android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
2012-09-29 14:33
288 查看
这周抽空研究了一下SurfaceFlinger,发现真正复杂的并不是SurfaceFlinger本身,而是android的display显示系统,网上关于这部分的介绍有不少,本不打算写的,但是发现还是记录一下研究代码的过程比较好,一是能够帮助自己理清思路,另一个原因就是以后当这块内容忘记的时候,能快速的通过这个记录捡起来。
SurfaceFlinger对于显示的管理是通过一个或多个GraphicPlane对象(目前android只实现了一个)来管理的,
@SurfaceFlinger.h
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
GraphicPlane mGraphicPlanes[1];
在这个函数中,主要为fbDev设备符指定一个fb_context_t实例,并通过函数mapFrameBuffer()对设备节点/dev/graphics/fb0进行操作,操作的目的有:
1.获得屏幕设备的信息,并将屏幕信息保存在HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM(上面代码中的module)中。
2. 向/dev/graphics/fb0请求page flip模式,page
flip模式需要至少2个屏幕大小的buffer,page flip模式在后面介绍。目前android系统中设置为2个屏幕大小的buffer。当然屏幕设备可能不支持page flip模式。
mapFrameBufferLocked()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/framebuffer.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
/*
* Request NUM_BUFFERS screens (at lest 2 for page flipping)
*/
info.yres_virtual = info.yres * NUM_BUFFERS;
uint32_t flags = PAGE_FLIP;
if (ioctl(fd, FBIOPUT_VSCREENINFO, &info) == -1) {
info.yres_virtual = info.yres;
flags &= ~PAGE_FLIP;
LOGW("FBIOPUT_VSCREENINFO failed, page flipping not supported");
}
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
sp<NativeBuffer> buffers[2];
gralloc_alloc_framebuffer_locked()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/gpu.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
const uint32_t bufferMask = m->bufferMask;
const uint32_t numBuffers = m->numBuffers;
const size_t bufferSize = m->finfo.line_length * m->info.yres;
if (numBuffers == 1) {
// If we have only one buffer, we never use page-flipping. Instead,
// we return a regular buffer which will be memcpy'ed to the main
// screen when post is called.
int newUsage = (usage & ~GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_FB) | GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_2D;
return gralloc_alloc_buffer(bufferSize, newUsage, pHandle);
}
used to draw complex three-dimensional scenes from simple primitives. OpenGL was developed by Silicon Graphics Inc. (SGI) in 1992[4] and is widely used in CAD, virtual reality, scientific visualization, information visualization, flight simulation, and video
games. OpenGL is managed by the non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group.。
android是默认支持OpenGL ES软件加速的,library为libGLES_android,源码路径为frameworks\base\opengl\libagl;如果手机设备支持硬件加速的话,那么复杂的图像处理工作将交由GPU去处理,那么效率将大大提高。但是如果系统真的存在硬件加速,它是如何选择何时用软件加速?何时用硬件加速的呢?
如何查看是否有GPU来实现硬件加速,很容易查看/system/lib/egl/egl.cfg文件内容
[java]
view plaincopyprint?
0 0 android
0 1 adreno200
软硬两种模式的OpenGL api被分别指定到了一个全局数组的对应位置。
frameworks/base/opengl/libs/EGL/egl.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
static egl_connection_t gEGLImpl[IMPL_NUM_IMPLEMENTATIONS];
gEGLImpl[IMPL_HARDWARE]中保存着硬件图形设备的OpenGL api地址,从
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
libGLESv1_CM_adreno200.so
libGLESv2_adreno200.so
libEGL_adreno200.so
上面枚举的EGL表示ELG api;GLESvq1_CM表示OpenGL ES 1.0的api;GLESv2表示OpenGL ES 2.0的api。
EGL api地址最终被存储在gEGLImpl[].egl中;
GLESvq1_CM api地址最终被存储在gEGLImpl[].hooks[GLESv1_INDEX]->gl中;
GLESv2 api地址最终被存储在gEGLImpl[].hooks[GLESv2_INDEX]->gl中;
3.2.1 EGL api
EGL is an interface between Khronos rendering APIs such as OpenGL ES or OpenVG and the underlying native platform window system. It handles graphics context management, surface/buffer binding, and rendering synchronization and enables high-performance,
accelerated, mixed-mode 2D and 3D rendering using other Khronos APIs.
