C++多线程(九)
2012-11-29 19:30
393 查看
多线程之线程局部存储
一 线程局部存储 (TLS)
来自:http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms686749.aspx
同一进程中的所有线程共享相同的虚拟地址空间。不同的线程中的局部变量有不同的副本,但是static和globl变量是同一进程中的所有线程共享的。使用TLS技术可以为static和globl的变量,根据当前进程的线程数量创建一个array,每个线程可以通过array的index来访问对应的变量,这样也就保证了static和global的变量为每一个线程都创建不同的副本。
二 线程局部存储(TLS)实现使用
1)TLS 的 API 实现
通过 Win32 API 层和编译器实现“线程本地存储”。有关详细信息,请参见 Win32 API 文档中的 TlsAlloc、TlsGetValue、TlsSetValue 和 TlsFree。 (下面的代码对msdn的稍加修改)

#include <windows.h>

#include <stdio.h>


#define THREADCOUNT 10

DWORD dwTlsIndex;


static int g_x = 100; // test static var for multiple threading


VOID ErrorExit(LPSTR);


VOID CommonFunc(VOID)



{

LPVOID lpvData;


// Retrieve a data pointer for the current thread.

lpvData = TlsGetValue(dwTlsIndex);

if ((lpvData == 0) && (GetLastError() != ERROR_SUCCESS))

ErrorExit("TlsGetValue error");

int *pg_x = (int*)lpvData;


// Use the data stored for the current thread.

printf("thread %d: g_x adress=%lx,g_x copy ++ = %d\n", GetCurrentThreadId(), pg_x, *pg_x);

Sleep(1000);

}


DWORD WINAPI ThreadFunc(VOID)



{&nbs
4000
p;

LPVOID lpvData;


// Initialize the TLS index for this thread.

lpvData = (LPVOID) LocalAlloc(LPTR, 256);

//*(int*)lpvData = g_x;

int *pg_x = (int*)lpvData;

*pg_x = g_x;

if (! TlsSetValue(dwTlsIndex, lpvData))

ErrorExit("TlsSetValue error");


printf("thread %d: g_x adress=%lx,g_x copy = %d\n", GetCurrentThreadId(), pg_x, *pg_x);


InterlockedExchangeAdd(reinterpret_cast<long*>(pg_x),1);

CommonFunc();


// Release the dynamic memory before the thread returns.

lpvData = TlsGetValue(dwTlsIndex);

if (lpvData != 0)

LocalFree((HLOCAL) lpvData);


return 0;

}


int main(VOID)



{

DWORD IDThread;

HANDLE hThread[THREADCOUNT];

int i;


printf("main thread: g_x is :%d\n",g_x);


// Allocate a TLS index.

if ((dwTlsIndex = TlsAlloc()) == TLS_OUT_OF_INDEXES)

ErrorExit("TlsAlloc failed");


//test for multiple static or global var

int dwTlsIndex2 = TlsAlloc();


// Create multiple threads.

for (i = 0; i < THREADCOUNT; i++)



{

hThread[i] = CreateThread(NULL, // default security attributes

0, // use default stack size

(LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE) ThreadFunc, // thread function

NULL, // no thread function argument

0, // use default creation flags

&IDThread); // returns thread identifier


// Check the return value for success.

if (hThread[i] == NULL)

ErrorExit("CreateThread error\n");

}


for (i = 0; i < THREADCOUNT; i++)

WaitForSingleObject(hThread[i], INFINITE);

10768

TlsFree(dwTlsIndex);


printf("main thread: g_x is :%d\n",g_x);

return 0;

}


VOID ErrorExit (LPSTR lpszMessage)



{

fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", lpszMessage);

ExitProcess(0);

