. using common I2C messages */12. /* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully13. processed, or a negative value on error */14. int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs,15. int num);16. int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,17. unsigned short flags, char read_write,18. u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);19. /* To determine what the adapter supports */20. u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adapter *);21. };
上述代码第4行对应为SMBus传输函数指针,SMBus大部分基于I2C总线规范,SMBus不需要增加额外引脚。与I2C总线相比,SMBus增加了一些新的功能特性,在访问时序也有一定的差异。
代码清单3 i2c_driver结构体1. /*2. * struct i2c_driver - represent an I2C device driver3. * @class: What kind of i2c device we instantiate (for detect)4. * @attach_adapter: Callback for bus addition (deprecated)5. * @detach_adapter: Callback for bus removal (deprecated)6. * @probe: Callback for device binding7. * @remove: Callback for device unbinding8. * @shutdown: Callback for device shutdown9. * @suspend: Callback for device suspend10. * @resume: Callback for device resume11. * @alert: Alert callback, for example for the SMBus alert protocol12. * @command: Callback for bus-wide signaling (optional)13. * @driver: Device driver model driver14. * @id_table: List of I2C devices supported by this driver15. * @detect: Callback for device detection16. * @address_list: The I2C addresses to probe (for detect)17. * @clients: List of detected clients we created (for i2c-core use only)18. *19. * The driver.owner field should be set to the module owner of this driver.20. * The driver.name field should be set to the name of this driver.21. *22. * For automatic device detection, both @detect and @address_data must23. * be defined. @class should also be set, otherwise only devices forced24. * with module parameters will be created. The detect function must25. * fill at least the name field of the i2c_board_info structure it is26. * handed upon successful detection, and possibly also the flags field.27. *28. * If @detect is missing, the driver will still work fine for enumerated29. * devices. Detected devices simply won't be supported. This is expected30. * for the many I2C/SMBus devices which can't be detected reliably, and31. * the ones which can always be enumerated in practice.32. *33. * The i2c_client structure which is handed to the @detect callback is34. * not a real i2c_client. It is initialized just enough so that you can35. * call i2c_smbus_read_byte_data and friends on it. Don't do anything36. * else with it. In particular, calling dev_dbg and friends on it is37. * not allowed.38. */39. struct i2c_driver {40. unsigned int class;41. /* Notifies the driver that a new bus has appeared or is about to be42. * removed. You should avoid using this, it will be removed in a43. * near future.44. */45. int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated;46. int (*detach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated;47. /* Standard driver model interfaces */48. int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);49. int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);50. /* driver model interfaces that don't relate to enumeration */51. void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);52. int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_message_t mesg);53. int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *);54. /* Alert callback, for example for the SMBus alert protocol.55. * The format and meaning of the data value depends on the protocol.56. * For the SMBus alert protocol, there is a single bit of data passed57. * as the alert response's low bit ("event flag").58. */59. void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, unsigned int data);60. /* a ioctl like command that can be used to perform specific functions61. * with the device.62. */63. int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);64. struct device_driver driver;65. const struct i2c_device_id *id_table;66. /* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */67. int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *);68. const unsigned short *address_list;69. struct list_head clients;70. };
代码清单4 i2c_client结构体1. /*2. * struct i2c_client - represent an I2C slave device3. * @flags: I2C_CLIENT_TEN indicates the device uses a ten bit chip address;4. * I2C_CLIENT_PEC indicates it uses SMBus Packet Error Checking5. * @addr: Address used on the I2C bus connected to the parent adapter.6. * @name: Indicates the type of the device, usually a chip name that's7. * generic enough to hide second-sourcing and compatible revisions.8. * @adapter: manages the bus segment hosting this I2C device9. * @driver: device's driver, hence pointer to access routines10. * @dev: Driver model device node for the slave.11. * @irq: indicates the IRQ generated by this device (if any)12. * @detected: member of an i2c_driver.clients list or i2c-core's13. * userspace_devices list14. *15. * An i2c_client identifies a single device (i.e. chip) connected to an16. * i2c bus. The behaviour exposed to Linux is defined by the driver17. * managing the device.18. */19. struct i2c_client {20. unsigned short flags; /* div., see below */21. unsigned short addr; /* chip address - NOTE: 7bit */22. /* addresses are stored in the */23. /* _LOWER_ 7 bits */24. char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE];25. struct i2c_adapter *adapter; /* the adapter we sit on */26. struct i2c_driver *driver; /* and our access routines */27. struct device dev; /* the device structure */28. int irq; /* irq issued by device */29. struct list_head detected;30. };
下面分析i2c_driver、i2c_client、i2c_adapter和i2c_algorithm这4个数据结构的作用及盘根错节的关系。
(1)2c_adapter与i2c_algorithmi2c_adapter对应于物理上的一个适配器,而i2c_algorithm对应一套通信方法。一个I2C适配器需要i2c_algorithm中提供的通信函数来控制适配器上产生特定的访问周期。缺少i2c_algorithm的i2c_adapter什么也做不了,因此i2c_adapter中包含其使用的i2c_algorithm的指针。
I2c_algorithm中关键函数master_xfer用于产生I2C访问周期需要的信号,以i2c_msg(即I2C消息)为单位。I2c_msg结构体非常关键,代码清单5给出了它的定义。
代码清单5 i2c_msg结构体/** * struct i2c_msg - an I2C transaction segment beginning with START * @addr: Slave address, either seven or ten bits. When this is a ten * bit address, I2C_M_TEN must be set in @flags and the adapter * must support I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR. * @flags: I2C_M_RD is handled by all adapters. No other flags may be * provided unless the adapter exported the relevant I2C_FUNC_* * flags through i2c_check_functionality(). * @len: Number of data bytes in @buf being read from or written to the * I2C slave address. For read transactions where I2C_M_RECV_LEN * is set, the caller guarantees that this buffer can hold up to * 32 bytes in addition to the initial length byte sent by the * slave (plus, if used, the SMBus PEC); and this value will be * incremented by the number of block data bytes received. * @buf: The buffer into which data is read, or from which it's written. * * An i2c_msg is the low level representation of one segment of an I2C * transaction. It is visible to drivers in the @i2c_transfer() procedure, * to userspace from i2c-dev, and to I2C adapter drivers through the * @i2c_adapter.@master_xfer() method. * * Except when I2C "protocol mangling" is used, all I2C adapters implement * the standard rules for I2C transactions. Each transaction begins with a * START. That is followed by the slave address, and a bit encoding read * versus write. Then follow all the data bytes, possibly including a byte * with SMBus PEC. The transfer terminates with a NAK, or when all those * bytes have been transferred and ACKed. If this is the last message in a * group, it is followed by a STOP. Otherwise it is followed by the next * @i2c_msg transaction segment, beginning with a (repeated) START. * * Alternatively, when the adapter supports I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING then * passing certain @flags may have changed those standard protocol behaviors. * Those flags are only for use with broken/nonconforming slaves, and with * adapters which are known to support the specific mangling options they * need (one or more of IGNORE_NAK, NO_RD_ACK, NOSTART, and REV_DIR_ADDR). */struct i2c_msg { __u16 addr; /* slave address */ __u16 flags;#define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */#define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */#define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */#define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */#define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */#define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */#define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */ __u16 len; /* msg length */ __u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */};