上面引用了官方的定义,可以看出,EGL是系统和OPENGL ES之间的接口,它的声明在文件frameworks\base\opengl\libs\EGL\egl_entries.in。

3.2.2 GLES
GLES才是真正的OpenGL ES的api,它的声明我们可以在frameworks\base\opengl\libs\entries.in找到。目前的android系统不但将EGL提供给系统使用,同时将GLES也提供给了系统使用,这个我们可以在最开始的显示系统的结构图中可以看到,surfacefliger和framework的opengl模块均可以访问EGL和GLES接口。
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
if(info.bits_per_pixel == 32) {
/*
* Explicitly request RGBA_8888
*/
/* Note: the GL driver does not have a r=8 g=8 b=8 a=0 config, so if we do
* not use the MDP for composition (i.e. hw composition == 0), ask for
* RGBA instead of RGBX. */
if (property_get("debug.sf.hw", property, NULL) > 0 && atoi(property) == 0)
module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBX_8888;
else if(property_get("debug.composition.type", property, NULL) > 0 && (strncmp(property,
"mdp", 3) == 0))
module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBX_8888;
else
module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888;
} else {
/*
* Explicitly request 5/6/5
*/
module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565;
}
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
// EGLDisplay are global, not attached to a given thread
const unsigned int NUM_DISPLAYS = 1;
代码在eglInitialize()@frameworks/base/opengl/libs/EGL/egl.cpp
init()@DisplayHardware.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
// initialize EGL
EGLint attribs[] = {
EGL_SURFACE_TYPE, EGL_WINDOW_BIT,
EGL_NONE, 0,
EGL_NONE
};
format信息,去和openGL的config比较,得到想要的config。
selectConfigForPixelFormat()@frameworks/base/libs/ui/EGLUtils.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
EGLConfig* const configs = (EGLConfig*)malloc(sizeof(EGLConfig)*numConfigs);
if (eglChooseConfig(dpy, attrs, configs, numConfigs, &n) == EGL_FALSE) {
free(configs);
return BAD_VALUE;
}
const int fbSzA = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_ALPHA);
const int fbSzR = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_RED);
const int fbSzG = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_GREEN);
const int fbSzB = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_BLUE);
int i;
EGLConfig config = NULL;
for (i=0 ; i<n ; i++) {
EGLint r,g,b,a;
EGLConfig curr = configs[i];
eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_RED_SIZE, &r);
eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_GREEN_SIZE, &g);
eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_BLUE_SIZE, &b);
eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_ALPHA_SIZE, &a);
if (fbSzA <= a && fbSzR <= r && fbSzG <= g && fbSzB <= b) {
config = curr;
break;
}
}
2. 在同一进程中,对于不同的线程对OpenGL库的访问,可能使用的GLES api version不同,同样可以使用TLS技术来保证多线程过程中,不同线程调用各自的GLES api。
前面我们介绍过GLES api地址被存放在gEGLImpl[].hooks[VERSION]->gl中,因此为保证多线程支持,android将gEGLImpl[].hooks[VERSION]保存到了TLS中,这样就实现了不同线程各自调用各自版本的GLES api。
eglMakeCurrent()@frameworks/base/opengl/libs/EGL/egl.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
// cur_c has to be valid here (but could be terminated)
if (ctx != EGL_NO_CONTEXT) {
setGlThreadSpecific(c->cnx->hooks[c->version]);
setContext(ctx);
_c.acquire();
} else {
setGlThreadSpecific(&gHooksNoContext);
setContext(EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
}
不过没关系,在所有的DisplayHardware创建完成之后,surfaceflinger会重新bind 主Display系统的context和surface。
readyToRun()@SurfaceFlinger.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
// initialize primary screen
// (other display should be initialized in the same manner, but
// asynchronously, as they could come and go. None of this is supported
// yet).
const GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
const DisplayHardware& hw = plane.displayHardware();
const uint32_t w = hw.getWidth();
const uint32_t h = hw.getHeight();
const uint32_t f = hw.getFormat();
hw.makeCurrent();
// initialize primary screen
// (other display should be initialized in the same manner, but
// asynchronously, as they could come and go. None of this is supported
// yet).
const GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
const DisplayHardware& hw = plane.displayHardware();
const uint32_t w = hw.getWidth();
const uint32_t h = hw.getHeight();
const uint32_t f = hw.getFormat();
hw.makeCurrent();
分类:
Linux Framebuffer
一. android显示系统的建立
我们看SurfaceFlinger的定义就知道,它其实是一个Thread, 因此SurfaceFlinger的初始化工作就理所当然的放在了SurfaceFlinger线程中,详见readyToRun()@SurfaceFlinger.cppSurfaceFlinger对于显示的管理是通过一个或多个GraphicPlane对象(目前android只实现了一个)来管理的,
@SurfaceFlinger.h
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
GraphicPlane mGraphicPlanes[1];
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? int fb_device_open(hw_module_t const* module, const char* name, hw_device_t** device) { int status = -EINVAL; if (!strcmp(name, GRALLOC_HARDWARE_FB0)) { alloc_device_t* gralloc_device; status = gralloc_open(module, &gralloc_device); /* initialize our state here */ fb_context_t *dev = (fb_context_t*)malloc(sizeof(*dev)); memset(dev, 0, sizeof(*dev)); /* initialize the procs */ dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG; private_module_t* m = (private_module_t*)module; status = mapFrameBuffer(m); } int fb_device_open(hw_module_t const* module, const char* name, hw_device_t** device) { int status = -EINVAL; if (!strcmp(name, GRALLOC_HARDWARE_FB0)) { alloc_device_t* gralloc_device; status = gralloc_open(module, &gralloc_device); /* initialize our state here */ fb_context_t *dev = (fb_context_t*)malloc(sizeof(*dev)); memset(dev, 0, sizeof(*dev)); /* initialize the procs */ dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG; private_module_t* m = (private_module_t*)module; status = mapFrameBuffer(m); }
在这个函数中,主要为fbDev设备符指定一个fb_context_t实例,并通过函数mapFrameBuffer()对设备节点/dev/graphics/fb0进行操作,操作的目的有:
1.获得屏幕设备的信息,并将屏幕信息保存在HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM(上面代码中的module)中。
2. 向/dev/graphics/fb0请求page flip模式,page
flip模式需要至少2个屏幕大小的buffer,page flip模式在后面介绍。目前android系统中设置为2个屏幕大小的buffer。当然屏幕设备可能不支持page flip模式。
mapFrameBufferLocked()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/framebuffer.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
/*
* Request NUM_BUFFERS screens (at lest 2 for page flipping)
*/
info.yres_virtual = info.yres * NUM_BUFFERS;
uint32_t flags = PAGE_FLIP;
if (ioctl(fd, FBIOPUT_VSCREENINFO, &info) == -1) {
info.yres_virtual = info.yres;
flags &= ~PAGE_FLIP;
LOGW("FBIOPUT_VSCREENINFO failed, page flipping not supported");
}
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? /* * map the framebuffer */ int err; size_t fbSize = roundUpToPageSize(finfo.line_length * info.yres_virtual); module->framebuffer = new private_handle_t(dup(fd), fbSize, private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM); module->numBuffers = info.yres_virtual / info.yres; module->bufferMask = 0; void* vaddr = mmap(0, fbSize, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0); if (vaddr == MAP_FAILED) { LOGE("Error mapping the framebuffer (%s)", strerror(errno)); return -errno; } module->framebuffer->base = intptr_t(vaddr); memset(vaddr, 0, fbSize); /* * map the framebuffer */ int err; size_t fbSize = roundUpToPageSize(finfo.line_length * info.yres_virtual); module->framebuffer = new private_handle_t(dup(fd), fbSize, private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM); module->numBuffers = info.yres_virtual / info.yres; module->bufferMask = 0; void* vaddr = mmap(0, fbSize, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0); if (vaddr == MAP_FAILED) { LOGE("Error mapping the framebuffer (%s)", strerror(errno)); return -errno; } module->framebuffer->base = intptr_t(vaddr); memset(vaddr, 0, fbSize);