}
运行结果:(可以看出不同的线程中的g_x变量有不同的地址,即有不同的拷贝,主线程变量在开始和最后都不被改变。)
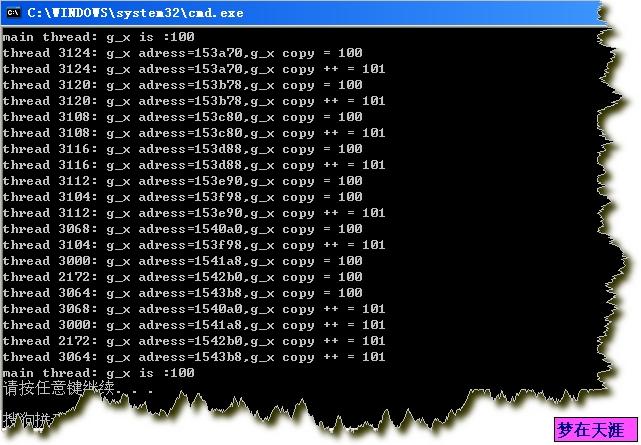
PS: (TLS的实现原理与API解释)
1:在多线程的进程中,为每一个static或是global变量创建一个void*的数组,使变量不同线程都有一个拷贝,然后拷贝的指针放入Void*的数组中。
2:TlsAlloc() 得到对应于一个static或global变量所对应的void*的数组的索引,这个用来标示不同static或global变量所对应的void*的数组。
3:LocalAlloc()用来分配变量在此线程的拷贝的指针。
4:TlsSetValue()用来把刚分配的指针加到所对应的void*的数组中,加入后一般对会对此指针赋值供此线程使用。
5:TlsGetValue()用来从对应的void*的数组中找到此线程所对应的拷贝的指针。
6: TlsFree() 释放整个void*的指针数组。
2)TLS 的编译器实现
为了支持 TLS,已将新属性 thread 添加到了 C 和 C++ 语言,并由 Visual C++ 编译器支持。使用 __declspec 关键字声明 thread 变量。例如,以下代码声明了一个整数线程局部变量,并用一个值对其进行初始化:
__declspec( thread ) int tls_i = 1;
下面的代码使用了VC提供的__declspec关键字来实现TLS,如果不使用TLS,全局变量g_x则在线程中输出的结果都是1,2,3,4.。。。但是如果使用TLS则在线程中输出的结果都是1,编译器帮我们保证了每个线程都有一个副本。 我们还可以看到主线程在开始和最后输出的g_x都是0,这也更说明了在线程有不同的副本。

#include <windows.h>

#include <stdio.h>


#define THREADCOUNT 10


DWORD dwTlsIndex;


//static int g_x = 0;


#define Thread __declspec(thread)

Thread static int g_x = 0;


VOID ErrorExit(LPSTR);


DWORD WINAPI ThreadFunc(VOID)



{

InterlockedExchangeAdd(reinterpret_cast<long*>(&g_x),1); //g_x+=1;

printf("thread id: %d, g_x++ = %d, g_x adress = %d\n",GetCurrentThreadId(),g_x,&g_x);

return 1;

}


int main(VOID)



{

DWORD IDThread;

HANDLE hThread[THREADCOUNT];

int i;


printf("main thread: g_x = %d, g_x adress = %d\n",g_x,&g_x);


// Create multiple threads.

for (i = 0; i < THREADCOUNT; i++)



{

hThread[i] = CreateThread(NULL, // default security attributes

0, // use default stack size

(LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE) ThreadFunc, // thread function

NULL, // no thread function argument

0, // use default creation flags

&IDThread); // returns thread identifier


// Check the return value for success.

if (hThread[i] == NULL)

ErrorExit("CreateThread error\n");

}


for (i = 0; i < THREADCOUNT; i++)

WaitForSingleObject(hThread[i], INFINITE);



printf("main thread: g_x = %d, g_x adress = %d\n",g_x,&g_x);

return 0;

}


VOID ErrorExit (LPSTR lpszMessage)



{

fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", lpszMessage);

ExitProcess(0);