(2)i2c_driver与i2c_clienti2c_driver对应一套驱动方法,其主要成员函数是probe()、remove()、suspend()、resume()等,另外id_table是该驱动所支持的I2C设备的ID表。i2c_client对应于真实的物理设备,每个I2C设备都需要一个i2c_client来描述。I2c_driver和i2c_client的关系是一对多,一个i2c_driver上可以支持多个同类型的i2c_client。
I2c_client信息通常在BSP的板文件中通过i2c_board_info填充,如下面代码就定义了一个I2C设备ID为“24c02”、地址为0x50的i2c_client:
代码清单6 i2c_board_info结构体定义1. static struct i2c_board_info __initdata smdk2440_i2c_devs[] = {2. {3. I2C_BOARD_INFO("24c02", 0x50),4. .platform_data = &at24c02,5. },6. /* more devices can be added using expansion connectors */7. };
在I2C总线驱动i2c_bus_type的match()函数i2c_device_match()中,会调用i2c_match_id()函数匹配板文件中定义的ID和i2c_driver所支持的ID表。
代码清单7 i2c_device_match函数在linux-3.0/drivers/i2c/i2c-core.c1. static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)2. {3. struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);4. struct i2c_driver *driver;5. if (!client)6. return 0;7. /* Attempt an OF style match */8. if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))9. return 1;10. driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);11. /* match on an id table if there is one */12. if (driver->id_table)13. return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL;14. return 0;15. }
(3)i2c_adpater与i2c_clienti2c_adapter与i2c_client的关系与I2C硬件体系中适配器和设备的关系一致,即i2c_client依附于i2c_adapter。由于一个适配器上可以连接多个I2C设备,所以一个i2c_adapter也可以被多个i2c_client依附,i2c_adapter中包含依附于它的i2c_client的链表。
代码清单8 i2c_client的链表1. struct list_head userspace_clients;
假设I2C总线适配器xxx上有两个使用相同驱动程序的yyyI2C设备,在打开I2C总线的设备节点后相关数据结构之间的逻辑组织关系将如下图所示:

[align=left] [/align]
图5 I2C总线的设备节点后相关数据结构之间的逻辑组织关系图
从上面的分析可知,虽然I2C硬件体系结构简单,但是I2C体系结构在linux中的实现却相当复杂。当工程师拿到实际的电路板,面对复杂的linux I2C子系统,应该如何下手写驱动呢?究竟要哪些是需要亲自做的,哪些是内核已经提供的呢?理清这个问题非常有意义,可以使我们面对具体问题时迅速地抓住重点。
一方面,适配器驱动可能是linux内核本身还不包含的;另一方面,挂接在适配器上的就提设备可能也是linux内核还不包含的。因此,工程师要实现的主要工作如下。
提供I2C适配器的硬件驱动,探测、初始化I2C适配器(如申请I2C的I/O地址和中断号)、驱动CPU控制的I2C适配器从硬件上产生各种信号以及处理I2C中断等。
提供I2C适配器的algorithm,具体适配器的xxx_xfer()函数填充i2c_algorithm的master_xfer指针,并把i2c_algorithm指针赋值给i2c_adapter的algo指针。
实现I2C设备驱动中的i2c_driver接口,具体设备yyy_probe()、yyy_remove()、yyy_suspend()、yyy_resume()函数指针和i2c_device_id设备ID表赋值给i2c_driver的probe、remove、suspend、resume和id_table指针。
实现I2C设备所对应类型的具体驱动,i2c_driver只是实现设备与总线的挂接,而挂接在总线上的设备则是千差万别的。例如,如果字符设备,就实现文件操作接口,即实现具体yyy的yyy_read()、yyy_write()和yyy_ioctl()函数等;如果是声卡,就实现ALSA驱动。
二、I2C的第一部分1.Linux I2C核心I2C核心(driver/i2c/i2c-core.c)文件中提供了一组不依赖与硬件平台的接口函数,这个文件一般不需要被工程师修改,但是理解其中的主要函数非常关键,因为I2C总线驱动和设备驱动之间依赖于I2C核心作为纽带I2C核心中的主要函数如下。
2.增加/删除i2c_adapter代码清单9 i2c_add_adapter函数:1. /**2. * i2c_add_adapter - declare i2c adapter, use dynamic bus number3. * @adapter: the adapter to add4. * Context: can sleep5. *6. * This routine is used to declare an I2C adapter when its bus number7. * doesn't matter. Examples: for I2C adapters dynamically added by8. * USB links or PCI plugin cards.9. *10. * When this returns zero, a new bus number was allocated and stored11. * in adap->nr, and the specified adapter became available for clients.12. * Otherwise, a negative errno value is returned.13. */14. int i2c_add_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adapter)15. {16. int id, res = 0;17. retry:18. if (idr_pre_get(&i2c_adapter_idr, GFP_KERNEL) == 0)19. return -ENOMEM;20. mutex_lock(&core_lock);21. /* "above" here means "above or equal to", sigh */22. res = idr_get_new_above(&i2c_adapter_idr, adapter,23. __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num, &id);24. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);25. if (res < 0) {26. if (res == -EAGAIN)27. goto retry;28. return res;29. }30. adapter->nr = id;31. return i2c_register_adapter(adapter);32. }33. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_add_adapter);
代码清单10 I2c_del_adapter函数:1. /**2. * i2c_del_adapter - unregister I2C adapter3. * @adap: the adapter being unregistered4. * Context: can sleep5. *6. * This unregisters an I2C adapter which was previously registered7. * by @i2c_add_adapter or @i2c_add_numbered_adapter.8. */9. int i2c_del_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)10. {11. int res = 0;12. struct i2c_adapter *found;13. struct i2c_client *client, *next;14. /* First make sure that this adapter was ever added */15. mutex_lock(&core_lock);16. found = idr_find(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap->nr);17. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);18. if (found != adap) {19. pr_debug("i2c-core: attempting to delete unregistered "20. "adapter [%s]\n", adap->name);21. return -EINVAL;22. }23. /* Tell drivers about this removal */24. mutex_lock(&core_lock);25. res = bus_for_each_drv(&i2c_bus_type, NULL, adap,26. __process_removed_adapter);27. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);28. if (res)29. return res;30. /* Remove devices instantiated from sysfs */31. mutex_lock(&adap->userspace_clients_lock);32. list_for_each_entry_safe(client, next, &adap->userspace_clients,33. detected) {34. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "Removing %s at 0x%x\n", client->name,35. client->addr);36. list_del(&client->detected);37. i2c_unregister_device(client);38. }39. mutex_unlock(&adap->userspace_clients_lock);40. 41. /* Detach any active clients. This can't fail, thus we do not42. * check the returned value. This is a two-pass process, because43. * we can't remove the dummy devices during the first pass: they44. * could have been instantiated by real devices wishing to clean45. * them up properly, so we give them a chance to do that first. */46. res = device_for_each_child(&adap->dev, NULL, __unregister_client);47. res = device_for_each_child(&adap->dev, NULL, __unregister_dummy);48. 49. #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT50. class_compat_remove_link(i2c_adapter_compat_class, &adap->dev,51. adap->dev.parent);52. #endif53. 54. /* device name is gone after device_unregister */55. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "adapter [%s] unregistered\n", adap->name);56. 57. /* clean up the sysfs representation */58. init_completion(&adap->dev_released);59. device_unregister(&adap->dev);60. 61. /* wait for sysfs to drop all references */62. wait_for_completion(&adap->dev_released);63. 64. /* free bus id */65. mutex_lock(&core_lock);66. idr_remove(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap->nr);67. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);68. 69. /* Clear the device structure in case this adapter is ever going to be70. added again */71. memset(&adap->dev, 0, sizeof(adap->dev));72. 73. return 0;74. }75. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_del_adapter);
3.增加/删除i2c_driver代码清单11 I2c_register_driver函数:1. static int i2c_register_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)2. {3. int res = 0;4. 5. /* Can't register until after driver model init */6. if (unlikely(WARN_ON(!i2c_bus_type.p))) {7. res = -EAGAIN;8. goto out_list;9. } 10. 11. /* Sanity checks */12. if (unlikely(adap->name[0] == '\0')) { 13. pr_err("i2c-core: Attempt to register an adapter with "14. "no name!\n");15. return -EINVAL;16. } 17. if (unlikely(!adap->algo)) { 18. pr_err("i2c-core: Attempt to register adapter '%s' with "19. "no algo!\n", adap->name); 20. return -EINVAL;21. } 22. 23. rt_mutex_init(&adap->bus_lock); 24. mutex_init(&adap->userspace_clients_lock);25. INIT_LIST_HEAD(&adap->userspace_clients);26. 27. /* Set default timeout to 1 second if not already set */28. if (adap->timeout == 0)29. adap->timeout = HZ; 30. 31. dev_set_name(&adap->dev, "i2c-%d", adap->nr);32. adap->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;33. adap->dev.type = &i2c_adapter_type;34. res = device_register(&adap->dev);35. if (res)36. goto out_list;37. 38. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "adapter [%s] registered\n", adap->name);39. 40. #ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT41. res = class_compat_create_link(i2c_adapter_compat_class, &adap->dev,42. adap->dev.parent);43. if (res)44. dev_warn(&adap->dev,45. "Failed to create compatibility class link\n");46. #endif47. 48. /* create pre-declared device nodes */49. if (adap->nr < __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num)50. i2c_scan_static_board_info(adap);51. 52. /* Notify drivers */53. mutex_lock(&core_lock);54. bus_for_each_drv(&i2c_bus_type, NULL, adap, __process_new_adapter);55. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);56. 57. return 0;58. 59. out_list:60. mutex_lock(&core_lock);61. idr_remove(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap->nr);62. mutex_unlock(&core_lock);63. return res;64. }