1.2 grDev设备符
在为framebuffer,也就是FramebufferNativeWindow申请内存之前,我们还要介绍一个概念,就是grDev设备符。它虽然也叫设备符,但是它和具体的设备没有直接关系,我们看它的类型就是知道了alloc_device_t,没错,grDev设备符就是为了FramebufferNativeWindow管理内存使用的。为FramebufferNativeWindow提供了申请/释放内存的接口。1.3 FramebufferNativeWindow内存管理
FramebufferNativeWindow维护了2个buffer,[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
sp<NativeBuffer> buffers[2];
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? // create a "fake" handles for it intptr_t vaddr = intptr_t(m->framebuffer->base); private_handle_t* hnd = new private_handle_t(dup(m->framebuffer->fd), size, private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM | private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_FRAMEBUFFER); // find a free slot for (uint32_t i=0 ; i<numBuffers ; i++) { if ((bufferMask & (1LU<<i)) == 0) { m->bufferMask |= (1LU<<i); break; } vaddr += bufferSize; } hnd->base = vaddr; hnd->offset = vaddr - intptr_t(m->framebuffer->base); *pHandle = hnd; // create a "fake" handles for it intptr_t vaddr = intptr_t(m->framebuffer->base); private_handle_t* hnd = new private_handle_t(dup(m->framebuffer->fd), size, private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_USES_PMEM | private_handle_t::PRIV_FLAGS_FRAMEBUFFER); // find a free slot for (uint32_t i=0 ; i<numBuffers ; i++) { if ((bufferMask & (1LU<<i)) == 0) { m->bufferMask |= (1LU<<i); break; } vaddr += bufferSize; } hnd->base = vaddr; hnd->offset = vaddr - intptr_t(m->framebuffer->base); *pHandle = hnd;
1.3.2 屏幕设备不支持page flip模式
在mapFrameBufferLocked()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/framebuffer.cpp中可以得知,如果屏幕设备不支持page flip模式,那么numBuffer值将为1而不是2,那么映射过来的屏幕缓存区将只有一个屏幕大小,不够支持page flip模式,那么此时将不使用这一个屏幕大小的屏幕缓存区,而改为去dev/pmem设备去申请。gralloc_alloc_framebuffer_locked()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/gpu.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
const uint32_t bufferMask = m->bufferMask;
const uint32_t numBuffers = m->numBuffers;
const size_t bufferSize = m->finfo.line_length * m->info.yres;
if (numBuffers == 1) {
// If we have only one buffer, we never use page-flipping. Instead,
// we return a regular buffer which will be memcpy'ed to the main
// screen when post is called.
int newUsage = (usage & ~GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_FB) | GRALLOC_USAGE_HW_2D;
return gralloc_alloc_buffer(bufferSize, newUsage, pHandle);
}
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? if (hw_get_module(OVERLAY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module) == 0) { overlay_control_open(module, &mOverlayEngine); } if (hw_get_module(OVERLAY_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module) == 0) { overlay_control_open(module, &mOverlayEngine); }
3. 选择OpenGL ES library(也即软/硬件加速)
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library)[3] is a standard specification defining a cross-language, cross-platform API for writing applications that produce 2D and 3D computer graphics. The interface consists of over 250 different function calls which can beused to draw complex three-dimensional scenes from simple primitives. OpenGL was developed by Silicon Graphics Inc. (SGI) in 1992[4] and is widely used in CAD, virtual reality, scientific visualization, information visualization, flight simulation, and video
games. OpenGL is managed by the non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group.。
android是默认支持OpenGL ES软件加速的,library为libGLES_android,源码路径为frameworks\base\opengl\libagl;如果手机设备支持硬件加速的话,那么复杂的图像处理工作将交由GPU去处理,那么效率将大大提高。但是如果系统真的存在硬件加速,它是如何选择何时用软件加速?何时用硬件加速的呢?
如何查看是否有GPU来实现硬件加速,很容易查看/system/lib/egl/egl.cfg文件内容
[java]
view plaincopyprint?
