限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法原理、实现及效果
2013-05-30 22:34
399 查看
http://blog.csdn.net/laviewpbt/article/details/8769877#comments
一、自适应直方图均衡化(Adaptive histgram equalization/AHE)
1.简述
自适应直方图均衡化(AHE)用来提升图像的对比度的一种计算机图像处理技术。和普通的直方图均衡算法不同,AHE算法通过计算图像的局部直方图,然后重新分布亮度来来改变图像对比度。因此,该算法更适合于改进图像的局部对比度以及获得更多的图像细节。
不过,AHE有过度放大图像中相同区域的噪音的问题,另外一种自适应的直方图均衡算法即限制对比度直方图均衡(CLAHE)算法能有限的限制这种不利的放大。
2. 算法的解释
普通的直方图均衡算法对于整幅图像的像素使用相同的直方图变换,对于那些像素值分布比较均衡的图像来说,算法的效果很好。然后,如果图像中包括明显比图像其它区域暗或者亮的部分,在这些部分的对比度将得不到有效的增强。
AHE算法通过对局部区域执行响应的直方图均衡来改变上述问题。该算法首先被开发出来适用于改进航天器驾驶舱的显示效果。其最简单的形式,就是每个像素通过其周边一个矩形范围内的像素的直方图进行均衡化。均衡的方式则完全同普通的均衡化算法:变换函数同像素周边的累积直方图函数(CDF)成比例。
图像边缘的像素需要特殊处理,因为边缘像素的领域不完全在图像内部。这个通过镜像图像边缘的行像素或列像素来解决。直接复制边缘的像素进行扩充是不合适的。因为这会导致带有剑锋的领域直方图。
3. AHE的属性
领域的大小是该方法的一个参数。领域小,对比度得到增强,领域大,则对比度降低。
当某个区域包含的像素值非常相似,其直方图就会尖状化,此时直方图的变换函数会将一个很窄范围内的像素映射到整个像素范围。这将使得某些平坦区域中的少量噪音经AHE处理后过度放大。
二、限制对比度自适应直方图均衡(Contrast Limited Adaptive histgram equalization/CLAHE)
1.简述
CLAHE同普通的自适应直方图均衡不同的地方主要是其对比度限幅。这个特性也可以应用到全局直方图均衡化中,即构成所谓的限制对比度直方图均衡(CLHE),但这在实际中很少使用。在CLAHE中,对于每个小区域都必须使用对比度限幅。CLAHE主要是用来克服AHE的过度放大噪音的问题。
这主要是通过限制AHE算法的对比提高程度来达到的。在指定的像素值周边的对比度放大主要是由变换函数的斜度决定的。这个斜度和领域的累积直方图的斜度成比例。CLAHE通过在计算CDF前用预先定义的阈值来裁剪直方图以达到限制放大幅度的目的。这限制了CDF的斜度因此,也限制了变换函数的斜度。直方图被裁剪的值,也就是所谓的裁剪限幅,取决于直方图的分布因此也取决于领域大小的取值。
通常,直接忽略掉那些超出直方图裁剪限幅的部分是不好的,而应该将这些裁剪掉的部分均匀的分布到直方图的其他部分。如下图所示。