代码清单12 i2c_del_driver函数:1. /*2. * i2c_del_driver - unregister I2C driver3. * @driver: the driver being unregistered4. * Context: can sleep5. */6. void i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *driver)7. {8. i2c_for_each_dev(driver, __process_removed_driver);9. 10. driver_unregister(&driver->driver);11. pr_debug("i2c-core: driver [%s] unregistered\n", driver->driver.name);12. }13. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_del_driver);
4.i2c_client依附/脱离当一个具体的client被侦测到并被关联的时候,设备和使用爽肤水文件件被注册。相反地,在client杯取消关联的时候,sysfs文件和设备也被注销。如下代码清单13。
代码清单13 i2c_new_device函数:1. /**2. * i2c_new_device - instantiate an i2c device3. * @adap: the adapter managing the device4. * @info: describes one I2C device; bus_num is ignored5. * Context: can sleep6. *7. * Create an i2c device. Binding is handled through driver model8. * probe()/remove() methods. A driver may be bound to this device when we9. * return from this function, or any later moment (e.g. maybe hotplugging will10. * load the driver module). This call is not appropriate for use by mainboard11. * initialization logic, which usually runs during an arch_initcall() long12. * before any i2c_adapter could exist.13. *14. * This returns the new i2c client, which may be saved for later use with15. * i2c_unregister_device(); or NULL to indicate an error.16. */17. struct i2c_client *18. i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_board_info const *info)19. {20. struct i2c_client *client;21. int status;22. 23. client = kzalloc(sizeof *client, GFP_KERNEL);24. if (!client)25. return NULL;26. 27. client->adapter = adap;28. 29. client->dev.platform_data = info->platform_data;30. 31. if (info->archdata)32. client->dev.archdata = *info->archdata;33. 34. client->flags = info->flags;35. client->addr = info->addr;36. client->irq = info->irq;37. 38. strlcpy(client->name, info->type, sizeof(client->name));39. 40. /* Check for address validity */41. status = i2c_check_client_addr_validity(client);42. if (status) {43. dev_err(&adap->dev, "Invalid %d-bit I2C address 0x%02hx\n",44. client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_TEN ? 10 : 7, client->addr);45. goto out_err_silent;46. }47. 48. /* Check for address business */49. status = i2c_check_addr_busy(adap, client->addr);50. if (status)51. goto out_err;52. 53. client->dev.parent = &client->adapter->dev;54. client->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;55. client->dev.type = &i2c_client_type;56. client->dev.of_node = info->of_node;57. 58. dev_set_name(&client->dev, "%d-%04x", i2c_adapter_id(adap),59. client->addr);60. status = device_register(&client->dev);61. if (status)62. goto out_err;63. 64. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "client [%s] registered with bus id %s\n",65. client->name, dev_name(&client->dev));66. 67. return client;68. 69. out_err:70. dev_err(&adap->dev, "Failed to register i2c client %s at 0x%02x "71. "(%d)\n", client->name, client->addr, status);72. out_err_silent:73. kfree(client);74. return NULL;75. }76. EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_new_device);77. 78. 代码清单14 i2c_unregister_device函数79. /**80. * i2c_unregister_device - reverse effect of i2c_new_device()81. * @client: value returned from i2c_new_device()82. * Context: can sleep83. */84. void i2c_unregister_device(struct i2c_client *client)85. {86. device_unregister(&client->dev);87. }88. EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_unregister_device);
5.I2C传输、发送和接收I2c_transfer()函数本身不具备驱动适配器物理硬件完成消息交互的能力,它只是寻找到i2c_adapter对应的i2c_algorithm,并使用i2c_algorithm的master_xfer()函数真正驱动硬件流程。
代码清单15 i2c_transfer函数1. /* ----------------------------------------------------2. * the functional interface to the i2c busses.3. * ----------------------------------------------------4. */5. 6. /**7. * i2c_transfer - execute a single or combined I2C message8. * @adap: Handle to I2C bus9. * @msgs: One or more messages to execute before STOP is issued to10. * terminate the operation; each message begins with a START.11. * @num: Number of messages to be executed.12. *13. * Returns negative errno, else the number of messages executed.14. *15. * Note that there is no requirement that each message be sent to16. * the same slave address, although that is the most common model.17. */18. int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)19. {20. unsigned long orig_jiffies;21. int ret, try;22. 23. /* REVISIT the fault reporting model here is weak:24. *25. * - When we get an error after receiving N bytes from a slave,26. * there is no way to report "N".27. *28. * - When we get a NAK after transmitting N bytes to a slave,29. * there is no way to report "N" ... or to let the master30. * continue executing the rest of this combined message, if31. * that's the appropriate response.32. *33. * - When for example "num" is two and we successfully complete34. * the first message but get an error part way through the35. * second, it's unclear whether that should be reported as36. * one (discarding status on the second message) or errno37. * (discarding status on the first one).38. */39. 40. if (adap->algo->master_xfer) {41. #ifdef DEBUG42. for (ret = 0; ret < num; ret++) {43. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "master_xfer[%d] %c, addr=0x%02x, "44. "len=%d%s\n", ret, (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RD)45. ? 'R' : 'W', msgs[ret].addr, msgs[ret].len,46. (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RECV_LEN) ? "+" : "");47. }48. #endif49. 50. if (in_atomic() || irqs_disabled()) {51. ret = i2c_trylock_adapter(adap);52. if (!ret)53. /* I2C activity is ongoing. */54. return -EAGAIN;55. } else {56. i2c_lock_adapter(adap);57. }58. 59. /* Retry automatically on arbitration loss */60. orig_jiffies = jiffies;61. for (ret = 0, try = 0; try <= adap->retries; try++) {62. ret = adap->algo->master_xfer(adap, msgs, num);63. if (ret != -EAGAIN)64. break;65. if (time_after(jiffies, orig_jiffies + adap->timeout))66. break;67. }68. i2c_unlock_adapter(adap);69. 70. return ret;71. } else {72. dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "I2C level transfers not supported\n");73. return -EOPNOTSUPP;74. }75. }76. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_transfer);
代码清单16 i2c_master_send函数1. /**2. * i2c_master_send - issue a single I2C message in master transmit mode3. * @client: Handle to slave device4. * @buf: Data that will be written to the slave5. * @count: How many bytes to write, must be less than 64k since msg.len is u166. *7. * Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes written.8. */9. int i2c_master_send(const struct i2c_client *client, const char *buf, int count)10. {11. int ret;12. struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter;13. struct i2c_msg msg;14. 15. msg.addr = client->addr;16. msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN;17. msg.len = count;18. msg.buf = (char *)buf;19. 20. ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1);21. 22. /* If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg transmitted), return #bytes23. transmitted, else error code. */24. return (ret == 1) ? count : ret;25. }26. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_master_send);