0 0 android
0 1 adreno200
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? libGLESv1_CM_adreno200.so libGLESv2_adreno200.so libEGL_adreno200.so libGLESv1_CM_adreno200.so libGLESv2_adreno200.so libEGL_adreno200.so那么假如我们的系统中软硬件加速都支持了,那么我们从代码来看能不能让用户自由的选择加速类型,我们带着问题来研究一下代码。
3.1 OpenGL初始化
在调用不管是软件加速的还是硬件加速的OpenGL api之前,我们都需要把软硬两种模式的各自的OpenGL api提取出来,抽象出一个interface来供系统使用,这个过程我称之为OpenGL初始化过程。软硬两种模式的OpenGL api被分别指定到了一个全局数组的对应位置。
frameworks/base/opengl/libs/EGL/egl.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
static egl_connection_t gEGLImpl[IMPL_NUM_IMPLEMENTATIONS];
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? enum { IMPL_HARDWARE = 0, IMPL_SOFTWARE, IMPL_NUM_IMPLEMENTATIONS }; enum { IMPL_HARDWARE = 0, IMPL_SOFTWARE, IMPL_NUM_IMPLEMENTATIONS };
gEGLImpl[IMPL_HARDWARE]中保存着硬件图形设备的OpenGL api地址,从
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
libGLESv1_CM_adreno200.so
libGLESv2_adreno200.so
libEGL_adreno200.so
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? enum { EGL = 0x01, GLESv1_CM = 0x02, GLESv2 = 0x04 }; enum { EGL = 0x01, GLESv1_CM = 0x02, GLESv2 = 0x04 };load_driver()@frameworks\base\opengl\libs\EGL\Loader.cpp
上面枚举的EGL表示ELG api;GLESvq1_CM表示OpenGL ES 1.0的api;GLESv2表示OpenGL ES 2.0的api。
EGL api地址最终被存储在gEGLImpl[].egl中;
GLESvq1_CM api地址最终被存储在gEGLImpl[].hooks[GLESv1_INDEX]->gl中;
GLESv2 api地址最终被存储在gEGLImpl[].hooks[GLESv2_INDEX]->gl中;
3.2.1 EGL api
EGL is an interface between Khronos rendering APIs such as OpenGL ES or OpenVG and the underlying native platform window system. It handles graphics context management, surface/buffer binding, and rendering synchronization and enables high-performance,
accelerated, mixed-mode 2D and 3D rendering using other Khronos APIs.
上面引用了官方的定义,可以看出,EGL是系统和OPENGL ES之间的接口,它的声明在文件frameworks\base\opengl\libs\EGL\egl_entries.in。

3.2.2 GLES
GLES才是真正的OpenGL ES的api,它的声明我们可以在frameworks\base\opengl\libs\entries.in找到。目前的android系统不但将EGL提供给系统使用,同时将GLES也提供给了系统使用,这个我们可以在最开始的显示系统的结构图中可以看到,surfacefliger和framework的opengl模块均可以访问EGL和GLES接口。
3.3 OpenGL config
每个OpenGL库都根据不同的像素格式(pixel format)提供了一系统的config,android根据framebuffer中设置的像素格式来选择合适的config,android根据中各config中的属性信息来创建main surface和openGL上下文。3.3.1 系统默认pixel format
当前的代码分析是基于gingerbread的,在mapFrameBufferLocked()@hardware/msm7k/libgralloc-qsd8k/framebuffer.cpp中我们可以找到framebuffer的pixel format的类型[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
if(info.bits_per_pixel == 32) {
/*
* Explicitly request RGBA_8888
*/
/* Note: the GL driver does not have a r=8 g=8 b=8 a=0 config, so if we do
* not use the MDP for composition (i.e. hw composition == 0), ask for
* RGBA instead of RGBX. */
if (property_get("debug.sf.hw", property, NULL) > 0 && atoi(property) == 0)
module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBX_8888;
else if(property_get("debug.composition.type", property, NULL) > 0 && (strncmp(property,
"mdp", 3) == 0))
module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBX_8888;
else
module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888;
} else {
/*
* Explicitly request 5/6/5
*/
module->fbFormat = HAL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565;
}
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? static egl_display_t gDisplay[NUM_DISPLAYS]; static egl_display_t gDisplay[NUM_DISPLAYS];
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