这个重分布的过程可能会导致那些倍裁剪掉的部分由重新超过了裁剪值(如上图的绿色部分所示)。如果这不是所希望的,可以不带使用重复不的过程指导这个超出的部分已经变得微不足道了。
2. 通过插值加快计算速度
如上所述的直接的自适应直方图,不管是否带有对比度限制,都需要对图像中的每个像素计算器领域直方图以及对应的变换函数,这使得算法及其耗时。
而插值使得上述算法效率上有极大的提升,并且质量上没有下降。首先,将图像均匀分成等份矩形大小,如下图的右侧部分所示(8行8列64个块是常用的选择)。然后计算个块的直方图、CDF以及对应的变换函数。这个变换函数对于块的中心像素(下图左侧部分的黑色小方块)是完全符合原始定义的。而其他的像素通过哪些于其临近的四个块的变换函数插值获取。位于图中蓝色阴影部分的像素采用双线性查插值,而位于便于边缘的(绿色阴影)部分采用线性插值,角点处(红色阴影处)直接使用块所在的变换函数。
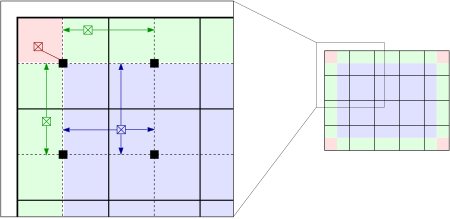
这样的过程极大的降低了变换函数需要计算的次数,只是增加了一些双线性插值的计算量。
CLAHE算法的源代码参考:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
View Code
/*
* ANSI C code from the article
* "Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization"
* by Karel Zuiderveld, karel@cv.ruu.nl
* in "Graphics Gems IV", Academic Press, 1994
*
*
* These functions implement Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization.
* The main routine (CLAHE) expects an input image that is stored contiguously in
* memory; the CLAHE output image overwrites the original input image and has the
* same minimum and maximum values (which must be provided by the user).
* This implementation assumes that the X- and Y image resolutions are an integer
* multiple of the X- and Y sizes of the contextual regions. A check on various other
* error conditions is performed.
*
* #define the symbol BYTE_IMAGE to make this implementation suitable for
* 8-bit images. The maximum number of contextual regions can be redefined
* by changing uiMAX_REG_X and/or uiMAX_REG_Y; the use of more than 256
* contextual regions is not recommended.
*
* The code is ANSI-C and is also C++ compliant.
*
* Author: Karel Zuiderveld, Computer Vision Research Group,
* Utrecht, The Netherlands (karel@cv.ruu.nl)
*/
#ifdef BYTE_IMAGE
typedef unsigned char kz_pixel_t; /* for 8 bit-per-pixel images */
#define uiNR_OF_GREY (256)
#else
typedef unsigned short kz_pixel_t; /* for 12 bit-per-pixel images (default) */
# define uiNR_OF_GREY (4096)
#endif
/******** Prototype of CLAHE function. Put this in a separate include file. *****/
int CLAHE(kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes, unsigned int uiYRes, kz_pixel_t Min,
kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrX, unsigned int uiNrY,
unsigned int uiNrBins, float fCliplimit);
/*********************** Local prototypes ************************/
static void ClipHistogram (unsigned long*, unsigned int, unsigned long);
static void MakeHistogram (kz_pixel_t*, unsigned int, unsigned int, unsigned int,
unsigned long*, unsigned int, kz_pixel_t*);
static void MapHistogram (unsigned long*, kz_pixel_t, kz_pixel_t,
unsigned int, unsigned long);
static void MakeLut (kz_pixel_t*, kz_pixel_t, kz_pixel_t, unsigned int);
static void Interpolate (kz_pixel_t*, int, unsigned long*, unsigned long*,
unsigned long*, unsigned long*, unsigned int, unsigned int, kz_pixel_t*);
/************** Start of actual code **************/
#include <stdlib.h> /* To get prototypes of malloc() and free() */
const unsigned int uiMAX_REG_X = 16; /* max. # contextual regions in x-direction */
const unsigned int uiMAX_REG_Y = 16; /* max. # contextual regions in y-direction */
/************************** main function CLAHE ******************/
int CLAHE (kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes, unsigned int uiYRes,
kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrX, unsigned int uiNrY,
unsigned int uiNrBins, float fCliplimit)
/* pImage - Pointer to the input/output image
* uiXRes - Image resolution in the X direction
* uiYRes - Image resolution in the Y direction
* Min - Minimum greyvalue of input image (also becomes minimum of output image)
* Max - Maximum greyvalue of input image (also becomes maximum of output image)
* uiNrX - Number of contextial regions in the X direction (min 2, max uiMAX_REG_X)
* uiNrY - Number of contextial regions in the Y direction (min 2, max uiMAX_REG_Y)
* uiNrBins - Number of greybins for histogram ("dynamic range")
* float fCliplimit - Normalized cliplimit (higher values give more contrast)
* The number of "effective" greylevels in the output image is set by uiNrBins; selecting
* a small value (eg. 128) speeds up processing and still produce an output image of
* good quality. The output image will have the same minimum and maximum value as the input
* image. A clip limit smaller than 1 results in standard (non-contrast limited) AHE.
*/
{
unsigned int uiX, uiY; /* counters */
unsigned int uiXSize, uiYSize, uiSubX, uiSubY; /* size of context. reg. and subimages */
unsigned int uiXL, uiXR, uiYU, uiYB; /* auxiliary variables interpolation routine */
unsigned long ulClipLimit, ulNrPixels;/* clip limit and region pixel count */
kz_pixel_t* pImPointer; /* pointer to image */
kz_pixel_t aLUT[uiNR_OF_GREY]; /* lookup table used for scaling of input image */
unsigned long* pulHist, *pulMapArray; /* pointer to histogram and mappings*/
unsigned long* pulLU, *pulLB, *pulRU, *pulRB; /* auxiliary pointers interpolation */
if (uiNrX > uiMAX_REG_X) return -1; /* # of regions x-direction too large */
if (uiNrY > uiMAX_REG_Y) return -2; /* # of regions y-direction too large */
if (uiXRes % uiNrX) return -3; /* x-resolution no multiple of uiNrX */
if (uiYRes & uiNrY) return -4; /* y-resolution no multiple of uiNrY */
if (Max >= uiNR_OF_GREY) return -5; /* maximum too large */
if (Min >= Max) return -6; /* minimum equal or larger than maximum */
if (uiNrX < 2 || uiNrY < 2) return -7;/* at least 4 contextual regions required */
if (fCliplimit == 1.0) return 0; /* is OK, immediately returns original image. */
if (uiNrBins == 0) uiNrBins = 128; /* default value when not specified */
pulMapArray=(unsigned long *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned long)*uiNrX*uiNrY*uiNrBins);
if (pulMapArray == 0) return -8; /* Not enough memory! (try reducing uiNrBins) */
uiXSize = uiXRes/uiNrX; uiYSize = uiYRes/uiNrY; /* Actual size of contextual regions */
ulNrPixels = (unsigned long)uiXSize * (unsigned long)uiYSize;
if(fCliplimit > 0.0) { /* Calculate actual cliplimit */
ulClipLimit = (unsigned long) (fCliplimit * (uiXSize * uiYSize) / uiNrBins);
ulClipLimit = (ulClipLimit < 1UL) ? 1UL : ulClipLimit;
}
else ulClipLimit = 1UL<<14; /* Large value, do not clip (AHE) */
MakeLut(aLUT, Min, Max, uiNrBins); /* Make lookup table for mapping of greyvalues */
/* Calculate greylevel mappings for each contextual region */
for (uiY = 0, pImPointer = pImage; uiY < uiNrY; uiY++) {
for (uiX = 0; uiX < uiNrX; uiX++, pImPointer += uiXSize) {
pulHist = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiY * uiNrX + uiX)];
MakeHistogram(pImPointer,uiXRes,uiXSize,uiYSize,pulHist,uiNrBins,aLUT);
ClipHistogram(pulHist, uiNrBins, ulClipLimit);
MapHistogram(pulHist, Min, Max, uiNrBins, ulNrPixels);
}
pImPointer += (uiYSize - 1) * uiXRes; /* skip lines, set pointer */
}
/* Interpolate greylevel mappings to get CLAHE image */
for (pImPointer = pImage, uiY = 0; uiY <= uiNrY; uiY++) {
if (uiY == 0) { /* special case: top row */
uiSubY = uiYSize >> 1; uiYU = 0; uiYB = 0;
}
else {
if (uiY == uiNrY) { /* special case: bottom row */
uiSubY = uiYSize >> 1; uiYU = uiNrY-1; uiYB = uiYU;
}
else { /* default values */
uiSubY = uiYSize; uiYU = uiY - 1; uiYB = uiYU + 1;
}
}
for (uiX = 0; uiX <= uiNrX; uiX++) {
if (uiX == 0) { /* special case: left column */
uiSubX = uiXSize >> 1; uiXL = 0; uiXR = 0;
}
else {
if (uiX == uiNrX) { /* special case: right column */
uiSubX = uiXSize >> 1; uiXL = uiNrX - 1; uiXR = uiXL;
}
else { /* default values */
uiSubX = uiXSize; uiXL = uiX - 1; uiXR = uiXL + 1;
}
}
pulLU = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYU * uiNrX + uiXL)];
pulRU = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYU * uiNrX + uiXR)];
pulLB = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYB * uiNrX + uiXL)];
pulRB = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYB * uiNrX + uiXR)];
Interpolate(pImPointer,uiXRes,pulLU,pulRU,pulLB,pulRB,uiSubX,uiSubY,aLUT);
pImPointer += uiSubX; /* set pointer on next matrix */
}
pImPointer += (uiSubY - 1) * uiXRes;
}
free(pulMapArray); /* free space for histograms */
return 0; /* return status OK */
}
void ClipHistogram (unsigned long* pulHistogram, unsigned int
uiNrGreylevels, unsigned long ulClipLimit)
/* This function performs clipping of the histogram and redistribution of bins.
* The histogram is clipped and the number of excess pixels is counted. Afterwards
* the excess pixels are equally redistributed across the whole histogram (providing
* the bin count is smaller than the cliplimit).
*/
{
unsigned long* pulBinPointer, *pulEndPointer, *pulHisto;
unsigned long ulNrExcess, ulUpper, ulBinIncr, ulStepSize, i;
long lBinExcess;
ulNrExcess = 0; pulBinPointer = pulHistogram;
for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) { /* calculate total number of excess pixels */
lBinExcess = (long) pulBinPointer[i] - (long) ulClipLimit;
if (lBinExcess > 0) ulNrExcess += lBinExcess; /* excess in current bin */
};
/* Second part: clip histogram and redistribute excess pixels in each bin */
ulBinIncr = ulNrExcess / uiNrGreylevels; /* average binincrement */
ulUpper = ulClipLimit - ulBinIncr; /* Bins larger than ulUpper set to cliplimit */
for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) {
if (pulHistogram[i] > ulClipLimit) pulHistogram[i] = ulClipLimit; /* clip bin */
else {
if (pulHistogram[i] > ulUpper) { /* high bin count */
ulNrExcess -= pulHistogram[i] - ulUpper; pulHistogram[i]=ulClipLimit;
}
else { /* low bin count */
ulNrExcess -= ulBinIncr; pulHistogram[i] += ulBinIncr;
}
}
}
while (ulNrExcess) { /* Redistribute remaining excess */
pulEndPointer = &pulHistogram[uiNrGreylevels]; pulHisto = pulHistogram;
while (ulNrExcess && pulHisto < pulEndPointer) {
ulStepSize = uiNrGreylevels / ulNrExcess;
if (ulStepSize < 1) ulStepSize = 1; /* stepsize at least 1 */
for (pulBinPointer=pulHisto; pulBinPointer < pulEndPointer && ulNrExcess;
pulBinPointer += ulStepSize) {
if (*pulBinPointer < ulClipLimit) {
(*pulBinPointer)++; ulNrExcess--; /* reduce excess */
}
}
pulHisto++; /* restart redistributing on other bin location */
}
}
}
void MakeHistogram (kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes,
unsigned int uiSizeX, unsigned int uiSizeY,
unsigned long* pulHistogram,
unsigned int uiNrGreylevels, kz_pixel_t* pLookupTable)
/* This function classifies the greylevels present in the array image into
* a greylevel histogram. The pLookupTable specifies the relationship
* between the greyvalue of the pixel (typically between 0 and 4095) and
* the corresponding bin in the histogram (usually containing only 128 bins).
*/
{
kz_pixel_t* pImagePointer;
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) pulHistogram[i] = 0L; /* clear histogram */
for (i = 0; i < uiSizeY; i++) {
pImagePointer = &pImage[uiSizeX];
while (pImage < pImagePointer) pulHistogram[pLookupTable[*pImage++]]++;
pImagePointer += uiXRes;
pImage = &pImagePointer[-uiSizeX];
}
}
void MapHistogram (unsigned long* pulHistogram, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max,
unsigned int uiNrGreylevels, unsigned long ulNrOfPixels)
/* This function calculates the equalized lookup table (mapping) by
* cumulating the input histogram. Note: lookup table is rescaled in range [Min..Max].
*/
{
unsigned int i; unsigned long ulSum = 0;
const float fScale = ((float)(Max - Min)) / ulNrOfPixels;
const unsigned long ulMin = (unsigned long) Min;
for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) {