代码清单17 i2c_master_recv函数1. /**2. * i2c_master_recv - issue a single I2C message in master receive mode3. * @client: Handle to slave device4. * @buf: Where to store data read from slave5. * @count: How many bytes to read, must be less than 64k since msg.len is u166. *7. * Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes read.8. */9. int i2c_master_recv(const struct i2c_client *client, char *buf, int count)10. {11. struct i2c_adapter *adap = client->adapter;12. struct i2c_msg msg;13. int ret;14. 15. msg.addr = client->addr;16. msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN;17. msg.flags |= I2C_M_RD;18. msg.len = count;19. msg.buf = buf;20. 21. ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1);22. 23. /* If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg transmitted), return #bytes24. transmitted, else error code. */25. return (ret == 1) ? count : ret;26. }27. EXPORT_SYMBOL(i2c_master_recv);
i2c_transfer()函数用于进行I2C适配器和I2C设备之间的一组消息交互,i2c_master_send()函数和i2c_master_recv()函数内部会调用i2c_transfer函数分别完成一条写消息和一条读消息。
三、I2c的第二部分1.2C总线驱动(1)I2c总线驱动模块的加载函数要完成两个工作。
l 第一个是初始化i2c适配器所使用的硬件资源,如申请I/O地址、中断号等。
l 第二个是通过i2c_add_adapter()添加i2c_adapter的数据结构,当然这个i2c_adapter数据结构的成员已经被xxx适配器的相应的函数指针所初始化。
(2)I2C总线驱动模块的卸载函数要完成的工作与加载函数相反。
l 释放I2C适配器所使用的硬件资源,如释放I/O地址,中断号等。
l 通过i2c_del_adapter()删除i2c_adapter的函数数据结构。
代码清单18所示为I2C适配器驱动的模块加载和卸载函数的模板。
代码清单18 I2C总线驱动的模板加载和卸载函数模板1. static int __init i2c_adap_xxx_init(void)2. {3. xxx_adapter_hw_init();4. I2c_add_adapter(&xxx_adapter);5. }6. subsys_initcall(i2c_adap_xxx_init);7. 8. static void __exit i2c_adap_xxx_exit(void)9. {10. xxx_adapter_hw_free();11. i2c_del_adapter(&xxx_adapter);12. }13. module_exit(i2c_adap_xxx_exit);
上述代码中xxx_adapter_hw_init()和xxx_adapter_hw_free()函数的实现都与具体的CPU和I2C适配器硬件直接相关。
2.I2C总线通信方法我们需要为特定的I2C适配器实现其通信方法,主要实现i2c_algorithm的master_xfer()函数和functionality()函数。
Functionality()函数非常简单,用于返回algorithm所支持的通信协议,如I2C_FUNC_I2C、I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR、I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE、I2C_FUNC_SUMBUS_WRITE_BYTE等。
Master_xfer()函数在I2C适配器上完成传递给它的i2c_msg数组中每个I2C消息,代码清单19所示为xxx设备的master_xfer()函数模板。
代码清单19 I2C总线驱动master_xfer()函数模板1. static int i2c_adapter_xxx_xfer(structi2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num) 2. { 3. ...... 4. for (i = 0; i < num; i++) { 5. i2c_adapter_xxx_start(); /*产生起始位*/ 6. if (msgs[i]->flags & I2C_M_RD) { /*读取*/ 7. i2c_adapter_xxx_setaddr((msg->addr << 1) | 1); /*发送从设备地址*/ 8. i2c_adapter_xxx_wait_ack(); /*获得从设备的ACK*/ 9. i2c_adapter_xxx_readbytes(msgs[i]->buf,msgs[i]->len); /*读取len长度的数据到buf中*/ 10. } else { 11. i2c_adapter_xxx_setaddr(msg->addr << 1); 12. i2c_adapter_xxx_wait_ack(); 13. i2c_adapter_xxx_writebytes(msgs[i]->buf, msgs[i]->len); 14. } 15. } 16. i2c_adapter_xxx_stop(); /*产生停止位*/ 17. }
上述代码实际上给出了一个master_xfer()函数处理I2C消息数组的流程,对于数组中的每个消息,判断消息类型,若为读消息,则赋从设备地址为(msg->addr<<1)|1,否则为msg->addr<<1,对每个消息产生一个开始位,紧接着传送从设备的地址,然后开始数据的发送或接收,队最后的消息还需产生一个停止位。
master_xfer()函数模板中i2c_adapter_xxx_start()、i2c_adapter_xxx_setaddr()、i2c_adapter_xxx_wait_ack()、i2c_adapter_xxx_readbytes()、i2c_adapter_xxx_stop()函数用于完成适配器底层硬件操作,与I2C适配器和CPU的具体硬件直接相关,需要由工程师根据芯片的数据手册来实现。
I2c_adapter_xxx_readbytes()用于从设备上接收一串数据,i2c_adapter_xxx_writebytes()用于向从设备写入一串数据,这两个函数的内部也会涉及I2C总线协议中的ACK应答。
master_xfer()函数的实现在形式上会有很多样,即便是linux内核源代码中已经给出了一些I2C总线驱动的master_xfer()函数,由于由不同的组织或个人完成,风格上的差别也非常大,不一定能与模板完全对应,如master_xfer()函数模板给出的消息处理顺序进行的,而有的驱动以中断方式来完成这个流程。不管具体怎么实施,流程的本质都是不变的。因为这个流程不以驱动工程师的意志为转移,最终由I2C总线硬件上的通信协议决定。
多数I2C总线驱动会定义一个xxx_i2c结构体,作为i2c_adapter的algo_data(类似“是有数据”),其中包含I2C消息数组指针、数组索引及I2C适配器algorithm访问控制用的自旋锁、等待队列等,而master_xfer()函数完成消息数组中消息的处理也可通过对xxx_i2c结构体相关成员的访问来控制。代码清单20所示为xxx_i2c结构体的定义。
代码清单20 xxx_i2c结构体模板1. struct xxx_i2c {2. spinlock_t lock;3. wait_queue_head_t wait;4. struct i2c_msg *msg;5. unsigned int msg_num;6. unsigned int msg_idx;7. unsigned int msg_ptr;8. struct i2c_adapter adap;9. };
对于s3c2440的i2c模块而言内核中做了如下的工作:
S3c2440处理器内部集成了一个I2C控制器,通过4个寄存器就可以方便地对其进行控制,这4个寄存器如下:
l IICCON:I2C控制寄存器。
l IICSTAT:I2C状态寄存器。
l IICDS:I2C收发数据移位寄存器。
l IICADD:I2C地址寄存器。
S3c2440处理器内部集成的I2C控制器可支持主、从两种模式,我们主要使用其主模式。通过对IICCON、IICDS和IICADD寄存器的操作,可
在I2C总线上产生开始位、停止位、数据和地址,而传输的状态则通过IICSTAT寄存器获取。
3.s3c2440 I2C 总线驱动总体分析s3c_2440的I2C总线驱动driver/i2c/busses/i2c-s3c2410.c支持s3c24xx、s3c64xx、s5pc1xx和s5p64xx处理器,在我们使用的3.0内核版本中,其名称任然叫2410,显然是历史原因引起的。它主要完成以下工作。
设计对应于i2c_adapter_xxx_init()模板的s3c_2440的模块加载函数和对应于i2c_adapter_xxx_exit()函数模板的模块卸载函数。
设计对应于i2c_adapter_xxx_xfer()模板的s3c_2440适配器的通信方法函数。
针对s3c24xx、s3c64xx、s5pc1xx和s5p64xx处理器,functionality()函数s3c24xx_i2c_func()只需要简单地返回I2C_FUNC_I2C|I2C_FUNC_SUMBUS_EMUL|I2C_FUNU_PROTOCOL_MANGLING表明其支持的功能。
下图给出了s3c2440驱动中的主要函数与总线模板函数的对应关系,由于实现通信方法的方式不一样,模板的一个函数可能对应于s3c2440 I2C总线驱动的多个函数。

图6 i2c总线驱动模板于s3c2440 I2C总线驱动的映射
4.S3c2440 I2C适配器驱动的模板加载于卸载I2C适配器驱动被作为一个单独的模块加载进内核,在模块的加载和卸载函数中,只需注册和注销一个platform——driver结构体,如代码清单21所示。
代码清单21 S3c2440 I2C1. static int __init i2c_adap_s3c_init(void)2. {3. return platform_driver_register(&s3c24xx_i2c_driver);4. }5. subsys_initcall(i2c_adap_s3c_init);6. 7. static void __exit i2c_adap_s3c_exit(void)8. {9. platform_driver_unregister(&s3c24xx_i2c_driver);10. }11. module_exit(i2c_adap_s3c_exit);
代码清单22 platfrom_driver_register()和platfrom_driver_unregister()函数1. /**2. * platform_driver_register - register a driver for platform-level devices3. * @drv: platform driver structure4. */5. int platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv)6. {7. drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type;8. if (drv->probe)9. drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe;10. if (drv->remove)11. drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove;12. if (drv->shutdown)13. drv->driver.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown;14. 15. return driver_register(&drv->driver);16. }17. EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_driver_register);18. 19. /** 20. * platform_driver_unregister - unregister a driver for platform-level devices21. * @drv: platform driver structure22. */23. void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *drv)24. { 25. driver_unregister(&drv->driver);26. } 27. EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_driver_unregister);
Platfrom_driver结构体包含了具体适配器的probe()函数、remove()函数、resume()函数指针等信息,它需要被定义和赋值,如代码清单23所示。
代码清单23 platfrom_driver结构体1. static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_i2c_driver = {2. .probe = s3c24xx_i2c_probe,3. .remove = s3c24xx_i2c_remove,4. .id_table = s3c24xx_driver_ids,5. .driver = {6. .owner = THIS_MODULE,7. .name = "s3c-i2c",8. .pm = S3C24XX_DEV_PM_OPS,9. },10. };
当通过linux内核源代码/drivers/base/platform.c文件中定义platform_driver_register()函数注册platfrom_driver结构体时,其中probe指针指向s3c24xx_i2c_probe()函数将被调用,以初始化适配器硬件。s3c24xx_i2c_init()函数会调用函数。
代码清单24 s3c24xx_i2c_init()函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_init2. *3. * initialise the controller, set the IO lines and frequency4. */5. 6. static int s3c24xx_i2c_init(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c)7. {8. unsigned long iicon = S3C2410_IICCON_IRQEN | S3C2410_IICCON_ACKEN;9. struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata;10. unsigned int freq;11. 12. /* get the plafrom data */13. 14. pdata = i2c->dev->platform_data;15. 16. /* inititalise the gpio */17. 18. if (pdata->cfg_gpio)19. pdata->cfg_gpio(to_platform_device(i2c->dev));20. 21. /* write slave address */22. 23. writeb(pdata->slave_addr, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICADD);24. 25. dev_info(i2c->dev, "slave address 0x%02x\n", pdata->slave_addr);26. 27. writel(iicon, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);28. 29. /* we need to work out the divisors for the clock... */30. 31. if (s3c24xx_i2c_clockrate(i2c, &freq) != 0) {32. writel(0, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);33. dev_err(i2c->dev, "cannot meet bus frequency required\n");34. return -EINVAL;35. }36. 37. /* todo - check that the i2c lines aren't being dragged anywhere */38. 39. dev_info(i2c->dev, "bus frequency set to %d KHz\n", freq);40. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "S3C2410_IICCON=0x%02lx\n", iicon);41. 42. return 0;43. }44.