// EGLDisplay are global, not attached to a given thread
const unsigned int NUM_DISPLAYS = 1;
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? <strong> </strong> // sort our configurations so we can do binary-searches qsort( dp->configs, dp->numTotalConfigs, sizeof(egl_config_t), cmp_configs);<strong> </strong> <strong> </strong> // sort our configurations so we can do binary-searches qsort( dp->configs, dp->numTotalConfigs, sizeof(egl_config_t), cmp_configs);<strong> </strong>最终,上述代码会将gDisplay[0].config中的配置按照先硬件的,后软件的规则做一个总体的排序。
代码在eglInitialize()@frameworks/base/opengl/libs/EGL/egl.cpp
3.3.3 config选择
上文说到,android会根据framebuffer的pixel format信息来获取对应的config,这个过程只选择一个合适的config,选到为止。3.3.3.1 满足属性要求
并不是所有的config都可以被选择,首先这个config的属性需要满足init()@DisplayHardware.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
// initialize EGL
EGLint attribs[] = {
EGL_SURFACE_TYPE, EGL_WINDOW_BIT,
EGL_NONE, 0,
EGL_NONE
};
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? static GGLFormat const gPixelFormatInfos[] = { // Alpha Red Green Blue { 0, 0, {{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }}, 0 }, // PIXEL_FORMAT_NONE { 4, 32, {{32,24, 8, 0, 16, 8, 24,16 }}, GGL_RGBA }, // PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888 static GGLFormat const gPixelFormatInfos[] = { // Alpha Red Green Blue { 0, 0, {{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }}, 0 }, // PIXEL_FORMAT_NONE { 4, 32, {{32,24, 8, 0, 16, 8, 24,16 }}, GGL_RGBA }, // PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888android会根据pixelflinger的pixel
format信息,去和openGL的config比较,得到想要的config。
selectConfigForPixelFormat()@frameworks/base/libs/ui/EGLUtils.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
EGLConfig* const configs = (EGLConfig*)malloc(sizeof(EGLConfig)*numConfigs);
if (eglChooseConfig(dpy, attrs, configs, numConfigs, &n) == EGL_FALSE) {
free(configs);
return BAD_VALUE;
}
const int fbSzA = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_ALPHA);
const int fbSzR = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_RED);
const int fbSzG = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_GREEN);
const int fbSzB = fbFormatInfo.getSize(PixelFormatInfo::INDEX_BLUE);
int i;
EGLConfig config = NULL;
for (i=0 ; i<n ; i++) {
EGLint r,g,b,a;
EGLConfig curr = configs[i];
eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_RED_SIZE, &r);
eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_GREEN_SIZE, &g);
eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_BLUE_SIZE, &b);
eglGetConfigAttrib(dpy, curr, EGL_ALPHA_SIZE, &a);
if (fbSzA <= a && fbSzR <= r && fbSzG <= g && fbSzB <= b) {
config = curr;
break;
}
}
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? ogles_context_t* current = (ogles_context_t*)getGlThreadSpecific(); if (gl) { egl_context_t* c = egl_context_t::context(gl); if (c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT) { if (current != gl) { // it is an error to set a context current, if it's already // current to another thread return -1; } } else { if (current) { // mark the current context as not current, and flush glFlush(); egl_context_t::context(current)->flags &= ~egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT; } } if (!