ulSum += pulHistogram[i]; pulHistogram[i]=(unsigned long)(ulMin+ulSum*fScale);
if (pulHistogram[i] > Max) pulHistogram[i] = Max;
}
}
void MakeLut (kz_pixel_t * pLUT, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrBins)
/* To speed up histogram clipping, the input image [Min,Max] is scaled down to
* [0,uiNrBins-1]. This function calculates the LUT.
*/
{
int i;
const kz_pixel_t BinSize = (kz_pixel_t) (1 + (Max - Min) / uiNrBins);
for (i = Min; i <= Max; i++) pLUT[i] = (i - Min) / BinSize;
}
void Interpolate (kz_pixel_t * pImage, int uiXRes, unsigned long * pulMapLU,
unsigned long * pulMapRU, unsigned long * pulMapLB, unsigned long * pulMapRB,
unsigned int uiXSize, unsigned int uiYSize, kz_pixel_t * pLUT)
/* pImage - pointer to input/output image
* uiXRes - resolution of image in x-direction
* pulMap* - mappings of greylevels from histograms
* uiXSize - uiXSize of image submatrix
* uiYSize - uiYSize of image submatrix
* pLUT - lookup table containing mapping greyvalues to bins
* This function calculates the new greylevel assignments of pixels within a submatrix
* of the image with size uiXSize and uiYSize. This is done by a bilinear interpolation
* between four different mappings in order to eliminate boundary artifacts.
* It uses a division; since division is often an expensive operation, I added code to
* perform a logical shift instead when feasible.
*/
{
const unsigned int uiIncr = uiXRes-uiXSize; /* Pointer increment after processing row */
kz_pixel_t GreyValue; unsigned int uiNum = uiXSize*uiYSize; /* Normalization factor */
unsigned int uiXCoef, uiYCoef, uiXInvCoef, uiYInvCoef, uiShift = 0;
if (uiNum & (uiNum - 1)) /* If uiNum is not a power of two, use division */
for (uiYCoef = 0, uiYInvCoef = uiYSize; uiYCoef < uiYSize;
uiYCoef++, uiYInvCoef--,pImage+=uiIncr) {
for (uiXCoef = 0, uiXInvCoef = uiXSize; uiXCoef < uiXSize;
uiXCoef++, uiXInvCoef--) {
GreyValue = pLUT[*pImage]; /* get histogram bin value */
*pImage++ = (kz_pixel_t ) ((uiYInvCoef * (uiXInvCoef*pulMapLU[GreyValue]
+ uiXCoef * pulMapRU[GreyValue])
+ uiYCoef * (uiXInvCoef * pulMapLB[GreyValue]
+ uiXCoef * pulMapRB[GreyValue])) / uiNum);
}
}
else { /* avoid the division and use a right shift instead */
while (uiNum >>= 1) uiShift++; /* Calculate 2log of uiNum */
for (uiYCoef = 0, uiYInvCoef = uiYSize; uiYCoef < uiYSize;
uiYCoef++, uiYInvCoef--,pImage+=uiIncr) {
for (uiXCoef = 0, uiXInvCoef = uiXSize; uiXCoef < uiXSize;
uiXCoef++, uiXInvCoef--) {
GreyValue = pLUT[*pImage]; /* get histogram bin value */
*pImage++ = (kz_pixel_t)((uiYInvCoef* (uiXInvCoef * pulMapLU[GreyValue]
+ uiXCoef * pulMapRU[GreyValue])
+ uiYCoef * (uiXInvCoef * pulMapLB[GreyValue]
+ uiXCoef * pulMapRB[GreyValue])) >> uiShift);
}
}
}
}
上面的代码中对于各块之间的插值部分的编码技巧很值得学习和参考。
以上描述均翻译自:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CLAHE#Contrast_Limited_AHE
Karel Zuiderveld提供的代码:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
if (pulHistogram[i] > ulUpper)
{ /* high bin count */
ulNrExcess -= (pulHistogram[i] - ulUpper); pulHistogram[i]=ulClipLimit;
}
应该修正为:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
if (pulHistogram[i] > ulUpper)
{ /* high bin count */
ulNrExcess -= (ulClipLimit -pulHistogram[i]); pulHistogram[i]=ulClipLimit;
}
同时,各位也可以参考下matlab的adapthisteq.m文件,该文件的代码基本是严格按照 Karel Zuiderveld作者的原文写的,贴出如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
View Code
function out = adapthisteq(varargin)
%ADAPTHISTEQ Contrast-limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE).
% ADAPTHISTEQ enhances the contrast of images by transforming the
% values in the intensity image I. Unlike HISTEQ, it operates on small
% data regions (tiles), rather than the entire image. Each tile's
% contrast is enhanced, so that the histogram of the output region
% approximately matches the specified histogram. The neighboring tiles
% are then combined using bilinear interpolation in order to eliminate
% artificially induced boundaries. The contrast, especially
% in homogeneous areas, can be limited in order to avoid amplifying the
% noise which might be present in the image.
%
% J = ADAPTHISTEQ(I) Performs CLAHE on the intensity image I.
%
% J = ADAPTHISTEQ(I,PARAM1,VAL1,PARAM2,VAL2...) sets various parameters.
% Parameter names can be abbreviated, and case does not matter. Each
% string parameter is followed by a value as indicated below:
%
% 'NumTiles' Two-element vector of positive integers: [M N].
% [M N] specifies the number of tile rows and
% columns. Both M and N must be at least 2.
% The total number of image tiles is equal to M*N.
%
% Default: [8 8].
%
% 'ClipLimit' Real scalar from 0 to 1.
% 'ClipLimit' limits contrast enhancement. Higher numbers
% result in more contrast.
%
% Default: 0.01.
%
% 'NBins' Positive integer scalar.
% Sets number of bins for the histogram used in building a
% contrast enhancing transformation. Higher values result
% in greater dynamic range at the cost of slower processing
% speed.
%
% Default: 256.
%
% 'Range' One of the strings: 'original' or 'full'.
% Controls the range of the output image data. If 'Range'
% is set to 'original', the range is limited to
% [min(I(:)) max(I(:))]. Otherwise, by default, or when
% 'Range' is set to 'full', the full range of the output
% image class is used (e.g. [0 255] for uint8).
%
% Default: 'full'.
%
% 'Distribution' Distribution can be one of three strings: 'uniform',
% 'rayleigh', 'exponential'.
% Sets desired histogram shape for the image tiles, by
% specifying a distribution type.
%
% Default: 'uniform'.
%
% 'Alpha' Nonnegative real scalar.
% 'Alpha' is a distribution parameter, which can be supplied
% when 'Dist' is set to either 'rayleigh' or 'exponential'.
%
% Default: 0.4.
%
% Notes
% -----
% - 'NumTiles' specify the number of rectangular contextual regions (tiles)
% into which the image is divided. The contrast transform function is
% calculated for each of these regions individually. The optimal number of
% tiles depends on the type of the input image, and it is best determined
% through experimentation.
%
% - The 'ClipLimit' is a contrast factor that prevents over-saturation of the
% image specifically in homogeneous areas. These areas are characterized
% by a high peak in the histogram of the particular image tile due to many
% pixels falling inside the same gray level range. Without the clip limit,
% the adaptive histogram equalization technique could produce results that,
% in some cases, are worse than the original image.
%
% - ADAPTHISTEQ can use Uniform, Rayleigh, or Exponential distribution as
% the basis for creating the contrast transform function. The distribution
% that should be used depends on the type of the input image.
% For example, underwater imagery appears to look more natural when the
% Rayleigh distribution is used.
%
% Class Support
% -------------
% Intensity image I can be uint8, uint16, int16, double, or single.
% The output image J has the same class as I.
%
% Example 1
% ---------
% Apply Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization to an
% image and display the results.
%
% I = imread('tire.tif');
% A = adapthisteq(I,'clipLimit',0.02,'Distribution','rayleigh');
% figure, imshow(I);
% figure, imshow(A);
%
% Example 2
% ---------
%
% Apply Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization to a color
% photograph.
%
% [X MAP] = imread('shadow.tif');
% RGB = ind2rgb(X,MAP); % convert indexed image to truecolor format
% cform2lab = makecform('srgb2lab');
% LAB = applycform(RGB, cform2lab); %convert image to L*a*b color space
% L = LAB(:,:,1)/100; % scale the values to range from 0 to 1
% LAB(:,:,1) = adapthisteq(L,'NumTiles',[8 8],'ClipLimit',0.005)*100;
% cform2srgb = makecform('lab2srgb');
% J = applycform(LAB, cform2srgb); %convert back to RGB
% figure, imshow(RGB); %display the results
% figure, imshow(J);
%
% See also HISTEQ.
% Copyright 1993-2010 The MathWorks, Inc.
% $Revision: 1.1.6.12 $ $Date: 2011/08/09 17:48:54 $
% References:
% Karel Zuiderveld, "Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization",
% Graphics Gems IV, p. 474-485, code: p. 479-484
%
% Hanumant Singh, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, personal
% communication
%--------------------------- The algorithm ----------------------------------
%
% 1. Obtain all the inputs:
% * image
% * number of regions in row and column directions
% * number of bins for the histograms used in building image transform
% function (dynamic range)
% * clip limit for contrast limiting (normalized from 0 to 1)
% * other miscellaneous options
% 2. Pre-process the inputs:
% * determine real clip limit from the normalized value
% * if necessary, pad the image before splitting it into regions
% 3. Process each contextual region (tile) thus producing gray level mappings
% * extract a single image region
% * make a histogram for this region using the specified number of bins
% * clip the histogram using clip limit
% * create a mapping (transformation function) for this region
% 4. Interpolate gray level mappings in order to assemble final CLAHE image
% * extract cluster of four neighboring mapping functions
% * process image region partly overlapping each of the mapping tiles
% * extract a single pixel, apply four mappings to that pixel, and
% interpolate between the results to obtain the output pixel; repeat
% over the entire image
%
% See code for further details.
%
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[I, selectedRange, fullRange, numTiles, dimTile, clipLimit, numBins, ...
noPadRect, distribution, alpha, int16ClassChange] = parseInputs(varargin{:});
tileMappings = makeTileMappings(I, numTiles, dimTile, numBins, clipLimit, ...
selectedRange, fullRange, distribution, alpha);
%Synthesize the output image based on the individual tile mappings.
out = makeClaheImage(I, tileMappings, numTiles, selectedRange, numBins,...
dimTile);
if int16ClassChange
% Change uint16 back to int16 so output has same class as input.
out = uint16toint16(out);
end
if ~isempty(noPadRect) %do we need to remove padding?
out = out(noPadRect.ulRow:noPadRect.lrRow, ...
noPadRect.ulCol:noPadRect.lrCol);
end
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function tileMappings = ...
makeTileMappings(I, numTiles, dimTile, numBins, clipLimit,...
selectedRange, fullRange, distribution, alpha)
numPixInTile = prod(dimTile);
tileMappings = cell(numTiles);
% extract and process each tile
imgCol = 1;
for col=1:numTiles(2),
imgRow = 1;
for row=1:numTiles(1),
tile = I(imgRow:imgRow+dimTile(1)-1,imgCol:imgCol+dimTile(2)-1);
% for speed, call MEX file directly thus avoiding costly
% input parsing of imhist
tileHist = imhistc(tile, numBins, 1, fullRange(2));
tileHist = clipHistogram(tileHist, clipLimit, numBins);
tileMapping = makeMapping(tileHist, selectedRange, fullRange, ...
numPixInTile, distribution, alpha);
% assemble individual tile mappings by storing them in a cell array;
tileMappings{row,col} = tileMapping;
imgRow = imgRow + dimTile(1);
end
imgCol = imgCol + dimTile(2); % move to the next column of tiles
end
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Calculate the equalized lookup table (mapping) based on cumulating the input
% histogram. Note: lookup table is rescaled in the selectedRange [Min..Max].
function mapping = makeMapping(imgHist, selectedRange, fullRange, ...
numPixInTile, distribution, alpha)
histSum = cumsum(imgHist);
valSpread = selectedRange(2) - selectedRange(1);
switch distribution
case 'uniform',
scale = valSpread/numPixInTile;
