通过webservice提交xml数据以及soap协议的使用
2012-08-15 22:30
274 查看
上次已经给大家分享了简单的webservice的使用,提交给服务器的数据只是简单类型的数据,这次呢换成了xml,并通过一个小例子来讲解soap协议的使用。废话就不多说了先来说下xml数据的上传
1.代码的结构没有多大的变化,只需修改一下请求头就可以了,代码如下
//封装数据,数据以byte方式传输
byte[] b=xml.getBytes();
//需要请求的连接
URL url=new URL("http://192.168.87.1:8080/LoginService/LoginWebService");
//打开连接
HttpURLConnection conn=(HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
//设置请求方式和消息头以及超时时间
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
//设置是否允许对外输出数据
conn.setDoOutput(true);
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "text/xml;charset=UTF-8");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", String.valueOf(b.length));
//取得输出流
OutputStream outPut=conn.getOutputStream();
outPut.write(b);
outPut.flush();
outPut.close();
//判断请求是否成功
if(conn.getResponseCode()==200){
// Log.i();
return "OK";
}else{
return "Err";
}
下面给大家写了点服务器端获取byte数据的代码,顺便在控制台打印xml,这个方法建议写成工具类,我这里就不这样做了
下面是运行效果图

后面的工作就是解析xml类似的工作了
2.HTTP协议的webservice差不多了下面就是使用soap协议请求webservice了,这里就来弄个手机号码归属地的webservice吧
先打开这个链接http://webservice.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/MobileCodeWS.asmx?op=getMobileCodeInfo
看一下下面的soap协议这里就是用soap1.2就可以
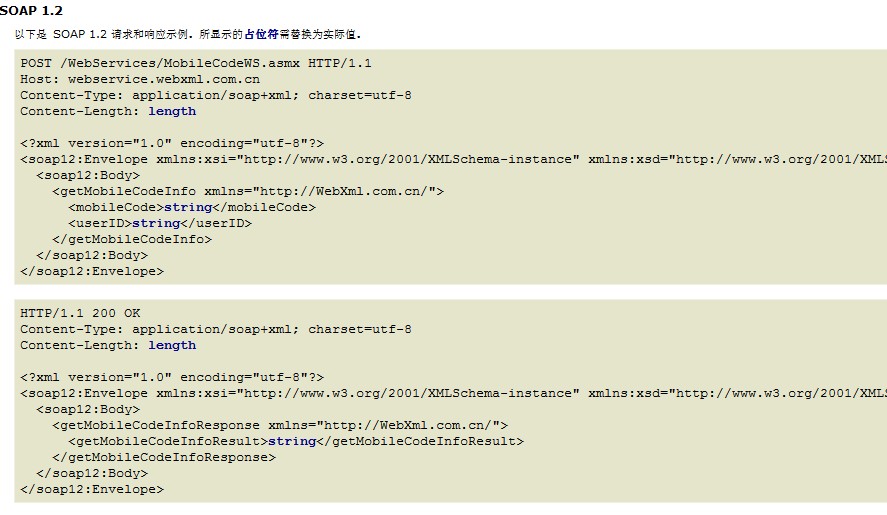
3.下面就根据协议的说明来换掉请求头,为了开发方便我们需要把用于请求的xml写在一个文件里,手机号码用个占位符代替
4.下面的工作就是替换占位符,请求该webservice
开始请求webservice并得到返回的xml字符串
下面来看下断点运行后的结果

我们能够看到webservice已经调用成功了,我们拿到了返回结果
下面我把测试类贴出来
1.代码的结构没有多大的变化,只需修改一下请求头就可以了,代码如下
//封装数据,数据以byte方式传输
byte[] b=xml.getBytes();
//需要请求的连接
URL url=new URL("http://192.168.87.1:8080/LoginService/LoginWebService");
//打开连接
HttpURLConnection conn=(HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
//设置请求方式和消息头以及超时时间
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
//设置是否允许对外输出数据
conn.setDoOutput(true);
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "text/xml;charset=UTF-8");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", String.valueOf(b.length));
//取得输出流
OutputStream outPut=conn.getOutputStream();
outPut.write(b);
outPut.flush();
outPut.close();
//判断请求是否成功
if(conn.getResponseCode()==200){
// Log.i();
return "OK";
}else{
return "Err";
}
下面给大家写了点服务器端获取byte数据的代码,顺便在控制台打印xml,这个方法建议写成工具类,我这里就不这样做了
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
InputStream in=request.getInputStream();
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
int temp=0;
while((temp=in.read())!=-1){
b[len]=(byte)temp;
len++;
}
System.out.println(new String(b,"UTF-8"));下面是运行效果图