代码清单25 s3c24xx_i2c_probe()函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_probe2. *3. * called by the bus driver when a suitable device is found4. */5. 6. static int s3c24xx_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)7. {8. struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c;9. struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata;10. struct resource *res;11. int ret;12. 13. pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data;14. if (!pdata) {15. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "no platform data\n");16. return -EINVAL;17. }18. 19. i2c = kzalloc(sizeof(struct s3c24xx_i2c), GFP_KERNEL);20. if (!i2c) {21. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "no memory for state\n");22. return -ENOMEM;23. }24. 25. strlcpy(i2c->adap.name, "s3c2410-i2c", sizeof(i2c->adap.name));26. i2c->adap.owner = THIS_MODULE;27. i2c->adap.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm;28. i2c->adap.retries = 2;29. i2c->adap.class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON | I2C_CLASS_SPD;30. i2c->tx_setup = 50;31. 32. spin_lock_init(&i2c->lock);33. init_waitqueue_head(&i2c->wait);34. 35. /* find the clock and enable it */36. 37. i2c->dev = &pdev->dev;38. i2c->clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "i2c");39. if (IS_ERR(i2c->clk)) {40. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot get clock\n");41. ret = -ENOENT;42. goto err_noclk;43. }44. 45. dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "clock source %p\n", i2c->clk);46. 47. clk_enable(i2c->clk);48. 49. /* map the registers */50. 51. res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);52. if (res == NULL) {53. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot find IO resource\n");54. ret = -ENOENT;55. goto err_clk;56. }57. 58. i2c->ioarea = request_mem_region(res->start, resource_size(res),59. pdev->name);60. 61. if (i2c->ioarea == NULL) {62. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot request IO\n");63. ret = -ENXIO;64. goto err_clk;65. }66. 67. i2c->regs = ioremap(res->start, resource_size(res));68. 69. if (i2c->regs == NULL) {70. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot map IO\n");71. ret = -ENXIO;72. goto err_ioarea;73. }74. 75. dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "registers %p (%p, %p)\n",76. i2c->regs, i2c->ioarea, res);77. 78. /* setup info block for the i2c core */79. 80. i2c->adap.algo_data = i2c;81. i2c->adap.dev.parent = &pdev->dev;82. 83. /* initialise the i2c controller */84. 85. ret = s3c24xx_i2c_init(i2c);86. if (ret != 0)87. goto err_iomap;88. 89. /* find the IRQ for this unit (note, this relies on the init call to90. * ensure no current IRQs pending91. */92. 93. i2c->irq = ret = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);94. if (ret <= 0) {95. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot find IRQ\n");96. goto err_iomap;97. }98. 99. ret = request_irq(i2c->irq, s3c24xx_i2c_irq, IRQF_DISABLED,100. dev_name(&pdev->dev), i2c);101. 102. if (ret != 0) {103. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "cannot claim IRQ %d\n", i2c->irq);104. goto err_iomap;105. }106. 107. ret = s3c24xx_i2c_register_cpufreq(i2c);108. if (ret < 0) {109. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to register cpufreq notifier\n");110. goto err_irq;111. }112. 113. /* Note, previous versions of the driver used i2c_add_adapter()114. * to add the bus at any number. We now pass the bus number via115. * the platform data, so if unset it will now default to always116. * being bus 0.117. */118. 119. i2c->adap.nr = pdata->bus_num;120. 121. ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&i2c->adap);122. if (ret < 0) {123. dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to add bus to i2c core\n");124. goto err_cpufreq;125. }126. 127. platform_set_drvdata(pdev, i2c);128. 129. dev_info(&pdev->dev, "%s: S3C I2C adapter\n", dev_name(&i2c->adap.dev));130. clk_disable(i2c->clk);131. return 0;132. 133. err_cpufreq:134. s3c24xx_i2c_deregister_cpufreq(i2c);135. 136. err_irq:137. free_irq(i2c->irq, i2c);138. 139. err_iomap:140. iounmap(i2c->regs);141. 142. err_ioarea:143. release_resource(i2c->ioarea);144. kfree(i2c->ioarea);145. 146. err_clk:147. clk_disable(i2c->clk);148. clk_put(i2c->clk);149. 150. err_noclk:151. kfree(i2c);152. return ret;153. }
上述代码中的主体工作是使能硬件并且申请I2C适配器使用I/O地址、中断号等,在这些工作都完成无误后,通过I2C核心提供i2c_add_adapter函数添加这个适配器。当处理器包含多个I2C控制器时,我们通过板文件定义的platform数据中bus_num进行区分。
与s3c24xx_i2c_probe()函数完全相反的功能的函数是s3c24xx_i2c_remove()函数,它在适配器模块函数调用platform_driver_unregister函数是通过platfrom_driver的remove指针方式被调用。Xxx_i2c_remove()的设计模块如代码清单26所示。
********************************************************************************************转载声明:希望大家能转载此文谢谢 原文链接
********************************************************************************************
代码清单26 s3c2440 I2C总线驱动中的s3c24xx_i2c_remove函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_remove2. *3. * called when device is removed from the bus4. */5. 6. static int s3c24xx_i2c_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)7. {8. struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);9. 10. s3c24xx_i2c_deregister_cpufreq(i2c);11. 12. i2c_del_adapter(&i2c->adap);13. free_irq(i2c->irq, i2c);14. 15. clk_disable(i2c->clk);16. clk_put(i2c->clk);17. 18. iounmap(i2c->regs);19. 20. release_resource(i2c->ioarea);21. kfree(i2c->ioarea);22. kfree(i2c);23. 24. return 0;25. }
上面的代码清单26中用到了s3c24xx_i2c结构体进行适配器所有信息的封装。类似于私有信息结构体,它与代码清单20所示的xxx_i2c结构体模板对应,代码清单27所示为s3c24xx_i2c结构体的定义。
代码清单27 s3c24xx_i2c结构体1. struct s3c24xx_i2c {2. spinlock_t lock;3. wait_queue_head_t wait;4. unsigned int suspended:1;5. 6. struct i2c_msg *msg;7. unsigned int msg_num;8. unsigned int msg_idx;9. unsigned int msg_ptr;10. 11. unsigned int tx_setup;12. unsigned int irq;13. 14. enum s3c24xx_i2c_state state;15. unsigned long clkrate;16. 17. void __iomem *regs;18. struct clk *clk;19. struct device *dev;20. struct resource *ioarea;21. struct i2c_adapter adap;22. 23. #ifdef CONFIG_CPU_FREQ24. struct notifier_block freq_transition;25. #endif26. };
5.s3c2440 I2C 总线通信方法由代码清单25的23行可以看出,I2C适配器对应的i2c_algorithm结构体实例为s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm,代码清单28所示为s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm的定义。
代码清单28 s3c2440的i2c_algorithm结构体1. /* i2c bus registration info */2. 3. static const struct i2c_algorithm s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm = {4. .master_xfer = s3c24xx_i2c_xfer,5. .functionality = s3c24xx_i2c_func,6. };
上述代码第一行指定了s3c2440 I2C总线通信传输函数s3c24xx_i2c_xfer(),这个函数非常关键,所有I2C总线上对设备的访问最终应该由它来完成,代码清单29所示为这个重要函数以及其依赖的s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()函数和s3c24xx_i2c_message_start()函数的源代码。
代码清单29 s3c2440 I2C总线驱动的master_xfer函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_xfer2. *3. * first port of call from the i2c bus code when an message needs4. * transferring across the i2c bus.5. */6. 7. static int s3c24xx_i2c_xfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap,8. struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)9. {10. struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c = (struct s3c24xx_i2c *)adap->algo_data;11. int retry;12. int ret;13. 14. clk_enable(i2c->clk);15. 16. for (retry = 0; retry < adap->retries; retry++) {17. 18. ret = s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer(i2c, msgs, num);19. 20. if (ret != -EAGAIN) {21. clk_disable(i2c->clk);22. return ret;23. }24. 25. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "Retrying transmission (%d)\n", retry);26. 27. udelay(100);28. }29. 30. clk_disable(i2c->clk);31. return -EREMOTEIO;32. }
s3c24xx_i2c_xfer()函数调用s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()函数传输I2C消息,第13行的循环意味着最多可以重试adap->retres次。