mapping = min(selectedRange(1) + histSum*scale,...
selectedRange(2)); %limit to max
case 'rayleigh', % suitable for underwater imagery
% pdf = (t./alpha^2).*exp(-t.^2/(2*alpha^2))*U(t)
% cdf = 1-exp(-t.^2./(2*alpha^2))
hconst = 2*alpha^2;
vmax = 1 - exp(-1/hconst);
val = vmax*(histSum/numPixInTile);
val(val>=1) = 1-eps; % avoid log(0)
temp = sqrt(-hconst*log(1-val));
mapping = min(selectedRange(1)+temp*valSpread,...
selectedRange(2)); %limit to max
case 'exponential',
% pdf = alpha*exp(-alpha*t)*U(t)
% cdf = 1-exp(-alpha*t)
vmax = 1 - exp(-alpha);
val = (vmax*histSum/numPixInTile);
val(val>=1) = 1-eps;
temp = -1/alpha*log(1-val);
mapping = min(selectedRange(1)+temp*valSpread,selectedRange(2));
otherwise,
error(message('images:adapthisteq:distributionType')) %should never get here
end
%rescale the result to be between 0 and 1 for later use by the GRAYXFORM
%private mex function
mapping = mapping/fullRange(2);
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
% This function clips the histogram according to the clipLimit and
% redistributes clipped pixels across bins below the clipLimit
function imgHist = clipHistogram(imgHist, clipLimit, numBins)
% total number of pixels overflowing clip limit in each bin
totalExcess = sum(max(imgHist - clipLimit,0));
% clip the histogram and redistribute the excess pixels in each bin
avgBinIncr = floor(totalExcess/numBins);
upperLimit = clipLimit - avgBinIncr; % bins larger than this will be
% set to clipLimit
% this loop should speed up the operation by putting multiple pixels
% into the "obvious" places first
for k=1:numBins
if imgHist(k) > clipLimit
imgHist(k) = clipLimit;
else
if imgHist(k) > upperLimit % high bin count
totalExcess = totalExcess - (clipLimit - imgHist(k));
imgHist(k) = clipLimit;
else
totalExcess = totalExcess - avgBinIncr;
imgHist(k) = imgHist(k) + avgBinIncr;
end
end
end
% this loops redistributes the remaining pixels, one pixel at a time
k = 1;
while (totalExcess ~= 0)
%keep increasing the step as fewer and fewer pixels remain for
%the redistribution (spread them evenly)
stepSize = max(floor(numBins/totalExcess),1);
for m=k:stepSize:numBins
if imgHist(m) < clipLimit
imgHist(m) = imgHist(m)+1;
totalExcess = totalExcess - 1; %reduce excess
if totalExcess == 0
break;
end
end
end
k = k+1; %prevent from always placing the pixels in bin #1
if k > numBins % start over if numBins was reached
k = 1;
end
end
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
% This function interpolates between neighboring tile mappings to produce a
% new mapping in order to remove artificially induced tile borders.
% Otherwise, these borders would become quite visible. The resulting
% mapping is applied to the input image thus producing a CLAHE processed
% image.
function claheI = makeClaheImage(I, tileMappings, numTiles, selectedRange,...
numBins, dimTile)
%initialize the output image to zeros (preserve the class of the input image)
claheI = I;
claheI(:) = 0;
%compute the LUT for looking up original image values in the tile mappings,
%which we created earlier
if ~(isa(I,'double') || isa(I,'single'))
k = selectedRange(1)+1 : selectedRange(2)+1;
aLut = zeros(length(k),1);
aLut(k) = (k-1)-selectedRange(1);
aLut = aLut/(selectedRange(2)-selectedRange(1));
else
% remap from 0..1 to 0..numBins-1
if numBins ~= 1
binStep = 1/(numBins-1);
start = ceil(selectedRange(1)/binStep);
stop = floor(selectedRange(2)/binStep);
k = start+1:stop+1;
aLut(k) = 0:1/(length(k)-1):1;
else
aLut(1) = 0; %in case someone specifies numBins = 1, which is just silly
end
end
imgTileRow=1;
for k=1:numTiles(1)+1
if k == 1 %special case: top row
imgTileNumRows = dimTile(1)/2; %always divisible by 2 because of padding
mapTileRows = [1 1];
else
if k == numTiles(1)+1 %special case: bottom row
imgTileNumRows = dimTile(1)/2;
mapTileRows = [numTiles(1) numTiles(1)];
else %default values
imgTileNumRows = dimTile(1);
mapTileRows = [k-1, k]; %[upperRow lowerRow]
end
end
% loop over columns of the tileMappings cell array
imgTileCol=1;
for l=1:numTiles(2)+1
if l == 1 %special case: left column
imgTileNumCols = dimTile(2)/2;
mapTileCols = [1, 1];
else
if l == numTiles(2)+1 % special case: right column
imgTileNumCols = dimTile(2)/2;
mapTileCols = [numTiles(2), numTiles(2)];
else %default values
imgTileNumCols = dimTile(2);
mapTileCols = [l-1, l]; % right left
end
end
% Extract four tile mappings
ulMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(1), mapTileCols(1)};
urMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(1), mapTileCols(2)};
blMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(2), mapTileCols(1)};
brMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(2), mapTileCols(2)};
% Calculate the new greylevel assignments of pixels
% within a submatrix of the image specified by imgTileIdx. This
% is done by a bilinear interpolation between four different mappings
% in order to eliminate boundary artifacts.
normFactor = imgTileNumRows*imgTileNumCols; %normalization factor
imgTileIdx = {imgTileRow:imgTileRow+imgTileNumRows-1, ...
imgTileCol:imgTileCol+imgTileNumCols-1};
imgPixVals = grayxform(I(imgTileIdx{1},imgTileIdx{2}), aLut);
% calculate the weights used for linear interpolation between the
% four mappings
rowW = repmat((0:imgTileNumRows-1)',1,imgTileNumCols);
colW = repmat(0:imgTileNumCols-1,imgTileNumRows,1);
rowRevW = repmat((imgTileNumRows:-1:1)',1,imgTileNumCols);
colRevW = repmat(imgTileNumCols:-1:1,imgTileNumRows,1);
claheI(imgTileIdx{1}, imgTileIdx{2}) = ...
(rowRevW .* (colRevW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,ulMapTile)) + ...
colW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,urMapTile)))+ ...
rowW .* (colRevW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,blMapTile)) + ...
colW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,brMapTile))))...
/normFactor;
imgTileCol = imgTileCol + imgTileNumCols;
end %over tile cols
imgTileRow = imgTileRow + imgTileNumRows;
end %over tile rows
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [I, selectedRange, fullRange, numTiles, dimTile, clipLimit,...
numBins, noPadRect, distribution, alpha, ...
int16ClassChange] = parseInputs(varargin)
narginchk(1,13);
I = varargin{1};
validateattributes(I, {'uint8', 'uint16', 'double', 'int16', 'single'}, ...
{'real', '2d', 'nonsparse', 'nonempty'}, ...
mfilename, 'I', 1);
% convert int16 to uint16
if isa(I,'int16')
I = int16touint16(I);
int16ClassChange = true;
else
int16ClassChange = false;
end
if any(size(I) < 2)
error(message('images:adapthisteq:inputImageTooSmall'))
end
%Other options
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%Set the defaults
distribution = 'uniform';
alpha = 0.4;
if isa(I, 'double') || isa(I,'single')
fullRange = [0 1];
else
fullRange(1) = I(1); %copy class of the input image
fullRange(1:2) = [-Inf Inf]; %will be clipped to min and max
fullRange = double(fullRange);
end
selectedRange = fullRange;
%Set the default to 256 bins regardless of the data type;
%the user can override this value at any time
numBins = 256;
normClipLimit = 0.01;
numTiles = [8 8];
checkAlpha = false;
validStrings = {'NumTiles','ClipLimit','NBins','Distribution',...
'Alpha','Range'};
if nargin > 1
done = false;
idx = 2;
while ~done
input = varargin{idx};
inputStr = validatestring(input, validStrings,mfilename,'PARAM',idx);
idx = idx+1; %advance index to point to the VAL portion of the input
if idx > nargin
error(message('images:adapthisteq:missingValue', inputStr))
end
switch inputStr
case 'NumTiles'
numTiles = varargin{idx};
validateattributes(numTiles, {'double'}, {'real', 'vector', ...
'integer', 'finite','positive'},...
mfilename, inputStr, idx);
if (any(size(numTiles) ~= [1,2]))
error(message('images:adapthisteq:invalidNumTilesVector', inputStr))
end
if any(numTiles < 2)
error(message('images:adapthisteq:invalidNumTilesValue', inputStr))
end
case 'ClipLimit'
normClipLimit = varargin{idx};
validateattributes(normClipLimit, {'double'}, ...
{'scalar','real','nonnegative'},...
mfilename, inputStr, idx);
if normClipLimit > 1
error(message('images:adapthisteq:invalidClipLimit', inputStr))
end
case 'NBins'
numBins = varargin{idx};
validateattributes(numBins, {'double'}, {'scalar','real','integer',...
'positive'}, mfilename, 'NBins', idx);
case 'Distribution'
validDist = {'rayleigh','exponential','uniform'};
distribution = validatestring(varargin{idx}, validDist, mfilename,...
'Distribution', idx);
case 'Alpha'
alpha = varargin{idx};
validateattributes(alpha, {'double'},{'scalar','real',...
'nonnan','positive','finite'},...
mfilename, 'Alpha',idx);
checkAlpha = true;
case 'Range'
validRangeStrings = {'original','full'};
rangeStr = validatestring(varargin{idx}, validRangeStrings,mfilename,...
'Range',idx);
if strmatch(rangeStr,'original')
selectedRange = double([min(I(:)), max(I(:))]);
end
otherwise
error(message('images:adapthisteq:inputString')) %should never get here
end
if idx >= nargin
done = true;
end
idx=idx+1;
end
end
%% Pre-process the inputs
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
dimI = size(I);
dimTile = dimI ./ numTiles;
%check if tile size is reasonable
if any(dimTile < 1)
error(message('images:adapthisteq:inputImageTooSmallToSplit', num2str( numTiles )))
end
if checkAlpha
if strcmp(distribution,'uniform')
error(message('images:adapthisteq:alphaShouldNotBeSpecified', distribution))
end
end
%check if the image needs to be padded; pad if necessary;
%padding occurs if any dimension of a single tile is an odd number
%and/or when image dimensions are not divisible by the selected
%number of tiles
rowDiv = mod(dimI(1),numTiles(1)) == 0;
colDiv = mod(dimI(2),numTiles(2)) == 0;
if rowDiv && colDiv
rowEven = mod(dimTile(1),2) == 0;
colEven = mod(dimTile(2),2) == 0;
end
noPadRect = [];
if ~(rowDiv && colDiv && rowEven && colEven)
padRow = 0;
padCol = 0;
if ~rowDiv
rowTileDim = floor(dimI(1)/numTiles(1)) + 1;
padRow = rowTileDim*numTiles(1) - dimI(1);
else
rowTileDim = dimI(1)/numTiles(1);
end
if ~colDiv
colTileDim = floor(dimI(2)/numTiles(2)) + 1;
padCol = colTileDim*numTiles(2) - dimI(2);
else
colTileDim = dimI(2)/numTiles(2);
end
%check if tile dimensions are even numbers
rowEven = mod(rowTileDim,2) == 0;
colEven = mod(colTileDim,2) == 0;
if ~rowEven
padRow = padRow+numTiles(1);
end
if ~colEven
padCol = padCol+numTiles(2);
end
padRowPre = floor(padRow/2);
padRowPost = ceil(padRow/2);
padColPre = floor(padCol/2);
padColPost = ceil(padCol/2);
I = padarray(I,[padRowPre padColPre ],'symmetric','pre');
I = padarray(I,[padRowPost padColPost],'symmetric','post');
%UL corner (Row, Col), LR corner (Row, Col)
noPadRect.ulRow = padRowPre+1;
noPadRect.ulCol = padColPre+1;
noPadRect.lrRow = padRowPre+dimI(1);
noPadRect.lrCol = padColPre+dimI(2);
end
%redefine this variable to include the padding
dimI = size(I);
%size of the single tile
dimTile = dimI ./ numTiles;
%compute actual clip limit from the normalized value entered by the user
%maximum value of normClipLimit=1 results in standard AHE, i.e. no clipping;
%the minimum value minClipLimit would uniformly distribute the image pixels
%across the entire histogram, which would result in the lowest possible
%contrast value
numPixInTile = prod(dimTile);
minClipLimit = ceil(numPixInTile/numBins);
clipLimit = minClipLimit + round(normClipLimit*(numPixInTile-minClipLimit));
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
参考上述代码,我分别用VB和C#实现了该算法,提供个编译好的文件给有兴趣研究该算法的朋友看看效果(不提供源代码的):
http://files.cnblogs.com/Imageshop/CLAHE.rar
截面如下:

其中AHE算法可以认为是裁剪限幅为1的CLAHE算法,CLHE是水平网格和垂直网格都为1的算法。
均衡分布方式和ALPHA的解释可参考matlab的代码.
CLAHE算法很多时候比直接的直方图均衡化算法的效果要好很多,比如下面这幅图像:

普通的直方图均衡化算法的效果为:

而CALHE的效果如下:

可以看出,在图像的上部,CALHE有效的抑制了噪音的增强。
对于彩色图像,matlab的那个函数不支持,我这里采用了两种方式处理,一种是各通道分开处理,一种是每个通道都放在一起,对于彩色的图像似乎放在一起处理的效果要比分开处理好很多。
比如界面中那个图像,如果各通道放在一起处理,效果如下:

而通道分开处理,则各通道的颜色不很匹配:

对于处理速度,这个函数由于只有一些分开+插值计算,速度很快。如果图像不能倍分成整块,一般需要扩充边缘,matlab的处理方式是上下左右四条边对称镜像扩充。这种方式很合理。
实例工程是用VB6编写的,由于VB不支持指针,在速度比C#之类的语言大概慢了50%左右。但是也还是很快的了。
一、自适应直方图均衡化(Adaptive histgram equalization/AHE)
1.简述
自适应直方图均衡化(AHE)用来提升图像的对比度的一种计算机图像处理技术。和普通的直方图均衡算法不同,AHE算法通过计算图像的局部直方图,然后重新分布亮度来来改变图像对比度。因此,该算法更适合于改进图像的局部对比度以及获得更多的图像细节。
不过,AHE有过度放大图像中相同区域的噪音的问题,另外一种自适应的直方图均衡算法即限制对比度直方图均衡(CLAHE)算法能有限的限制这种不利的放大。
2. 算法的解释
普通的直方图均衡算法对于整幅图像的像素使用相同的直方图变换,对于那些像素值分布比较均衡的图像来说,算法的效果很好。然后,如果图像中包括明显比图像其它区域暗或者亮的部分,在这些部分的对比度将得不到有效的增强。
AHE算法通过对局部区域执行响应的直方图均衡来改变上述问题。该算法首先被开发出来适用于改进航天器驾驶舱的显示效果。其最简单的形式,就是每个像素通过其周边一个矩形范围内的像素的直方图进行均衡化。均衡的方式则完全同普通的均衡化算法:变换函数同像素周边的累积直方图函数(CDF)成比例。
图像边缘的像素需要特殊处理,因为边缘像素的领域不完全在图像内部。这个通过镜像图像边缘的行像素或列像素来解决。直接复制边缘的像素进行扩充是不合适的。因为这会导致带有剑锋的领域直方图。
3. AHE的属性
领域的大小是该方法的一个参数。领域小,对比度得到增强,领域大,则对比度降低。
当某个区域包含的像素值非常相似,其直方图就会尖状化,此时直方图的变换函数会将一个很窄范围内的像素映射到整个像素范围。这将使得某些平坦区域中的少量噪音经AHE处理后过度放大。
二、限制对比度自适应直方图均衡(Contrast Limited Adaptive histgram equalization/CLAHE)
1.简述
CLAHE同普通的自适应直方图均衡不同的地方主要是其对比度限幅。这个特性也可以应用到全局直方图均衡化中,即构成所谓的限制对比度直方图均衡(CLHE),但这在实际中很少使用。在CLAHE中,对于每个小区域都必须使用对比度限幅。CLAHE主要是用来克服AHE的过度放大噪音的问题。
这主要是通过限制AHE算法的对比提高程度来达到的。在指定的像素值周边的对比度放大主要是由变换函数的斜度决定的。这个斜度和领域的累积直方图的斜度成比例。CLAHE通过在计算CDF前用预先定义的阈值来裁剪直方图以达到限制放大幅度的目的。这限制了CDF的斜度因此,也限制了变换函数的斜度。直方图被裁剪的值,也就是所谓的裁剪限幅,取决于直方图的分布因此也取决于领域大小的取值。
通常,直接忽略掉那些超出直方图裁剪限幅的部分是不好的,而应该将这些裁剪掉的部分均匀的分布到直方图的其他部分。如下图所示。

这个重分布的过程可能会导致那些倍裁剪掉的部分由重新超过了裁剪值(如上图的绿色部分所示)。如果这不是所希望的,可以不带使用重复不的过程指导这个超出的部分已经变得微不足道了。
2. 通过插值加快计算速度
如上所述的直接的自适应直方图,不管是否带有对比度限制,都需要对图像中的每个像素计算器领域直方图以及对应的变换函数,这使得算法及其耗时。
而插值使得上述算法效率上有极大的提升,并且质量上没有下降。首先,将图像均匀分成等份矩形大小,如下图的右侧部分所示(8行8列64个块是常用的选择)。然后计算个块的直方图、CDF以及对应的变换函数。这个变换函数对于块的中心像素(下图左侧部分的黑色小方块)是完全符合原始定义的。而其他的像素通过哪些于其临近的四个块的变换函数插值获取。位于图中蓝色阴影部分的像素采用双线性查插值,而位于便于边缘的(绿色阴影)部分采用线性插值,角点处(红色阴影处)直接使用块所在的变换函数。