(c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT)) { // The context is not current, make it current! setGlThreadSpecific(gl); c->flags |= egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT; } ogles_context_t* current = (ogles_context_t*)getGlThreadSpecific(); if (gl) { egl_context_t* c = egl_context_t::context(gl); if (c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT) { if (current != gl) { // it is an error to set a context current, if it's already // current to another thread return -1; } } else { if (current) { // mark the current context as not current, and flush glFlush(); egl_context_t::context(current)->flags &= ~egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT; } } if (!(c->flags & egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT)) { // The context is not current, make it current! setGlThreadSpecific(gl); c->flags |= egl_context_t::IS_CURRENT; }
2. 在同一进程中,对于不同的线程对OpenGL库的访问,可能使用的GLES api version不同,同样可以使用TLS技术来保证多线程过程中,不同线程调用各自的GLES api。
前面我们介绍过GLES api地址被存放在gEGLImpl[].hooks[VERSION]->gl中,因此为保证多线程支持,android将gEGLImpl[].hooks[VERSION]保存到了TLS中,这样就实现了不同线程各自调用各自版本的GLES api。
eglMakeCurrent()@frameworks/base/opengl/libs/EGL/egl.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
// cur_c has to be valid here (but could be terminated)
if (ctx != EGL_NO_CONTEXT) {
setGlThreadSpecific(c->cnx->hooks[c->version]);
setContext(ctx);
_c.acquire();
} else {
setGlThreadSpecific(&gHooksNoContext);
setContext(EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
}
[cpp] view plaincopyprint? // Unbind the context from this thread eglMakeCurrent(display, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT); // Unbind the context from this thread eglMakeCurrent(display, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT);这么做的目的应该是支持多display系统中的特殊处理,目的是当系统有多个display系统的话,那么surfaceflinger就会去定义多个DisplayHardware对象,那么为了保证下一个DisplayHardware对象的创建不受影响,在当前的DisplayHardware创建完成后,将context从当前的进程中unbind掉。
不过没关系,在所有的DisplayHardware创建完成之后,surfaceflinger会重新bind 主Display系统的context和surface。
readyToRun()@SurfaceFlinger.cpp
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
// initialize primary screen
// (other display should be initialized in the same manner, but
// asynchronously, as they could come and go. None of this is supported
// yet).
const GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
const DisplayHardware& hw = plane.displayHardware();
const uint32_t w = hw.getWidth();
const uint32_t h = hw.getHeight();
const uint32_t f = hw.getFormat();
hw.makeCurrent();
// initialize primary screen
// (other display should be initialized in the same manner, but
// asynchronously, as they could come and go. None of this is supported
// yet).
const GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy));
const DisplayHardware& hw = plane.displayHardware();
const uint32_t w = hw.getWidth();
const uint32_t h = hw.getHeight();
const uint32_t f = hw.getFormat();
hw.makeCurrent();
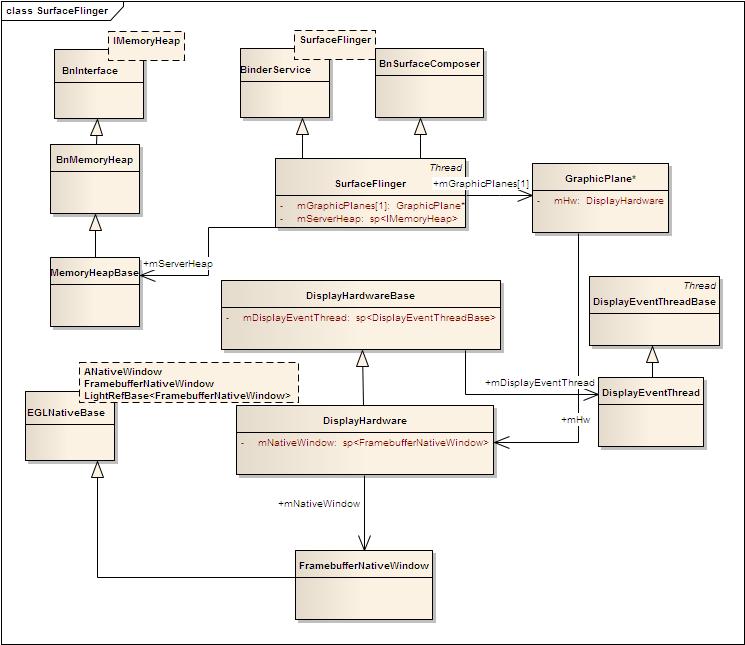
下图为这个图形系统的类图结构。

分类:
Linux Framebuffer
相关文章推荐
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统, Surface机制, SurfaceFlinger loop
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统 .
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统, Surface机制, SurfaceFlinger loop
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统.
- (转)android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
- android surfaceflinger研究----显示系统