运行结果:
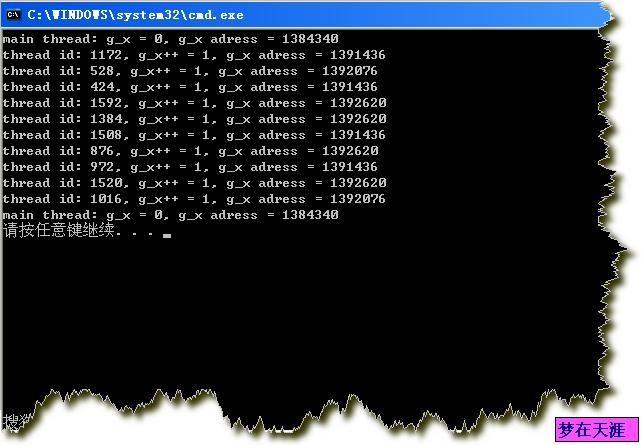
三 使用VC关键字实现TLS需要注意:
声明静态绑定线程的本地对象和变量时必须遵守下列原则:
thread 属性只能应用于数据声明和定义。它不能用于函数声明或定义。例如,以下代码将生成一个编译器错误:
只能在具有 static 作用域的数据项上指定 thread 修饰符。包括全局数据对象(包括
static 和 extern)、本地静态对象和 C++ 类的静态数据成员。不可以用
thread 属性声明自动数据对象。以下代码将生成编译器错误:
线程本地对象的声明和定义必须全都指定 thread 属性。例如,以下代码将生成错误:
thread 属性不能用作类型修饰符。例如,以下代码将生成一个编译器错误:
C++ 类不能使用 thread 属性。但是,可以使用 thread 属性将 C++ 类对象实例化。例如,以下代码将生成一个编译器错误:
因为允许使用 thread 属性的 C++ 对象的声明,因此下面两个示例在语义上是等效的:
不将线程本地对象的地址视为常数,并且涉及此类地址的任何表达式都不视为常数。在标准 C 中,这种作法的效果是禁止将线程本地变量的地址用作对象或指针的初始值设定项。例如,C 编译器将以下代码标记为错误:
但是,此限制不适用于 C++。因为 C++ 允许动态初始化所有对象,因此可以用使用线程本地变量地址的表达式初始化对象。实现此操作的方式与实现线程本地对象结构的方式相同。例如,以上显示的代码在作为 C++ 源文件编译时不会生成错误。请注意:只有在其中获取地址的线程仍然存在的情况下,线程本地变量的地址才有效。
标准 C 允许使用涉及引用自身的表达式初始化对象或变量,但只适用于非静态作用域的对象。虽然 C++ 通常允许使用涉及引用自身的表达式动态初始化对象,但是这种类型的初始化不允许用于线程本地对象。例如:
请注意:包含正在初始化的对象的
C++ 不允许此类对线程数据的动态初始化,因为将来可能要对线程本地存储功能进行增强。
如果 DLL 将任何非本地数据或对象声明为 __declspec(线程),动态加载该 DLL 时会导致保护错误。使用 LoadLibrary 加载所有 DLL 后,每当代码引用非本地
__declspec(线程)数据时,将导致系统故障。由于线程的全局变量空间是在运行时分配的,因此此空间的大小是以应用程序的需求和所有静态链接的 DLL 的需求相加为基础计算出来的。使用
LoadLibrary 时,无法扩展此空间以允许放置用 __declspec(线程)声明的线程本地变量。如果 DLL 可能是用
LoadLibrary 加载的,请在 DLL 中使用 TLS API(如 TlsAlloc)来分配 TLS。
四 DLL使用TLS :http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms686997.aspx
一 线程局部存储 (TLS)
来自:http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms686749.aspx
同一进程中的所有线程共享相同的虚拟地址空间。不同的线程中的局部变量有不同的副本,但是static和globl变量是同一进程中的所有线程共享的。使用TLS技术可以为static和globl的变量,根据当前进程的线程数量创建一个array,每个线程可以通过array的index来访问对应的变量,这样也就保证了static和global的变量为每一个线程都创建不同的副本。
二 线程局部存储(TLS)实现使用
1)TLS 的 API 实现
通过 Win32 API 层和编译器实现“线程本地存储”。有关详细信息,请参见 Win32 API 文档中的 TlsAlloc、TlsGetValue、TlsSetValue 和 TlsFree。 (下面的代码对msdn的稍加修改)

#include <windows.h>

#include <stdio.h>


#define THREADCOUNT 10

DWORD dwTlsIndex;


static int g_x = 100; // test static var for multiple threading


VOID ErrorExit(LPSTR);


VOID CommonFunc(VOID)



{

LPVOID lpvData;


// Retrieve a data pointer for the current thread.

lpvData = TlsGetValue(dwTlsIndex);

if ((lpvData == 0) && (GetLastError() != ERROR_SUCCESS))

ErrorExit("TlsGetValue error");

int *pg_x = (int*)lpvData;


// Use the data stored for the current thread.

printf("thread %d: g_x adress=%lx,g_x copy ++ = %d\n", GetCurrentThreadId(), pg_x, *pg_x);

Sleep(1000);

}


DWORD WINAPI ThreadFunc(VOID)



{&nbs
4000
p;

LPVOID lpvData;


// Initialize the TLS index for this thread.

lpvData = (LPVOID) LocalAlloc(LPTR, 256);

//*(int*)lpvData = g_x;

int *pg_x = (int*)lpvData;

*pg_x = g_x;

if (! TlsSetValue(dwTlsIndex, lpvData))

ErrorExit("TlsSetValue error");


printf("thread %d: g_x adress=%lx,g_x copy = %d\n", GetCurrentThreadId(), pg_x, *pg_x);


InterlockedExchangeAdd(reinterpret_cast<long*>(pg_x),1);

CommonFunc();


// Release the dynamic memory before the thread returns.

lpvData = TlsGetValue(dwTlsIndex);

if (lpvData != 0)