这样的过程极大的降低了变换函数需要计算的次数,只是增加了一些双线性插值的计算量。
CLAHE算法的源代码参考:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
View Code
/*
* ANSI C code from the article
* "Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization"
* by Karel Zuiderveld, karel@cv.ruu.nl
* in "Graphics Gems IV", Academic Press, 1994
*
*
* These functions implement Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization.
* The main routine (CLAHE) expects an input image that is stored contiguously in
* memory; the CLAHE output image overwrites the original input image and has the
* same minimum and maximum values (which must be provided by the user).
* This implementation assumes that the X- and Y image resolutions are an integer
* multiple of the X- and Y sizes of the contextual regions. A check on various other
* error conditions is performed.
*
* #define the symbol BYTE_IMAGE to make this implementation suitable for
* 8-bit images. The maximum number of contextual regions can be redefined
* by changing uiMAX_REG_X and/or uiMAX_REG_Y; the use of more than 256
* contextual regions is not recommended.
*
* The code is ANSI-C and is also C++ compliant.
*
* Author: Karel Zuiderveld, Computer Vision Research Group,
* Utrecht, The Netherlands (karel@cv.ruu.nl)
*/
#ifdef BYTE_IMAGE
typedef unsigned char kz_pixel_t; /* for 8 bit-per-pixel images */
#define uiNR_OF_GREY (256)
#else
typedef unsigned short kz_pixel_t; /* for 12 bit-per-pixel images (default) */
# define uiNR_OF_GREY (4096)
#endif
/******** Prototype of CLAHE function. Put this in a separate include file. *****/
int CLAHE(kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes, unsigned int uiYRes, kz_pixel_t Min,
kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrX, unsigned int uiNrY,
unsigned int uiNrBins, float fCliplimit);
/*********************** Local prototypes ************************/
static void ClipHistogram (unsigned long*, unsigned int, unsigned long);
static void MakeHistogram (kz_pixel_t*, unsigned int, unsigned int, unsigned int,
unsigned long*, unsigned int, kz_pixel_t*);
static void MapHistogram (unsigned long*, kz_pixel_t, kz_pixel_t,
unsigned int, unsigned long);
static void MakeLut (kz_pixel_t*, kz_pixel_t, kz_pixel_t, unsigned int);
static void Interpolate (kz_pixel_t*, int, unsigned long*, unsigned long*,
unsigned long*, unsigned long*, unsigned int, unsigned int, kz_pixel_t*);
/************** Start of actual code **************/
#include <stdlib.h> /* To get prototypes of malloc() and free() */
const unsigned int uiMAX_REG_X = 16; /* max. # contextual regions in x-direction */
const unsigned int uiMAX_REG_Y = 16; /* max. # contextual regions in y-direction */
/************************** main function CLAHE ******************/
int CLAHE (kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes, unsigned int uiYRes,
kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrX, unsigned int uiNrY,
unsigned int uiNrBins, float fCliplimit)
/* pImage - Pointer to the input/output image
* uiXRes - Image resolution in the X direction
* uiYRes - Image resolution in the Y direction
* Min - Minimum greyvalue of input image (also becomes minimum of output image)
* Max - Maximum greyvalue of input image (also becomes maximum of output image)
* uiNrX - Number of contextial regions in the X direction (min 2, max uiMAX_REG_X)
* uiNrY - Number of contextial regions in the Y direction (min 2, max uiMAX_REG_Y)
* uiNrBins - Number of greybins for histogram ("dynamic range")
* float fCliplimit - Normalized cliplimit (higher values give more contrast)
* The number of "effective" greylevels in the output image is set by uiNrBins; selecting
* a small value (eg. 128) speeds up processing and still produce an output image of
* good quality. The output image will have the same minimum and maximum value as the input
* image. A clip limit smaller than 1 results in standard (non-contrast limited) AHE.
*/
{
unsigned int uiX, uiY; /* counters */
unsigned int uiXSize, uiYSize, uiSubX, uiSubY; /* size of context. reg. and subimages */
unsigned int uiXL, uiXR, uiYU, uiYB; /* auxiliary variables interpolation routine */
unsigned long ulClipLimit, ulNrPixels;/* clip limit and region pixel count */
kz_pixel_t* pImPointer; /* pointer to image */
kz_pixel_t aLUT[uiNR_OF_GREY]; /* lookup table used for scaling of input image */
unsigned long* pulHist, *pulMapArray; /* pointer to histogram and mappings*/
unsigned long* pulLU, *pulLB, *pulRU, *pulRB; /* auxiliary pointers interpolation */
if (uiNrX > uiMAX_REG_X) return -1; /* # of regions x-direction too large */
if (uiNrY > uiMAX_REG_Y) return -2; /* # of regions y-direction too large */
if (uiXRes % uiNrX) return -3; /* x-resolution no multiple of uiNrX */
if (uiYRes & uiNrY) return -4; /* y-resolution no multiple of uiNrY */
if (Max >= uiNR_OF_GREY) return -5; /* maximum too large */
if (Min >= Max) return -6; /* minimum equal or larger than maximum */
if (uiNrX < 2 || uiNrY < 2) return -7;/* at least 4 contextual regions required */
if (fCliplimit == 1.0) return 0; /* is OK, immediately returns original image. */
if (uiNrBins == 0) uiNrBins = 128; /* default value when not specified */
pulMapArray=(unsigned long *)malloc(sizeof(unsigned long)*uiNrX*uiNrY*uiNrBins);
if (pulMapArray == 0) return -8; /* Not enough memory! (try reducing uiNrBins) */
uiXSize = uiXRes/uiNrX; uiYSize = uiYRes/uiNrY; /* Actual size of contextual regions */
ulNrPixels = (unsigned long)uiXSize * (unsigned long)uiYSize;
if(fCliplimit > 0.0) { /* Calculate actual cliplimit */
ulClipLimit = (unsigned long) (fCliplimit * (uiXSize * uiYSize) / uiNrBins);
ulClipLimit = (ulClipLimit < 1UL) ? 1UL : ulClipLimit;
}
else ulClipLimit = 1UL<<14; /* Large value, do not clip (AHE) */
MakeLut(aLUT, Min, Max, uiNrBins); /* Make lookup table for mapping of greyvalues */
/* Calculate greylevel mappings for each contextual region */
for (uiY = 0, pImPointer = pImage; uiY < uiNrY; uiY++) {
for (uiX = 0; uiX < uiNrX; uiX++, pImPointer += uiXSize) {
pulHist = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiY * uiNrX + uiX)];
MakeHistogram(pImPointer,uiXRes,uiXSize,uiYSize,pulHist,uiNrBins,aLUT);
ClipHistogram(pulHist, uiNrBins, ulClipLimit);
MapHistogram(pulHist, Min, Max, uiNrBins, ulNrPixels);
}
pImPointer += (uiYSize - 1) * uiXRes; /* skip lines, set pointer */
}
/* Interpolate greylevel mappings to get CLAHE image */
for (pImPointer = pImage, uiY = 0; uiY <= uiNrY; uiY++) {
if (uiY == 0) { /* special case: top row */
uiSubY = uiYSize >> 1; uiYU = 0; uiYB = 0;
}
else {
if (uiY == uiNrY) { /* special case: bottom row */
uiSubY = uiYSize >> 1; uiYU = uiNrY-1; uiYB = uiYU;
}
else { /* default values */
uiSubY = uiYSize; uiYU = uiY - 1; uiYB = uiYU + 1;
}
}
for (uiX = 0; uiX <= uiNrX; uiX++) {
if (uiX == 0) { /* special case: left column */
uiSubX = uiXSize >> 1; uiXL = 0; uiXR = 0;
}
else {
if (uiX == uiNrX) { /* special case: right column */
uiSubX = uiXSize >> 1; uiXL = uiNrX - 1; uiXR = uiXL;
}
else { /* default values */
uiSubX = uiXSize; uiXL = uiX - 1; uiXR = uiXL + 1;
}
}
pulLU = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYU * uiNrX + uiXL)];
pulRU = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYU * uiNrX + uiXR)];
pulLB = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYB * uiNrX + uiXL)];
pulRB = &pulMapArray[uiNrBins * (uiYB * uiNrX + uiXR)];
Interpolate(pImPointer,uiXRes,pulLU,pulRU,pulLB,pulRB,uiSubX,uiSubY,aLUT);
pImPointer += uiSubX; /* set pointer on next matrix */
}
pImPointer += (uiSubY - 1) * uiXRes;
}
free(pulMapArray); /* free space for histograms */
return 0; /* return status OK */
}
void ClipHistogram (unsigned long* pulHistogram, unsigned int
uiNrGreylevels, unsigned long ulClipLimit)
/* This function performs clipping of the histogram and redistribution of bins.
* The histogram is clipped and the number of excess pixels is counted. Afterwards
* the excess pixels are equally redistributed across the whole histogram (providing
* the bin count is smaller than the cliplimit).
*/
{
unsigned long* pulBinPointer, *pulEndPointer, *pulHisto;
unsigned long ulNrExcess, ulUpper, ulBinIncr, ulStepSize, i;
long lBinExcess;
ulNrExcess = 0; pulBinPointer = pulHistogram;
for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) { /* calculate total number of excess pixels */
lBinExcess = (long) pulBinPointer[i] - (long) ulClipLimit;
if (lBinExcess > 0) ulNrExcess += lBinExcess; /* excess in current bin */
};
/* Second part: clip histogram and redistribute excess pixels in each bin */
ulBinIncr = ulNrExcess / uiNrGreylevels; /* average binincrement */
ulUpper = ulClipLimit - ulBinIncr; /* Bins larger than ulUpper set to cliplimit */
for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) {
if (pulHistogram[i] > ulClipLimit) pulHistogram[i] = ulClipLimit; /* clip bin */
else {
if (pulHistogram[i] > ulUpper) { /* high bin count */
ulNrExcess -= pulHistogram[i] - ulUpper; pulHistogram[i]=ulClipLimit;
}
else { /* low bin count */
ulNrExcess -= ulBinIncr; pulHistogram[i] += ulBinIncr;
}
}
}
while (ulNrExcess) { /* Redistribute remaining excess */
pulEndPointer = &pulHistogram[uiNrGreylevels]; pulHisto = pulHistogram;
while (ulNrExcess && pulHisto < pulEndPointer) {
ulStepSize = uiNrGreylevels / ulNrExcess;
if (ulStepSize < 1) ulStepSize = 1; /* stepsize at least 1 */
for (pulBinPointer=pulHisto; pulBinPointer < pulEndPointer && ulNrExcess;
pulBinPointer += ulStepSize) {
if (*pulBinPointer < ulClipLimit) {
(*pulBinPointer)++; ulNrExcess--; /* reduce excess */
}
}
pulHisto++; /* restart redistributing on other bin location */
}
}
}
void MakeHistogram (kz_pixel_t* pImage, unsigned int uiXRes,
unsigned int uiSizeX, unsigned int uiSizeY,
unsigned long* pulHistogram,
unsigned int uiNrGreylevels, kz_pixel_t* pLookupTable)
/* This function classifies the greylevels present in the array image into
* a greylevel histogram. The pLookupTable specifies the relationship
* between the greyvalue of the pixel (typically between 0 and 4095) and
* the corresponding bin in the histogram (usually containing only 128 bins).
*/
{
kz_pixel_t* pImagePointer;
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) pulHistogram[i] = 0L; /* clear histogram */
for (i = 0; i < uiSizeY; i++) {
pImagePointer = &pImage[uiSizeX];
while (pImage < pImagePointer) pulHistogram[pLookupTable[*pImage++]]++;
pImagePointer += uiXRes;
pImage = &pImagePointer[-uiSizeX];
}
}
void MapHistogram (unsigned long* pulHistogram, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max,
unsigned int uiNrGreylevels, unsigned long ulNrOfPixels)
/* This function calculates the equalized lookup table (mapping) by
* cumulating the input histogram. Note: lookup table is rescaled in range [Min..Max].
*/
{
unsigned int i; unsigned long ulSum = 0;
const float fScale = ((float)(Max - Min)) / ulNrOfPixels;
const unsigned long ulMin = (unsigned long) Min;
for (i = 0; i < uiNrGreylevels; i++) {
ulSum += pulHistogram[i]; pulHistogram[i]=(unsigned long)(ulMin+ulSum*fScale);
if (pulHistogram[i] > Max) pulHistogram[i] = Max;
}
}
void MakeLut (kz_pixel_t * pLUT, kz_pixel_t Min, kz_pixel_t Max, unsigned int uiNrBins)
/* To speed up histogram clipping, the input image [Min,Max] is scaled down to
* [0,uiNrBins-1]. This function calculates the LUT.
*/
{
int i;
const kz_pixel_t BinSize = (kz_pixel_t) (1 + (Max - Min) / uiNrBins);
for (i = Min; i <= Max; i++) pLUT[i] = (i - Min) / BinSize;
}
void Interpolate (kz_pixel_t * pImage, int uiXRes, unsigned long * pulMapLU,
unsigned long * pulMapRU, unsigned long * pulMapLB, unsigned long * pulMapRB,
unsigned int uiXSize, unsigned int uiYSize, kz_pixel_t * pLUT)
/* pImage - pointer to input/output image
* uiXRes - resolution of image in x-direction
* pulMap* - mappings of greylevels from histograms
* uiXSize - uiXSize of image submatrix
* uiYSize - uiYSize of image submatrix
* pLUT - lookup table containing mapping greyvalues to bins
* This function calculates the new greylevel assignments of pixels within a submatrix
* of the image with size uiXSize and uiYSize. This is done by a bilinear interpolation
* between four different mappings in order to eliminate boundary artifacts.
* It uses a division; since division is often an expensive operation, I added code to
* perform a logical shift instead when feasible.
*/
{
const unsigned int uiIncr = uiXRes-uiXSize; /* Pointer increment after processing row */
kz_pixel_t GreyValue; unsigned int uiNum = uiXSize*uiYSize; /* Normalization factor */
unsigned int uiXCoef, uiYCoef, uiXInvCoef, uiYInvCoef, uiShift = 0;
if (uiNum & (uiNum - 1)) /* If uiNum is not a power of two, use division */
for (uiYCoef = 0, uiYInvCoef = uiYSize; uiYCoef < uiYSize;
uiYCoef++, uiYInvCoef--,pImage+=uiIncr) {
for (uiXCoef = 0, uiXInvCoef = uiXSize; uiXCoef < uiXSize;
uiXCoef++, uiXInvCoef--) {
GreyValue = pLUT[*pImage]; /* get histogram bin value */
*pImage++ = (kz_pixel_t ) ((uiYInvCoef * (uiXInvCoef*pulMapLU[GreyValue]
+ uiXCoef * pulMapRU[GreyValue])
+ uiYCoef * (uiXInvCoef * pulMapLB[GreyValue]
+ uiXCoef * pulMapRB[GreyValue])) / uiNum);
}
}
else { /* avoid the division and use a right shift instead */
while (uiNum >>= 1) uiShift++; /* Calculate 2log of uiNum */
for (uiYCoef = 0, uiYInvCoef = uiYSize; uiYCoef < uiYSize;
uiYCoef++, uiYInvCoef--,pImage+=uiIncr) {
for (uiXCoef = 0, uiXInvCoef = uiXSize; uiXCoef < uiXSize;
uiXCoef++, uiXInvCoef--) {
GreyValue = pLUT[*pImage]; /* get histogram bin value */
*pImage++ = (kz_pixel_t)((uiYInvCoef* (uiXInvCoef * pulMapLU[GreyValue]
+ uiXCoef * pulMapRU[GreyValue])
+ uiYCoef * (uiXInvCoef * pulMapLB[GreyValue]
+ uiXCoef * pulMapRB[GreyValue])) >> uiShift);
}
}
}
}
上面的代码中对于各块之间的插值部分的编码技巧很值得学习和参考。
以上描述均翻译自:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CLAHE#Contrast_Limited_AHE
Karel Zuiderveld提供的代码:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
if (pulHistogram[i] > ulUpper)
{ /* high bin count */
ulNrExcess -= (pulHistogram[i] - ulUpper); pulHistogram[i]=ulClipLimit;
}
应该修正为:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
if (pulHistogram[i] > ulUpper)
{ /* high bin count */
ulNrExcess -= (ulClipLimit -pulHistogram[i]); pulHistogram[i]=ulClipLimit;
}
同时,各位也可以参考下matlab的adapthisteq.m文件,该文件的代码基本是严格按照 Karel Zuiderveld作者的原文写的,贴出如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
View Code
function out = adapthisteq(varargin)
%ADAPTHISTEQ Contrast-limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE).
% ADAPTHISTEQ enhances the contrast of images by transforming the
% values in the intensity image I. Unlike HISTEQ, it operates on small
% data regions (tiles), rather than the entire image. Each tile's
% contrast is enhanced, so that the histogram of the output region
% approximately matches the specified histogram. The neighboring tiles
% are then combined using bilinear interpolation in order to eliminate
% artificially induced boundaries. The contrast, especially
% in homogeneous areas, can be limited in order to avoid amplifying the
% noise which might be present in the image.
%
% J = ADAPTHISTEQ(I) Performs CLAHE on the intensity image I.
%
% J = ADAPTHISTEQ(I,PARAM1,VAL1,PARAM2,VAL2...) sets various parameters.
% Parameter names can be abbreviated, and case does not matter. Each
% string parameter is followed by a value as indicated below:
%
% 'NumTiles' Two-element vector of positive integers: [M N].
% [M N] specifies the number of tile rows and
% columns. Both M and N must be at least 2.
% The total number of image tiles is equal to M*N.
%
% Default: [8 8].
%
% 'ClipLimit' Real scalar from 0 to 1.
% 'ClipLimit' limits contrast enhancement. Higher numbers
% result in more contrast.
%
% Default: 0.01.
%
% 'NBins' Positive integer scalar.
% Sets number of bins for the histogram used in building a
% contrast enhancing transformation. Higher values result
% in greater dynamic range at the cost of slower processing
% speed.
%
% Default: 256.
%
% 'Range' One of the strings: 'original' or 'full'.
% Controls the range of the output image data. If 'Range'
% is set to 'original', the range is limited to
% [min(I(:)) max(I(:))]. Otherwise, by default, or when
% 'Range' is set to 'full', the full range of the output
% image class is used (e.g. [0 255] for uint8).
%
% Default: 'full'.
%
% 'Distribution' Distribution can be one of three strings: 'uniform',
% 'rayleigh', 'exponential'.
% Sets desired histogram shape for the image tiles, by
% specifying a distribution type.
%
% Default: 'uniform'.
%
% 'Alpha' Nonnegative real scalar.
% 'Alpha' is a distribution parameter, which can be supplied
% when 'Dist' is set to either 'rayleigh' or 'exponential'.
%
% Default: 0.4.
%
% Notes
% -----
% - 'NumTiles' specify the number of rectangular contextual regions (tiles)
% into which the image is divided. The contrast transform function is
% calculated for each of these regions individually. The optimal number of
% tiles depends on the type of the input image, and it is best determined