代码清单30 s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer2. *3. * this starts an i2c transfer4. */5. 6. static int s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c,7. struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)8. {9. unsigned long iicstat, timeout;10. int spins = 20;11. int ret;12. 13. if (i2c->suspended)14. return -EIO;15. 16. ret = s3c24xx_i2c_set_master(i2c);17. if (ret != 0) {18. dev_err(i2c->dev, "cannot get bus (error %d)\n", ret);19. ret = -EAGAIN;20. goto out;21. }22. 23. spin_lock_irq(&i2c->lock);24. 25. i2c->msg = msgs;26. i2c->msg_num = num;27. i2c->msg_ptr = 0;28. i2c->msg_idx = 0;29. i2c->state = STATE_START;30. 31. s3c24xx_i2c_enable_irq(i2c);32. s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(i2c, msgs);33. spin_unlock_irq(&i2c->lock);34. 35. timeout = wait_event_timeout(i2c->wait, i2c->msg_num == 0, HZ * 5);36. 37. ret = i2c->msg_idx;38. 39. /* having these next two as dev_err() makes life very40. * noisy when doing an i2cdetect */41. 42. if (timeout == 0)43. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "timeout\n");44. else if (ret != num)45. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "incomplete xfer (%d)\n", ret);46. 47. /* ensure the stop has been through the bus */48. 49. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "waiting for bus idle\n");50. 51. /* first, try busy waiting briefly */52. do {53. iicstat = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);54. } while ((iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_START) && --spins);55. 56. /* if that timed out sleep */57. if (!spins) {58. msleep(1);59. iicstat = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);60. }61. 62. if (iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_START)63. dev_warn(i2c->dev, "timeout waiting for bus idle\n");64. 65. out:66. return ret;67. }
s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()首先将s3c2440的I2C适配器设置为I2C主设备,其后初始化s3c24xx_i2c结构体,使能I2C中断,并调用s3c24xx_i2c_message_start()函数启动I2C消息的传输。
代码清单31 s3c24xx_i2c_message_start()函数1. /* s3c24xx_i2c_message_start2. *3. * put the start of a message onto the bus4. */5. 6. static void s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c,7. struct i2c_msg *msg)8. {9. unsigned int addr = (msg->addr & 0x7f) << 1;10. unsigned long stat;11. unsigned long iiccon;12. 13. stat = 0;14. stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_TXRXEN;15. 16. if (msg->flags & I2C_M_RD) {17. stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_MASTER_RX;18. addr |= 1;19. } else20. stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_MASTER_TX;21. 22. if (msg->flags & I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR)23. addr ^= 1;24. 25. /* todo - check for wether ack wanted or not */26. s3c24xx_i2c_enable_ack(i2c);27. 28. iiccon = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);29. writel(stat, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);30. 31. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "START: %08lx to IICSTAT, %02x to DS\n", stat, addr);32. writeb(addr, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS);33. 34. /* delay here to ensure the data byte has gotten onto the bus35. * before the transaction is started */36. 37. ndelay(i2c->tx_setup);38. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "iiccon, %08lx\n", iiccon);39. writel(iiccon, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);40. 41. stat |= S3C2410_IICSTAT_START;42. writel(stat, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICSTAT);43. }
s3c24xx_i2c_message_start()函数写s3c2440适配器对应的控制寄存器,向I2C从设备传递开始位和从设备地址。
上述代码只是启动了I2C消息数组的传输周期,并没有完整实现algorithm master_xfer时序的流程。这个流程的完整实现需要借助I2C适配器上的中断来步步推进。代码清单32所示为s3c2440 I2C适配器中断处理函数以及其依赖的i2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte()函数的源码。
代码清单32 s3c2440 I2C适配器中断处理函数1. /* i2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte2. *3. * process an interrupt and work out what to do4. */5. 6. static int i2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c, unsigned long iicstat)7. {8. unsigned long tmp;9. unsigned char byte;10. int ret = 0;11. 12. switch (i2c->state) {13. 14. case STATE_IDLE:15. dev_err(i2c->dev, "%s: called in STATE_IDLE\n", __func__);16. goto out;17. 18. case STATE_STOP:19. dev_err(i2c->dev, "%s: called in STATE_STOP\n", __func__);20. s3c24xx_i2c_disable_irq(i2c);21. goto out_ack;22. 23. case STATE_START:24. /* last thing we did was send a start condition on the25. * bus, or started a new i2c message26. */27. 28. if (iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_LASTBIT &&29. !(i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK)) {30. /* ack was not received... */31. 32. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "ack was not received\n");33. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -ENXIO);34. goto out_ack;35. }36. 37. if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_RD)38. i2c->state = STATE_READ;39. else40. i2c->state = STATE_WRITE;41. 42. /* terminate the transfer if there is nothing to do43. * as this is used by the i2c probe to find devices. */44. 45. if (is_lastmsg(i2c) && i2c->msg->len == 0) {46. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0);47. goto out_ack;48. }49. 50. if (i2c->state == STATE_READ)51. goto prepare_read;52. 53. /* fall through to the write state, as we will need to54. * send a byte as well */55. 56. case STATE_WRITE:57. /* we are writing data to the device... check for the58. * end of the message, and if so, work out what to do59. */60. 61. if (!(i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK)) {62. if (iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_LASTBIT) {63. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "WRITE: No Ack\n");64. 65. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -ECONNREFUSED);66. goto out_ack;67. }68. }69. 70. retry_write:71. 72. if (!is_msgend(i2c)) {73. byte = i2c->msg->buf[i2c->msg_ptr++];74. writeb(byte, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS);75. 76. /* delay after writing the byte to allow the77. * data setup time on the bus, as writing the78. * data to the register causes the first bit79. * to appear on SDA, and SCL will change as80. * soon as the interrupt is acknowledged */81. 82. ndelay(i2c->tx_setup);83. 84. } else if (!is_lastmsg(i2c)) {85. /* we need to go to the next i2c message */86. 87. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "WRITE: Next Message\n");88. 89. i2c->msg_ptr = 0;90. i2c->msg_idx++;91. i2c->msg++;92. 93. /* check to see if we need to do another message */94. if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_NOSTART) {95. 96. if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_RD) {97. /* cannot do this, the controller98. * forces us to send a new START99. * when we change direction */100. 101. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -EINVAL);102. }103. 104. goto retry_write;105. } else {106. /* send the new start */107. s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(i2c, i2c->msg);108. i2c->state = STATE_START;109. }110. 111. } else {112. /* send stop */113. 114. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0);115. }116. break;117. 118. case STATE_READ:119. /* we have a byte of data in the data register, do120. * something with it, and then work out wether we are121. * going to do any more read/write122. */123. 124. byte = readb(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS);125. i2c->msg->buf[i2c->msg_ptr++] = byte;126. 127. prepare_read:128. if (is_msglast(i2c)) {129. /* last byte of buffer */130. 131. if (is_lastmsg(i2c))132. s3c24xx_i2c_disable_ack(i2c);133. 134. } else if (is_msgend(i2c)) {135. /* ok, we've read the entire buffer, see if there136. * is anything else we need to do */137. 138. if (is_lastmsg(i2c)) {139. /* last message, send stop and complete */140. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "READ: Send Stop\n");141. 142. s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0);143. } else {144. /* go to the next transfer */145. dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "READ: Next Transfer\n");146. 147. i2c->msg_ptr = 0;148. i2c->msg_idx++;149. i2c->msg++;150. }151. }152. 153. break;154. }155. 156. /* acknowlegde the IRQ and get back on with the work */157. 158. out_ack:159. tmp = readl(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);160. tmp &= ~S3C2410_IICCON_IRQPEND;161. writel(tmp, i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICCON);162. out:163. return ret;164. }
中断处理函数s3c24xx_i2c_irq()主要通过调用i2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte()函数进行传输工作的进一步推进。I2c_s3c_irq_nextbyte()函数通过switch(i2c->state)的不同状态进行处理,在每种状态下,先检查i2c->state的状态与硬件寄存器应该处于的状态是否一致,如果不一致,则证明有误,直接返回。当I2C处于读状态STATE_READ或是写状态STATE_WRITE时,通过is_lastmsg()函数判断是否传输的最后一条I2C消息,如果是,则产生停止位,否则通过i2c->msg_idx++、i2c->msg++推进到下一条消息。
四、I2C的第三部分1.Linux I2C 设备驱动I2C设备驱动要使用i2c_driver和i2c_client数据结构并填充i2c_driver中的成员函数。I2c_client一般被包含在设备的私有信息结构体yyy_data中,而i2c_driver则适合被定义为全局变量并初始化,代码清单33所示为已被初始化的i2c_driver。
代码清单33 已被初始化的i2c_driver1. static struct i2c_driver yyy_driver= {2. .driver = {3. .name = “yyy”,4. },5. .probe = yyy_probe,6. .remove = yyy_remove,7. .id_table = yyy_id,8. };
2.Linux I2C 设备驱动的模块加载与卸载I2C设备驱动的模块加载函数通用的方法是在I2C设备驱动模块加载函数进行通过I2C核心的i2c_add_driver()函数添加i2c_driver的工作,而在模块卸载函数中需要做相反的工作:通过I2C核心的i2c_del_driver()函数删除i2c_driver。代码清单34所示为I2C设备驱动的加载与卸载函数模板
