Another Eight Puzzle
2013-05-31 19:11
330 查看
| Fill the following 8 circles with digits 1~8,with each number exactly once . Conntcted circles cannot be filled with two consecutive numbers. There are 17 pairs of connected cicles: A-B , A-C, A-D B-C, B-E, B-F C-D, C-E, C-F, C-G D-F, D-G E-F, E-H F-G, F-H G-H 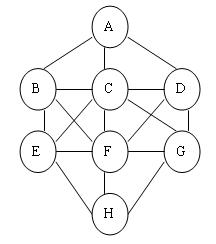 Filling G with 1 and D with 2 (or G with 2 and D with 1) is illegal since G and D are connected and 1 and 2 are consecutive .However ,filling A with 8 and B with 1 is legal since 8 and 1 are not consecutive . In this problems,some circles are already filled,your tast is to fill the remaining circles to obtain a solution (if possivle). |
| Input The first line contains a single integer T(1≤T≤10),the number of test cases. Each test case is a single line containing 8 integers 0~8,the numbers in circle A~H.0 indicates an empty circle. |
| Output For each test case ,print the case number and the solution in the same format as the input . if there is no solution ,print “No answer”.If there more than one solution,print “Not unique”. |
Sample Input3 7 3 1 4 5 8 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 |
Sample OutputCase 1: 7 3 1 4 5 8 6 2 Case 2: Not unique Case 3: No answer |
| Source ECJTU 2008 Autumn Contest |
| Recommend |
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
int a[10],vis[10],ans[10],anscnt;
int abs(int q)
{
if(q<0) return -q;
return q;
}
int ok()
{
if(abs(a[2]-a[1])!=1&&
abs(a[3]-a[1])!=1&&
abs(a[4]-a[1])!=1&&
abs(a[2]-a[3])!=1&&
abs(a[2]-a[5])!=1&&
abs(a[2]-a[6])!=1&&
abs(a[3]-a[4])!=1&&
abs(a[3]-a[5])!=1&&
abs(a[3]-a[6])!=1&&
abs(a[3]-a[7])!=1&&
abs(a[4]-a[6])!=1&&
abs(a[4]-a[7])!=1&&
abs(a[5]-a[6])!=1&&
abs(a[5]-a[8])!=1&&
abs(a[6]-a[7])!=1&&
abs(a[6]-a[8])!=1&&
abs(a[7]-a[8])!=1
)
return 1;
else return 0;
}
void DFS(int k)
{
int i,cnt=0;
if(k==9)
//注意这里是k==9 而不是把让它等于8之后放在调用函数的最后面 那样的话 最后一次的赋值就会被还原为0
{
if(ok())
{
anscnt++;
if(anscnt==1)
{
for(i=1;i<=8;i++)
ans[i]=a[i];
}
}
return;
}
if(anscnt>=2) return;
if(a[k]!=0) DFS(k+1);
else
for(i=1;i<=8;i++)
{
if(!vis[i])
{
a[k]=i;
vis[i]=1;
DFS(k+1);
a[k]=0;
vis[i]=0;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t,cas=0;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
anscnt=0;
int i;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
scanf("%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d",&a[1],&a[2],&a[3],&a[4],&a[5],&a[6],&a[7],&a[8]);
for(i=1;i<=8;i++) vis[a[i]]=1;
DFS(1);
printf("Case %d: ",++cas);
if(anscnt==1)
{
for(i=1;i<8;i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]);
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}
else if(anscnt==0) printf("No answer\n");
else printf("Not unique\n");
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- HDU 2514 Another Eight Puzzle
- hdu 2541 Another Eight Puzzle(dfs)
- HDOJ Another Eight Puzzle
- (全排列)Another Eight Puzzle--HDOJ
- Problem V:Another Eight Puzzle(HDU 2514)
- hdu 2518(dfs)Another Eight Puzzle
- ACM--steps--4.3.8--Another Eight Puzzle
- HDU 2514--Another Eight Puzzle【DFS】
- HDU [ Another Eight Puzzle ]——dfs全排列变式
- hdu 2514 Another Eight Puzzle
- hdu2514 Another Eight Puzzle 填数字 搜索水题
- Another Eight Puzzle (枚举深搜)
- HDU 2514 Another Eight Puzzle
- hdu 2514 Another Eight Puzzle(DFS暴搜)
- Another Eight Puzzle
- HDU2514 Another Eight Puzzle
- Another Eight Puzzle
- HDU2514 Another Eight Puzzle
- HDU 2514 Another Eight Puzzle
- hdu 2514 Another Eight Puzzle 枚举