% through experimentation.
%
% - The 'ClipLimit' is a contrast factor that prevents over-saturation of the
% image specifically in homogeneous areas. These areas are characterized
% by a high peak in the histogram of the particular image tile due to many
% pixels falling inside the same gray level range. Without the clip limit,
% the adaptive histogram equalization technique could produce results that,
% in some cases, are worse than the original image.
%
% - ADAPTHISTEQ can use Uniform, Rayleigh, or Exponential distribution as
% the basis for creating the contrast transform function. The distribution
% that should be used depends on the type of the input image.
% For example, underwater imagery appears to look more natural when the
% Rayleigh distribution is used.
%
% Class Support
% -------------
% Intensity image I can be uint8, uint16, int16, double, or single.
% The output image J has the same class as I.
%
% Example 1
% ---------
% Apply Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization to an
% image and display the results.
%
% I = imread('tire.tif');
% A = adapthisteq(I,'clipLimit',0.02,'Distribution','rayleigh');
% figure, imshow(I);
% figure, imshow(A);
%
% Example 2
% ---------
%
% Apply Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization to a color
% photograph.
%
% [X MAP] = imread('shadow.tif');
% RGB = ind2rgb(X,MAP); % convert indexed image to truecolor format
% cform2lab = makecform('srgb2lab');
% LAB = applycform(RGB, cform2lab); %convert image to L*a*b color space
% L = LAB(:,:,1)/100; % scale the values to range from 0 to 1
% LAB(:,:,1) = adapthisteq(L,'NumTiles',[8 8],'ClipLimit',0.005)*100;
% cform2srgb = makecform('lab2srgb');
% J = applycform(LAB, cform2srgb); %convert back to RGB
% figure, imshow(RGB); %display the results
% figure, imshow(J);
%
% See also HISTEQ.
% Copyright 1993-2010 The MathWorks, Inc.
% $Revision: 1.1.6.12 $ $Date: 2011/08/09 17:48:54 $
% References:
% Karel Zuiderveld, "Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization",
% Graphics Gems IV, p. 474-485, code: p. 479-484
%
% Hanumant Singh, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, personal
% communication
%--------------------------- The algorithm ----------------------------------
%
% 1. Obtain all the inputs:
% * image
% * number of regions in row and column directions
% * number of bins for the histograms used in building image transform
% function (dynamic range)
% * clip limit for contrast limiting (normalized from 0 to 1)
% * other miscellaneous options
% 2. Pre-process the inputs:
% * determine real clip limit from the normalized value
% * if necessary, pad the image before splitting it into regions
% 3. Process each contextual region (tile) thus producing gray level mappings
% * extract a single image region
% * make a histogram for this region using the specified number of bins
% * clip the histogram using clip limit
% * create a mapping (transformation function) for this region
% 4. Interpolate gray level mappings in order to assemble final CLAHE image
% * extract cluster of four neighboring mapping functions
% * process image region partly overlapping each of the mapping tiles
% * extract a single pixel, apply four mappings to that pixel, and
% interpolate between the results to obtain the output pixel; repeat
% over the entire image
%
% See code for further details.
%
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[I, selectedRange, fullRange, numTiles, dimTile, clipLimit, numBins, ...
noPadRect, distribution, alpha, int16ClassChange] = parseInputs(varargin{:});
tileMappings = makeTileMappings(I, numTiles, dimTile, numBins, clipLimit, ...
selectedRange, fullRange, distribution, alpha);
%Synthesize the output image based on the individual tile mappings.
out = makeClaheImage(I, tileMappings, numTiles, selectedRange, numBins,...
dimTile);
if int16ClassChange
% Change uint16 back to int16 so output has same class as input.
out = uint16toint16(out);
end
if ~isempty(noPadRect) %do we need to remove padding?
out = out(noPadRect.ulRow:noPadRect.lrRow, ...
noPadRect.ulCol:noPadRect.lrCol);
end
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function tileMappings = ...
makeTileMappings(I, numTiles, dimTile, numBins, clipLimit,...
selectedRange, fullRange, distribution, alpha)
numPixInTile = prod(dimTile);
tileMappings = cell(numTiles);
% extract and process each tile
imgCol = 1;
for col=1:numTiles(2),
imgRow = 1;
for row=1:numTiles(1),
tile = I(imgRow:imgRow+dimTile(1)-1,imgCol:imgCol+dimTile(2)-1);
% for speed, call MEX file directly thus avoiding costly
% input parsing of imhist
tileHist = imhistc(tile, numBins, 1, fullRange(2));
tileHist = clipHistogram(tileHist, clipLimit, numBins);
tileMapping = makeMapping(tileHist, selectedRange, fullRange, ...
numPixInTile, distribution, alpha);
% assemble individual tile mappings by storing them in a cell array;
tileMappings{row,col} = tileMapping;
imgRow = imgRow + dimTile(1);
end
imgCol = imgCol + dimTile(2); % move to the next column of tiles
end
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Calculate the equalized lookup table (mapping) based on cumulating the input
% histogram. Note: lookup table is rescaled in the selectedRange [Min..Max].
function mapping = makeMapping(imgHist, selectedRange, fullRange, ...
numPixInTile, distribution, alpha)
histSum = cumsum(imgHist);
valSpread = selectedRange(2) - selectedRange(1);
switch distribution
case 'uniform',
scale = valSpread/numPixInTile;
mapping = min(selectedRange(1) + histSum*scale,...
selectedRange(2)); %limit to max
case 'rayleigh', % suitable for underwater imagery
% pdf = (t./alpha^2).*exp(-t.^2/(2*alpha^2))*U(t)
% cdf = 1-exp(-t.^2./(2*alpha^2))
hconst = 2*alpha^2;
vmax = 1 - exp(-1/hconst);
val = vmax*(histSum/numPixInTile);
val(val>=1) = 1-eps; % avoid log(0)
temp = sqrt(-hconst*log(1-val));
mapping = min(selectedRange(1)+temp*valSpread,...
selectedRange(2)); %limit to max
case 'exponential',
% pdf = alpha*exp(-alpha*t)*U(t)
% cdf = 1-exp(-alpha*t)
vmax = 1 - exp(-alpha);
val = (vmax*histSum/numPixInTile);
val(val>=1) = 1-eps;
temp = -1/alpha*log(1-val);
mapping = min(selectedRange(1)+temp*valSpread,selectedRange(2));
otherwise,
error(message('images:adapthisteq:distributionType')) %should never get here
end
%rescale the result to be between 0 and 1 for later use by the GRAYXFORM
%private mex function
mapping = mapping/fullRange(2);
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
% This function clips the histogram according to the clipLimit and
% redistributes clipped pixels across bins below the clipLimit
function imgHist = clipHistogram(imgHist, clipLimit, numBins)
% total number of pixels overflowing clip limit in each bin
totalExcess = sum(max(imgHist - clipLimit,0));
% clip the histogram and redistribute the excess pixels in each bin
avgBinIncr = floor(totalExcess/numBins);
upperLimit = clipLimit - avgBinIncr; % bins larger than this will be
% set to clipLimit
% this loop should speed up the operation by putting multiple pixels
% into the "obvious" places first
for k=1:numBins
if imgHist(k) > clipLimit
imgHist(k) = clipLimit;
else
if imgHist(k) > upperLimit % high bin count
totalExcess = totalExcess - (clipLimit - imgHist(k));
imgHist(k) = clipLimit;
else
totalExcess = totalExcess - avgBinIncr;
imgHist(k) = imgHist(k) + avgBinIncr;
end
end
end
% this loops redistributes the remaining pixels, one pixel at a time
k = 1;
while (totalExcess ~= 0)
%keep increasing the step as fewer and fewer pixels remain for
%the redistribution (spread them evenly)
stepSize = max(floor(numBins/totalExcess),1);
for m=k:stepSize:numBins
if imgHist(m) < clipLimit
imgHist(m) = imgHist(m)+1;
totalExcess = totalExcess - 1; %reduce excess
if totalExcess == 0
break;
end
end
end
k = k+1; %prevent from always placing the pixels in bin #1
if k > numBins % start over if numBins was reached
k = 1;
end
end
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
% This function interpolates between neighboring tile mappings to produce a
% new mapping in order to remove artificially induced tile borders.
% Otherwise, these borders would become quite visible. The resulting
% mapping is applied to the input image thus producing a CLAHE processed
% image.
function claheI = makeClaheImage(I, tileMappings, numTiles, selectedRange,...
numBins, dimTile)
%initialize the output image to zeros (preserve the class of the input image)
claheI = I;
claheI(:) = 0;
%compute the LUT for looking up original image values in the tile mappings,
%which we created earlier
if ~(isa(I,'double') || isa(I,'single'))
k = selectedRange(1)+1 : selectedRange(2)+1;
aLut = zeros(length(k),1);
aLut(k) = (k-1)-selectedRange(1);
aLut = aLut/(selectedRange(2)-selectedRange(1));
else
% remap from 0..1 to 0..numBins-1
if numBins ~= 1
binStep = 1/(numBins-1);
start = ceil(selectedRange(1)/binStep);
stop = floor(selectedRange(2)/binStep);
k = start+1:stop+1;
aLut(k) = 0:1/(length(k)-1):1;
else
aLut(1) = 0; %in case someone specifies numBins = 1, which is just silly
end
end
imgTileRow=1;
for k=1:numTiles(1)+1
if k == 1 %special case: top row
imgTileNumRows = dimTile(1)/2; %always divisible by 2 because of padding
mapTileRows = [1 1];
else
if k == numTiles(1)+1 %special case: bottom row
imgTileNumRows = dimTile(1)/2;
mapTileRows = [numTiles(1) numTiles(1)];
else %default values
imgTileNumRows = dimTile(1);
mapTileRows = [k-1, k]; %[upperRow lowerRow]
end
end
% loop over columns of the tileMappings cell array
imgTileCol=1;
for l=1:numTiles(2)+1
if l == 1 %special case: left column
imgTileNumCols = dimTile(2)/2;
mapTileCols = [1, 1];
else
if l == numTiles(2)+1 % special case: right column
imgTileNumCols = dimTile(2)/2;
mapTileCols = [numTiles(2), numTiles(2)];
else %default values
imgTileNumCols = dimTile(2);
mapTileCols = [l-1, l]; % right left
end
end
% Extract four tile mappings
ulMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(1), mapTileCols(1)};
urMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(1), mapTileCols(2)};
blMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(2), mapTileCols(1)};
brMapTile = tileMappings{mapTileRows(2), mapTileCols(2)};
% Calculate the new greylevel assignments of pixels
% within a submatrix of the image specified by imgTileIdx. This
% is done by a bilinear interpolation between four different mappings
% in order to eliminate boundary artifacts.
normFactor = imgTileNumRows*imgTileNumCols; %normalization factor
imgTileIdx = {imgTileRow:imgTileRow+imgTileNumRows-1, ...
imgTileCol:imgTileCol+imgTileNumCols-1};
imgPixVals = grayxform(I(imgTileIdx{1},imgTileIdx{2}), aLut);
% calculate the weights used for linear interpolation between the
% four mappings
rowW = repmat((0:imgTileNumRows-1)',1,imgTileNumCols);
colW = repmat(0:imgTileNumCols-1,imgTileNumRows,1);
rowRevW = repmat((imgTileNumRows:-1:1)',1,imgTileNumCols);
colRevW = repmat(imgTileNumCols:-1:1,imgTileNumRows,1);
claheI(imgTileIdx{1}, imgTileIdx{2}) = ...
(rowRevW .* (colRevW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,ulMapTile)) + ...
colW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,urMapTile)))+ ...
rowW .* (colRevW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,blMapTile)) + ...
colW .* double(grayxform(imgPixVals,brMapTile))))...
/normFactor;
imgTileCol = imgTileCol + imgTileNumCols;
end %over tile cols
imgTileRow = imgTileRow + imgTileNumRows;
end %over tile rows
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
function [I, selectedRange, fullRange, numTiles, dimTile, clipLimit,...
numBins, noPadRect, distribution, alpha, ...
int16ClassChange] = parseInputs(varargin)
narginchk(1,13);
I = varargin{1};
validateattributes(I, {'uint8', 'uint16', 'double', 'int16', 'single'}, ...
{'real', '2d', 'nonsparse', 'nonempty'}, ...
mfilename, 'I', 1);
% convert int16 to uint16
if isa(I,'int16')
I = int16touint16(I);
int16ClassChange = true;
else
int16ClassChange = false;
end
if any(size(I) < 2)
error(message('images:adapthisteq:inputImageTooSmall'))
end
%Other options
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%Set the defaults
distribution = 'uniform';
alpha = 0.4;
if isa(I, 'double') || isa(I,'single')
fullRange = [0 1];
else
fullRange(1) = I(1); %copy class of the input image
fullRange(1:2) = [-Inf Inf]; %will be clipped to min and max
fullRange = double(fullRange);
end
selectedRange = fullRange;
%Set the default to 256 bins regardless of the data type;
%the user can override this value at any time
numBins = 256;
normClipLimit = 0.01;
numTiles = [8 8];
checkAlpha = false;
validStrings = {'NumTiles','ClipLimit','NBins','Distribution',...
'Alpha','Range'};
if nargin > 1
done = false;
idx = 2;
while ~done
input = varargin{idx};
inputStr = validatestring(input, validStrings,mfilename,'PARAM',idx);
idx = idx+1; %advance index to point to the VAL portion of the input
if idx > nargin
error(message('images:adapthisteq:missingValue', inputStr))
end
switch inputStr
case 'NumTiles'
numTiles = varargin{idx};
validateattributes(numTiles, {'double'}, {'real', 'vector', ...
'integer', 'finite','positive'},...
mfilename, inputStr, idx);
if (any(size(numTiles) ~= [1,2]))
error(message('images:adapthisteq:invalidNumTilesVector', inputStr))
end
if any(numTiles < 2)
error(message('images:adapthisteq:invalidNumTilesValue', inputStr))
end
case 'ClipLimit'
normClipLimit = varargin{idx};
validateattributes(normClipLimit, {'double'}, ...
{'scalar','real','nonnegative'},...
mfilename, inputStr, idx);
if normClipLimit > 1
error(message('images:adapthisteq:invalidClipLimit', inputStr))
end
case 'NBins'
numBins = varargin{idx};
validateattributes(numBins, {'double'}, {'scalar','real','integer',...
'positive'}, mfilename, 'NBins', idx);
case 'Distribution'
validDist = {'rayleigh','exponential','uniform'};
distribution = validatestring(varargin{idx}, validDist, mfilename,...
'Distribution', idx);
case 'Alpha'
alpha = varargin{idx};
validateattributes(alpha, {'double'},{'scalar','real',...
'nonnan','positive','finite'},...
mfilename, 'Alpha',idx);
checkAlpha = true;
case 'Range'
validRangeStrings = {'original','full'};
rangeStr = validatestring(varargin{idx}, validRangeStrings,mfilename,...
'Range',idx);
if strmatch(rangeStr,'original')
selectedRange = double([min(I(:)), max(I(:))]);
end
otherwise
error(message('images:adapthisteq:inputString')) %should never get here
end
if idx >= nargin
done = true;
end
idx=idx+1;
end
end
%% Pre-process the inputs
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
dimI = size(I);
dimTile = dimI ./ numTiles;
%check if tile size is reasonable
if any(dimTile < 1)
error(message('images:adapthisteq:inputImageTooSmallToSplit', num2str( numTiles )))
end
if checkAlpha
if strcmp(distribution,'uniform')
error(message('images:adapthisteq:alphaShouldNotBeSpecified', distribution))
end
end
%check if the image needs to be padded; pad if necessary;
%padding occurs if any dimension of a single tile is an odd number
%and/or when image dimensions are not divisible by the selected
%number of tiles
rowDiv = mod(dimI(1),numTiles(1)) == 0;
colDiv = mod(dimI(2),numTiles(2)) == 0;
if rowDiv && colDiv
rowEven = mod(dimTile(1),2) == 0;
colEven = mod(dimTile(2),2) == 0;
end
noPadRect = [];
if ~(rowDiv && colDiv && rowEven && colEven)
padRow = 0;
padCol = 0;
if ~rowDiv
rowTileDim = floor(dimI(1)/numTiles(1)) + 1;
padRow = rowTileDim*numTiles(1) - dimI(1);
else
rowTileDim = dimI(1)/numTiles(1);
end
if ~colDiv
colTileDim = floor(dimI(2)/numTiles(2)) + 1;
padCol = colTileDim*numTiles(2) - dimI(2);
else
colTileDim = dimI(2)/numTiles(2);
end
%check if tile dimensions are even numbers
rowEven = mod(rowTileDim,2) == 0;
colEven = mod(colTileDim,2) == 0;
if ~rowEven
padRow = padRow+numTiles(1);
end
if ~colEven
padCol = padCol+numTiles(2);
end
padRowPre = floor(padRow/2);
padRowPost = ceil(padRow/2);
padColPre = floor(padCol/2);
padColPost = ceil(padCol/2);
I = padarray(I,[padRowPre padColPre ],'symmetric','pre');
I = padarray(I,[padRowPost padColPost],'symmetric','post');
%UL corner (Row, Col), LR corner (Row, Col)
noPadRect.ulRow = padRowPre+1;
noPadRect.ulCol = padColPre+1;
noPadRect.lrRow = padRowPre+dimI(1);
noPadRect.lrCol = padColPre+dimI(2);
end
%redefine this variable to include the padding
dimI = size(I);
%size of the single tile
dimTile = dimI ./ numTiles;
%compute actual clip limit from the normalized value entered by the user
%maximum value of normClipLimit=1 results in standard AHE, i.e. no clipping;
%the minimum value minClipLimit would uniformly distribute the image pixels
%across the entire histogram, which would result in the lowest possible
%contrast value
numPixInTile = prod(dimTile);
minClipLimit = ceil(numPixInTile/numBins);
clipLimit = minClipLimit + round(normClipLimit*(numPixInTile-minClipLimit));
%-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
参考上述代码,我分别用VB和C#实现了该算法,提供个编译好的文件给有兴趣研究该算法的朋友看看效果(不提供源代码的):
http://files.cnblogs.com/Imageshop/CLAHE.rar
截面如下:

其中AHE算法可以认为是裁剪限幅为1的CLAHE算法,CLHE是水平网格和垂直网格都为1的算法。
均衡分布方式和ALPHA的解释可参考matlab的代码.
CLAHE算法很多时候比直接的直方图均衡化算法的效果要好很多,比如下面这幅图像:

普通的直方图均衡化算法的效果为:

而CALHE的效果如下:

可以看出,在图像的上部,CALHE有效的抑制了噪音的增强。
对于彩色图像,matlab的那个函数不支持,我这里采用了两种方式处理,一种是各通道分开处理,一种是每个通道都放在一起,对于彩色的图像似乎放在一起处理的效果要比分开处理好很多。
比如界面中那个图像,如果各通道放在一起处理,效果如下:

而通道分开处理,则各通道的颜色不很匹配:

对于处理速度,这个函数由于只有一些分开+插值计算,速度很快。如果图像不能倍分成整块,一般需要扩充边缘,matlab的处理方式是上下左右四条边对称镜像扩充。这种方式很合理。
实例工程是用VB6编写的,由于VB不支持指针,在速度比C#之类的语言大概慢了50%左右。但是也还是很快的了。
相关文章推荐
- 限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法原理、实现及效果
- 限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法原理、实现及效果
- 限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法原理、实现及效果
- 限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法原理、实现及效果
- 限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法原理、实现及效果
- 限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法原理、实现及效果
- 限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法原理、实现及效果
- 自适应对比度增强(ACE)算法原理及实现
- MUSICA(多尺度图像对比度增强)算法的简要原理及VC实现
- 基于灰度世界、完美反射、动态阈值等图像自动白平衡算法的原理、实现及效果
- 【计算机视觉】【图像处理】对比度增强方法:伽马变换、全局直方图均衡化、限制对比度的自适应直方图均衡化
- 十三种基于直方图的图像全局二值化算法原理、实现、代码及效果。
- [图像去雾](一)限制对比度的自适应直方图均衡化(CLAHE)的学习体会——图像分块
- 限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法(CLAHE)实现
- 十三种基于直方图的图像全局二值化算法原理、实现、代码及效果(转)
- 十三种基于直方图的图像全局二值化算法原理、实现、代码及效果
- 十三种基于直方图的图像全局二值化算法原理、实现、代码及效果。
- 图像增强算法之 限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化算法原理
- 图像增强—限制对比度自适应直方图均衡化
- 任意半径中值滤波(扩展至百分比滤波器)O(1)时间复杂度算法的原理、实现及效果。