代码清单34 I2C设备驱动的加载与卸载函数模板1. Static int __init yyy_init(void)2. {3. return i2c_add_driver(&yyy_driver);4. };5. void __exit yyy_exit(void)6. {7. i2c_del_driver(&yyy_driver);8. }
3.Linux I2C设备驱动的数据传输在I2C设备上读写数据的时序和数据通常通过i2c_msg数组组织,最后i2c_transfer()函数完成,代码清单35所示为一个读取指定偏移offs寄存器的例子。
代码清单35 I2C设备驱动数据传输范例1. struct i2c_msg msg[2];2. /*第一条消息是写消息*/3. msg[0].addr = client->addr;4. msg[0].flags = 0;5. msg[0].len = 1;6. msg[0].buf = &offs;7. /*第二条消息是读消息*/8. msg[1].addr = client->addr;9. msg[1].flags = I2C_M_RD;10. msg[1].len = sizeof(buf);11. msg[1].buf = &buf[0];
i2c_transfer(client->adapter, msg, 2);
4.Linux的i2c-dev.c文件分析I2c_dev.c文件完全可以被看作一个I2C设备驱动,不过,它实现的一个i2c_client是虚拟、临时的、随着设备文件的打开而产生,并随着设备文件的关闭而撤销,并没有被添加到i2c_adapter的client链表中。i2c-dev.c针对每个I2C适配器生成一个主设备号为89的设备文件,实现了i2c_driver的成员函数以及文件操作接口,所以i2c-dev.c的主体是“i2c_driver成员函数+字符设备驱动”。
i2c-dev.c中提供i2cdev_read()、i2cdev_write()函数来对应用户空间要使用的read()和write()文件操作接口,这两个函数分别调用I2C核心的i2c_master_recv()和i2c_master_send()函数来构造一条I2C消息并引发适配器algorithm通信函数的调用,完成消息的传输,对应于图所示的时序。但是很遗憾,大多数稍微复杂一点I2C设备的读写流程并不对应于一条消息,往往需要两条甚至跟多的消息来进行一次读写周期(即如图所示的重复开始位RepStart模式),这种情况下,在应用层仍然调用read()、write()文件API来读写I2C设备,将不能正确地读写。许多工程师碰到过类似的问题,往往经过相当长时间的调试都没法解决I2C设备的读写,连错误的原因也无法找到,显然是对i2cdev_read()和i2cdev_write()函数的作用有所误解。

[align=left] [/align]
图7 i2cdev_read()和i2cdev_write()函数对应的时序

[align=left] [/align]
图8 RepStart模式
鉴于上述的原因,i2c-dev.c中i2cdev_read()和i2cdev_write()函数不具备太强的通用性,没有太大的实用价值,只能实用于非RepStart模式的情况。对于两条以上消息组成的读写,在用户空间需要组织i2c_msg消息数组并调用I2C_RDWRIOCTL命令。代码清单36所示i2cdev_ioctl()函数的框架。
代码清单36 i2c-dev.c中的i2cdev_ioctl函数1. static long i2cdev_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)2. {3. struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data;4. unsigned long funcs;5. dev_dbg(&client->adapter->dev, "ioctl, cmd=0x%02x, arg=0x%02lx\n",6. cmd, arg);7. switch (cmd) {8. case I2C_SLAVE:9. case I2C_SLAVE_FORCE:10. /* NOTE: devices set up to work with "new style" drivers11. * can't use I2C_SLAVE, even when the device node is not12. * bound to a driver. Only I2C_SLAVE_FORCE will work.13. *14. * Setting the PEC flag here won't affect kernel drivers,15. * which will be using the i2c_client node registered with16. * the driver model core. Likewise, when that client has17. * the PEC flag already set, the i2c-dev driver won't see18. * (or use) this setting.19. */20. if ((arg > 0x3ff) ||21. (((client->flags & I2C_M_TEN) == 0) && arg > 0x7f))22. return -EINVAL;23. if (cmd == I2C_SLAVE && i2cdev_check_addr(client->adapter, arg))24. return -EBUSY;25. /* REVISIT: address could become busy later */26. client->addr = arg;27. return 0;28. case I2C_TENBIT:29. if (arg)30. client->flags |= I2C_M_TEN;31. else32. client->flags &= ~I2C_M_TEN;33. return 0;34. case I2C_PEC:35. if (arg)36. client->flags |= I2C_CLIENT_PEC;37. else38. client->flags &= ~I2C_CLIENT_PEC;39. return 0;40. case I2C_FUNCS:41. funcs = i2c_get_functionality(client->adapter);42. return put_user(funcs, (unsigned long __user *)arg);43. case I2C_RDWR:44. return i2cdev_ioctl_rdrw(client, arg);45. case I2C_SMBUS:46. return i2cdev_ioctl_smbus(client, arg);47. case I2C_RETRIES:48. client->adapter->retries = arg;49. break;50. case I2C_TIMEOUT:51. /* For historical reasons, user-space sets the timeout52. * value in units of 10 ms.53. */54. client->adapter->timeout = msecs_to_jiffies(arg * 10);55. break;56. default:57. /* NOTE: returning a fault code here could cause trouble58. * in buggy userspace code. Some old kernel bugs returned59. * zero in this case, and userspace code might accidentally60. * have depended on that bug.61. */62. return -ENOTTY;63. }64. return 0;65. }
常用的IOCTL包含I2C_SLAVE(设备从设备地址)、I2C_RETRIES(没有收到设备ACK情况下的重试次数,默认为1)、I2C_TIMEOUT以及I2C_RDWR。
5.AT24C02 EEPROM的I2C设备驱动实例I2c设备驱动(也称为客户驱动)是对I2c硬件体系结构中设备端的实现,我们这里是AT24C02的I2c设备驱动,设备一般挂接在受CPU控制的I2c适配器上,通过I2c适配器与CPU交换数据。
drivers/misc/eeprom/at24.c文件支持大多数I2C接口的EEPROM,正如我们前面所述,一个具体的I2C设备驱动有两部分组成,一部分是i2c_driver,用于将设备挂接于I2C总线,一部分是设备本身的驱动。对于EEPROM而言,设备本身的驱动以bin_attribute二进制sysfs结点形式呈现。代码清单37给出了该驱动的框架。
代码清单37 at24_bin_read()函数1. static ssize_t at24_bin_read(struct file *filp, struct kobject *kobj,2. struct bin_attribute *attr,3. char *buf, loff_t off, size_t count)4. {5. struct at24_data *at24;6. 7. at24 = dev_get_drvdata(container_of(kobj, struct device, kobj));8. return at24_read(at24, buf, off, count);9. }
代码清单38 at24_bin_write()函数1. /*2. * Note that if the hardware write-protect pin is pulled high, the whole3. * chip is normally write protected. But there are plenty of product4. * variants here, including OTP fuses and partial chip protect.5. *6. * We only use page mode writes; the alternative is sloooow. This routine7. * writes at most one page.8. */9. static ssize_t at24_eeprom_write(struct at24_data *at24, const char *buf,10. unsigned offset, size_t count)11. {12. struct i2c_client *client;13. struct i2c_msg msg;14. ssize_t status;15. unsigned long timeout, write_time;16. unsigned next_page;17. 18. /* Get corresponding I2C address and adjust offset */19. client = at24_translate_offset(at24, &offset);20. 21. /* write_max is at most a page */22. if (count > at24->write_max)23. count = at24->write_max;24. 25. /* Never roll over backwards, to the start of this page */26. next_page = roundup(offset + 1, at24->chip.page_size);27. if (offset + count > next_page)28. count = next_page - offset;29. 30. /* If we'll use I2C calls for I/O, set up the message */31. if (!at24->use_smbus) {32. int i = 0;33. 34. msg.addr = client->addr;35. msg.flags = 0;36. 37. /* msg.buf is u8 and casts will mask the values */38. msg.buf = at24->writebuf;39. if (at24->chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_ADDR16)40. msg.buf[i++] = offset >> 8;41. 42. msg.buf[i++] = offset;43. memcpy(&msg.buf[i], buf, count);44. msg.len = i + count;45. }46. 47. /*48. * Writes fail if the previous one didn't complete yet. We may49. * loop a few times until this one succeeds, waiting at least50. * long enough for one entire page write to work.51. */52. timeout = jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(write_timeout);53. do {54. write_time = jiffies;55. if (at24->use_smbus) {56. status = i2c_smbus_write_i2c_block_data(client,57. offset, count, buf);58. if (status == 0)59. status = count;60. } else {61. status = i2c_transfer(client->adapter, &msg, 1);62. if (status == 1)63. status = count;64. }65. dev_dbg(&client->dev, "write %zu@%d --> %zd (%ld)\n",66. count, offset, status, jiffies);67. 68. if (status == count)69. return count;70. 71. /* REVISIT: at HZ=100, this is sloooow */72. msleep(1);73. } while (time_before(write_time, timeout));74. 75. return -ETIMEDOUT;76. }
代码清单39 i2c_device_id结构体1. static const struct i2c_device_id at24_ids[] = {2. /* needs 8 addresses as A0-A2 are ignored */3. { "24c00", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(128 / 8, AT24_FLAG_TAKE8ADDR) },4. /* old variants can't be handled with this generic entry! */5. { "24c01", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(1024 / 8, 0) },6. { "24c02", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(2048 / 8, 0) },7. /* spd is a 24c02 in memory DIMMs */8. { "spd", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(2048 / 8,9. AT24_FLAG_READONLY | AT24_FLAG_IRUGO) },10. { "24c04", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(4096 / 8, 0) },11. /* 24rf08 quirk is handled at i2c-core */12. { "24c08", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(8192 / 8, 0) },13. { "24c16", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(16384 / 8, 0) },14. { "24c32", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(32768 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },15. { "24c64", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(65536 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },16. { "24c128", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(131072 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },17. { "24c256", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(262144 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },18. { "24c512", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(524288 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },19. { "24c1024", AT24_DEVICE_MAGIC(1048576 / 8, AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) },20. { "at24", 0 },21. { /* END OF LIST */ }22. };23. MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(i2c, at24_ids);
代码清单40 初始化at24xx设备的i2c_driver结构体1. /*-------------------------------------------------------------------------*/2. 3. static struct i2c_driver at24_driver = {4. .driver = {5. .name = "at24",6. .owner = THIS_MODULE,7. },8. .probe = at24_probe,9. .remove = __devexit_p(at24_remove),10. .id_table = at24_ids,11. };