LocalFree((HLOCAL) lpvData);


return 0;

}


int main(VOID)



{

DWORD IDThread;

HANDLE hThread[THREADCOUNT];

int i;


printf("main thread: g_x is :%d\n",g_x);


// Allocate a TLS index.

if ((dwTlsIndex = TlsAlloc()) == TLS_OUT_OF_INDEXES)

ErrorExit("TlsAlloc failed");


//test for multiple static or global var

int dwTlsIndex2 = TlsAlloc();


// Create multiple threads.

for (i = 0; i < THREADCOUNT; i++)



{

hThread[i] = CreateThread(NULL, // default security attributes

0, // use default stack size

(LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE) ThreadFunc, // thread function

NULL, // no thread function argument

0, // use default creation flags

&IDThread); // returns thread identifier


// Check the return value for success.

if (hThread[i] == NULL)

ErrorExit("CreateThread error\n");

}


for (i = 0; i < THREADCOUNT; i++)

WaitForSingleObject(hThread[i], INFINITE);

10768

TlsFree(dwTlsIndex);


printf("main thread: g_x is :%d\n",g_x);

return 0;

}


VOID ErrorExit (LPSTR lpszMessage)



{

fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", lpszMessage);

ExitProcess(0);

}
运行结果:(可以看出不同的线程中的g_x变量有不同的地址,即有不同的拷贝,主线程变量在开始和最后都不被改变。)

PS: (TLS的实现原理与API解释)
1:在多线程的进程中,为每一个static或是global变量创建一个void*的数组,使变量不同线程都有一个拷贝,然后拷贝的指针放入Void*的数组中。
2:TlsAlloc() 得到对应于一个static或global变量所对应的void*的数组的索引,这个用来标示不同static或global变量所对应的void*的数组。
3:LocalAlloc()用来分配变量在此线程的拷贝的指针。
4:TlsSetValue()用来把刚分配的指针加到所对应的void*的数组中,加入后一般对会对此指针赋值供此线程使用。
5:TlsGetValue()用来从对应的void*的数组中找到此线程所对应的拷贝的指针。
6: TlsFree() 释放整个void*的指针数组。
2)TLS 的编译器实现
为了支持 TLS,已将新属性 thread 添加到了 C 和 C++ 语言,并由 Visual C++ 编译器支持。使用 __declspec 关键字声明 thread 变量。例如,以下代码声明了一个整数线程局部变量,并用一个值对其进行初始化:
__declspec( thread ) int tls_i = 1;
下面的代码使用了VC提供的__declspec关键字来实现TLS,如果不使用TLS,全局变量g_x则在线程中输出的结果都是1,2,3,4.。。。但是如果使用TLS则在线程中输出的结果都是1,编译器帮我们保证了每个线程都有一个副本。 我们还可以看到主线程在开始和最后输出的g_x都是0,这也更说明了在线程有不同的副本。

#include <windows.h>

#include <stdio.h>


#define THREADCOUNT 10


DWORD dwTlsIndex;


//static int g_x = 0;


#define Thread __declspec(thread)

Thread static int g_x = 0;


VOID ErrorExit(LPSTR);


DWORD WINAPI ThreadFunc(VOID)



{

InterlockedExchangeAdd(reinterpret_cast<long*>(&g_x),1); //g_x+=1;

printf("thread id: %d, g_x++ = %d, g_x adress = %d\n",GetCurrentThreadId(),g_x,&g_x);

return 1;

}


int main(VOID)



{

DWORD IDThread;

HANDLE hThread[THREADCOUNT];

int i;


printf("main thread: g_x = %d, g_x adress = %d\n",g_x,&g_x);


// Create multiple threads.

for (i = 0; i < THREADCOUNT; i++)



{

hThread[i] = CreateThread(NULL, // default security attributes

0, // use default stack size

(LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE) ThreadFunc, // thread function

NULL, // no thread function argument

0, // use default creation flags

&IDThread); // returns thread identifier


// Check the return value for success.

if (hThread[i] == NULL)

ErrorExit("CreateThread error\n");

}


for (i = 0; i < THREADCOUNT; i++)

WaitForSingleObject(hThread[i], INFINITE);



printf("main thread: g_x = %d, g_x adress = %d\n",g_x,&g_x);

return 0;

}


VOID ErrorExit (LPSTR lpszMessage)



{

fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", lpszMessage);

ExitProcess(0);

运行结果:

三 使用VC关键字实现TLS需要注意:
声明静态绑定线程的本地对象和变量时必须遵守下列原则:
thread 属性只能应用于数据声明和定义。它不能用于函数声明或定义。例如,以下代码将生成一个编译器错误:
#define Thread __declspec( thread ) Thread void func(); // This will generate an error.
只能在具有 static 作用域的数据项上指定 thread 修饰符。包括全局数据对象(包括
static 和 extern)、本地静态对象和 C++ 类的静态数据成员。不可以用
thread 属性声明自动数据对象。以下代码将生成编译器错误:
#define Thread __declspec( thread )
void func1()
{
Thread int tls_i; // This will generate an error.
}
int func2( Thread int tls_i ) // This will generate an error.
{
return tls_i;
}线程本地对象的声明和定义必须全都指定 thread 属性。例如,以下代码将生成错误:
#define Thread __declspec( thread ) extern int tls_i; // This will generate an error, since the int Thread tls_i; // declaration and definition differ.
thread 属性不能用作类型修饰符。例如,以下代码将生成一个编译器错误:
char __declspec( thread ) *ch; // Error
C++ 类不能使用 thread 属性。但是,可以使用 thread 属性将 C++ 类对象实例化。例如,以下代码将生成一个编译器错误:
#define Thread __declspec( thread )
class Thread C // Error: classes cannot be declared Thread.
{
// Code
};
C CObject;因为允许使用 thread 属性的 C++ 对象的声明,因此下面两个示例在语义上是等效的:
#define Thread __declspec( thread )
Thread class B
{
// Code
} BObject; // OK--BObject is declared thread local.
class B
{
// Code
};
Thread B BObject; // OK--BObject is declared thread local.不将线程本地对象的地址视为常数,并且涉及此类地址的任何表达式都不视为常数。在标准 C 中,这种作法的效果是禁止将线程本地变量的地址用作对象或指针的初始值设定项。例如,C 编译器将以下代码标记为错误:
#define Thread __declspec( thread ) Thread int tls_i; int *p = &tls_i; //This will generate an error in C.
但是,此限制不适用于 C++。因为 C++ 允许动态初始化所有对象,因此可以用使用线程本地变量地址的表达式初始化对象。实现此操作的方式与实现线程本地对象结构的方式相同。例如,以上显示的代码在作为 C++ 源文件编译时不会生成错误。请注意:只有在其中获取地址的线程仍然存在的情况下,线程本地变量的地址才有效。
标准 C 允许使用涉及引用自身的表达式初始化对象或变量,但只适用于非静态作用域的对象。虽然 C++ 通常允许使用涉及引用自身的表达式动态初始化对象,但是这种类型的初始化不允许用于线程本地对象。例如:
#define Thread __declspec( thread ) Thread int tls_i = tls_i; // Error in C and C++ int j = j; // OK in C++, error in C Thread int tls_i = sizeof( tls_i ) // Legal in C and C++
请注意:包含正在初始化的对象的
sizeof表达式不建立对自身的引用且在 C 和 C++ 中都是合法的。
C++ 不允许此类对线程数据的动态初始化,因为将来可能要对线程本地存储功能进行增强。
如果 DLL 将任何非本地数据或对象声明为 __declspec(线程),动态加载该 DLL 时会导致保护错误。使用 LoadLibrary 加载所有 DLL 后,每当代码引用非本地
__declspec(线程)数据时,将导致系统故障。由于线程的全局变量空间是在运行时分配的,因此此空间的大小是以应用程序的需求和所有静态链接的 DLL 的需求相加为基础计算出来的。使用
LoadLibrary 时,无法扩展此空间以允许放置用 __declspec(线程)声明的线程本地变量。如果 DLL 可能是用
LoadLibrary 加载的,请在 DLL 中使用 TLS API(如 TlsAlloc)来分配 TLS。
四 DLL使用TLS :http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms686997.aspx
相关文章推荐
- c++多线程时 undefined reference to 'pthread_create'问题解决
- c++多线程使用printf输出的bug
- C++多线程
- c++多线程 及mutex锁
- c++多线程8event
- C++多线程之使用Mutex和Critical_Section
- C++多线程框架-----Mutex互斥和Sem信号量
- [置顶] c++多线程(多线程处理vector)
- c++多线程(四)
- C++多线程实例
- C++多线程之使用Mutex和Critical_Section
- c++多线程编程1----具体概念理解
- C++多线程编程总结
- C++多线程编程入门之经典实例
- c++多线程编程:常见面试题
- C++多线程(四)
- C++多线程实例之临界区同步
- C++多线程-第三篇-Thread(线程)
- C++多线程编程——线程的挂起、唤醒与终止
- C++多线程实例-信号量