代码清单41 at24_probe函数1. static int at24_probe(struct i2c_client *client, const struct i2c_device_id *id)2. {3. struct at24_platform_data chip;4. bool writable;5. int use_smbus = 0;6. struct at24_data *at24;7. int err;8. unsigned i, num_addresses;9. kernel_ulong_t magic;10. 11. if (client->dev.platform_data) {12. chip = *(struct at24_platform_data *)client->dev.platform_data;13. } else {14. if (!id->driver_data) {15. err = -ENODEV;16. goto err_out;17. }18. magic = id->driver_data;19. chip.byte_len = BIT(magic & AT24_BITMASK(AT24_SIZE_BYTELEN));20. magic >>= AT24_SIZE_BYTELEN;21. chip.flags = magic & AT24_BITMASK(AT24_SIZE_FLAGS);22. /*23. * This is slow, but we can't know all eeproms, so we better24. * play safe. Specifying custom eeprom-types via platform_data25. * is recommended anyhow.26. */27. chip.page_size = 1;28. 29. /* update chipdata if OF is present */30. at24_get_ofdata(client, &chip);31. 32. chip.setup = NULL;33. chip.context = NULL;34. }35. 36. if (!is_power_of_2(chip.byte_len))37. dev_warn(&client->dev,38. "byte_len looks suspicious (no power of 2)!\n");39. if (!chip.page_size) {40. dev_err(&client->dev, "page_size must not be 0!\n");41. err = -EINVAL;42. goto err_out;43. }44. if (!is_power_of_2(chip.page_size))45. dev_warn(&client->dev,46. "page_size looks suspicious (no power of 2)!\n");47. 48. /* Use I2C operations unless we're stuck with SMBus extensions. */49. if (!i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter, I2C_FUNC_I2C)) {50. if (chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) {51. err = -EPFNOSUPPORT;52. goto err_out;53. } 54. if (i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter,55. I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_I2C_BLOCK)) {56. use_smbus = I2C_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK_DATA;57. } else if (i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter,58. I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_WORD_DATA)) {59. use_smbus = I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA;60. } else if (i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter,61. I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE_DATA)) {62. use_smbus = I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA;63. } else {64. err = -EPFNOSUPPORT;65. goto err_out;66. }67. }68. 69. if (chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_TAKE8ADDR)70. num_addresses = 8;71. else72. num_addresses = DIV_ROUND_UP(chip.byte_len,73. (chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_ADDR16) ? 65536 : 256);74. 75. at24 = kzalloc(sizeof(struct at24_data) +76. num_addresses * sizeof(struct i2c_client *), GFP_KERNEL);77. if (!at24) {78. err = -ENOMEM;79. goto err_out;80. }81. 82. mutex_init(&at24->lock);83. at24->use_smbus = use_smbus;84. at24->chip = chip;85. at24->num_addresses = num_addresses;86. 87. /*88. * Export the EEPROM bytes through sysfs, since that's convenient.89. * By default, only root should see the data (maybe passwords etc)90. */91. sysfs_bin_attr_init(&at24->bin);92. at24->bin.attr.name = "eeprom";93. at24->bin.attr.mode = chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_IRUGO ? S_IRUGO : S_IRUSR;94. at24->bin.read = at24_bin_read;95. at24->bin.size = chip.byte_len;96. 97. at24->macc.read = at24_macc_read;98. 99. writable = !(chip.flags & AT24_FLAG_READONLY);100. if (writable) {101. if (!use_smbus || i2c_check_functionality(client->adapter,102. I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_I2C_BLOCK)) {103. 104. unsigned write_max = chip.page_size;105. 106. at24->macc.write = at24_macc_write;107. 108. at24->bin.write = at24_bin_write;109. at24->bin.attr.mode |= S_IWUSR;110. 111. if (write_max > io_limit)112. write_max = io_limit;113. if (use_smbus && write_max > I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_MAX)114. write_max = I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_MAX;115. at24->write_max = write_max;116. 117. /* buffer (data + address at the beginning) */118. at24->writebuf = kmalloc(write_max + 2, GFP_KERNEL);119. if (!at24->writebuf) {120. err = -ENOMEM;121. goto err_struct;122. }123. } else {124. dev_warn(&client->dev,125. "cannot write due to controller restrictions.");126. }127. }128. 129. at24->client[0] = client;130. 131. /* use dummy devices for multiple-address chips */132. for (i = 1; i < num_addresses; i++) {133. at24->client[i] = i2c_new_dummy(client->adapter,134. client->addr + i);135. if (!at24->client[i]) {136. dev_err(&client->dev, "address 0x%02x unavailable\n",137. client->addr + i);138. err = -EADDRINUSE;139. goto err_clients;140. }141. }142. err = sysfs_create_bin_file(&client->dev.kobj, &at24->bin);143. if (err)144. goto err_clients;145. 146. i2c_set_clientdata(client, at24);147. 148. dev_info(&client->dev, "%zu byte %s EEPROM, %s, %u bytes/write\n",149. at24->bin.size, client->name,150. writable ? "writable" : "read-only", at24->write_max);151. if (use_smbus == I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA ||152. use_smbus == I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA) {153. dev_notice(&client->dev, "Falling back to %s reads, "154. "performance will suffer\n", use_smbus ==155. I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA ? "word" : "byte");156. }157. 158. /* export data to kernel code */159. if (chip.setup)160. chip.setup(&at24->macc, chip.context);161. 162. return 0;163. 164. err_clients:165. for (i = 1; i < num_addresses; i++)166. if (at24->client[i])167. i2c_unregister_device(at24->client[i]);168. 169. kfree(at24->writebuf);170. err_struct:171. kfree(at24);172. err_out:173. dev_dbg(&client->dev, "probe error %d\n", err);174. return err;175. }176. 177. 代码清单42 at24_remove函数178. static int __devexit at24_remove(struct i2c_client *client)179. {180. struct at24_data *at24;181. int i;182. 183. at24 = i2c_get_clientdata(client);184. sysfs_remove_bin_file(&client->dev.kobj, &at24->bin);185. 186. for (i = 1; i < at24->num_addresses; i++)187. i2c_unregister_device(at24->client[i]);188. 189. kfree(at24->writebuf);190. kfree(at24);191. return 0;192. }
代码清单43 at24xx设备驱动模块的加载和卸载函数1. static int __init at24_init(void)2. {3. if (!io_limit) {4. pr_err("at24: io_limit must not be 0!\n");5. return -EINVAL;6. } 7. 8. io_limit = rounddown_pow_of_two(io_limit);9. return i2c_add_driver(&at24_driver);10. } 11. module_init(at24_init);12. 13. static void __exit at24_exit(void)14. {15. i2c_del_driver(&at24_driver);16. }17. module_exit(at24_exit);18. 19. MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Driver for most I2C EEPROMs");20. MODULE_AUTHOR("David Brownell and Wolfram Sang");21. MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
At24_bin_read()和at24_bin_write()俩个函数是EEPROM驱动本身的读写实现即bin_attribute驱动,之后一部分是i2c_driver,两者在i2c_driver的probe()、remove函数中建立关联。I2c_driver的probe()函数中的初始化并通过sysfs_create_bin_file()注册了二进制sysfs结点,而remove()函数则通过sysfs_remove_bin_file()注销了sysfs结点。
6.添加板级信息drivers/misc/eeprom/at24.c不依赖于具体的CPU和I2C控制寄存器硬件特性,因此,如果某一电路板包含该外设,只需要在板文件中添加对应的i2c_board_info,如对于s3c2440要使其支持at24c02 eeprom只需要作如下工作:
首先是要在内核中注册板级信息,因为设备和驱动需要匹配,它们是通过设备名和驱动名进行匹配的。因为AT24C02芯片是由2048bits构成,所以有2048 / 8 = 256byte,并将其分成32页每页有8byte大小,是8bits寻址,如果AT24C02芯片的A0,A1,A2,这三个引脚接地,着AT24C02芯片从地址是01010000b(即0x50),如果AT24C02芯片的A0结高电平,A1,A2两个引脚接地,着AT24C02芯片从地址是01010001b(即0x51),这些都是AT24C02的datasheet上有的,不同芯片不同情况。下面在linux-3.0/arch/arm/mach-s3c2440/mach-smdk2440.c添加AT24C02设备的板级信息如下:1. [fulinux@ubuntu linux-3.0]$ vim arch/arm/mach-s3c2440/mach-smdk2440.c 2. #include <linux/i2c.h> 3. #include <linux/i2c/at24.h> 4. 5. static struct at24_platform_data at24c02= {6. .byte_len = SZ_2K / 8,7. .page_size = 8,8. .flags = AT24_FLAG_ADDR8,9. };10. 11. static struct i2c_board_info __initdata smdk2440_i2c_devs[] = {12. {13. I2C_BOARD_INFO("24c02", 0x50),14. .platform_data = &at24c02,15. },16. /* more devices can be added using expansion connectors */17. };
********************************************************************************************装载声明:希望大家能转载此文谢谢:原文链接
********************************************************************************************
相关文章推荐
- Linux 设备驱动篇之-------I2c设备驱动(待续) .
- [置顶] linux设备驱动篇之LED驱动(一)
- Linux 设备驱动篇之-------I2c设备驱动(待续)
- Linux 设备驱动篇之I2c设备驱动
- Linux设备驱动篇——[I2C设备驱动-1]
- Linux 设备驱动篇之I2c设备驱动
- Linux 设备驱动篇之I2c设备驱动
- [置顶] linux设备驱动篇之LED驱动(二)
- Linux 设备驱动篇之I2c设备驱动
- linux设备驱动之i2c i2c_master_send
- Linux I2C驱动分析(二)----I2C板级设备扫描和数据传输
- 手把手教你写Linux I2C设备驱动
- Linux内核---32.I2C设备驱动分析
- I2C设备驱动(三)--linux i2c驱动框架
- Linux&nbsp;I2C核心、总线与设备驱动
- 嵌入式Linux系统下I2C设备驱动程式的研发
- Linux设备驱动之——I2C总线
- linux i2c设备驱动
- Linux I2C核心、总线与设备驱动
- Linux的I2C 设备驱动 -- mini2440 上i2c接口触摸屏驱动