后面的工作就是解析xml类似的工作了
2.HTTP协议的webservice差不多了下面就是使用soap协议请求webservice了,这里就来弄个手机号码归属地的webservice吧
先打开这个链接http://webservice.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/MobileCodeWS.asmx?op=getMobileCodeInfo
看一下下面的soap协议这里就是用soap1.2就可以

3.下面就根据协议的说明来换掉请求头,为了开发方便我们需要把用于请求的xml写在一个文件里,手机号码用个占位符代替
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <soap12:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soap12="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope"> <soap12:Body> <getMobileCodeInfo xmlns="http://WebXml.com.cn/"> <mobileCode>$number</mobileCode> <userID></userID> </getMobileCodeInfo> </soap12:Body> </soap12:Envelope>
4.下面的工作就是替换占位符,请求该webservice
public String readSoapFile(InputStream input,String number) throws Exception{
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
int temp=0;
while((temp=input.read())!=-1){
b[len]=(byte)temp;
len++;
}
String soapxml=new String(b);
//替换xml文件的占位符
Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("number", number);
return replace(soapxml, map);
}
public String replace(String param,Map<String,String> params) throws Exception{
//拼凑占位符使用正则表达式替换之
String result=param;
if(params!=null&&!params.isEmpty()){
//拼凑占位符
for(Map.Entry<String,String> entry:params.entrySet()){
String name="\\$"+entry.getKey();
Pattern p=Pattern.compile(name);
Matcher m=p.matcher(result);
if(m.find()){
result=m.replaceAll(entry.getValue());
}
}
}
return result;
}开始请求webservice并得到返回的xml字符串
public String soapService(InputStream input,String number) throws Exception{
String str="";
String soap=readSoapFile(input,number);
//封装数据,数据以byte方式传输
byte[] b=soap.getBytes();
//需要请求的连接
URL url=new URL("http://webservice.webxml.com.cn/WebServices/MobileCodeWS.asmx");
//打开连接
HttpURLConnection conn=(HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
//设置请求方式和消息头以及超时时间
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
//设置是否允许对外输出数据
conn.setDoOutput(true);
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/soap+xml; charset=utf-8");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", String.valueOf(b.length));
//取得输出流
OutputStream outPut=conn.getOutputStream();
outPut.write(b);
outPut.flush();
outPut.close();
//判断请求是否成功
if(conn.getResponseCode()==200){
InputStream in=conn.getInputStream();
byte[] b1=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
int temp=0;
while((temp=in.read())!=-1){
b1[len]=(byte)temp;
len++;
}
str=new String(b1,"UTF-8");
}
return str;
}下面来看下断点运行后的结果

我们能够看到webservice已经调用成功了,我们拿到了返回结果
下面我把测试类贴出来
UseHttpPost use=new UseHttpPost();
try {
InputStream in=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("soap.xml");
use.soapService(in, "13764928990");
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getMessage());
}
相关文章推荐
- 经过webservice提交xml数据以及soap协议的使用
- 使用.NET向webService传double、int、DateTime类型数据, 在发送包的XML中没有提交数据到 服务器
- WCF:读取 XML 数据时,超出最大字符串内容长度配额 (8192)。通过更改在创建 XML 读取器时所使用的 XmlDictionaryReaderQuotas 对象的 MaxStringContentLength 属性,可增加此配额。
- Android通过Get方式提交数据以及乱码处理
- Android学习笔记---29_构建soap协议内容,发送xml数据和调用webservice,手机号码归属地查询器
- Java 通过HttpURLConnection Post方式提交xml,并从服务端返回数据
- WebService XML 提交数据
- 在SSIS 中使用 Web Service 以及 解析XML 数据
- 使用webservice 并通过sax动态解析xml
- Android之通过向WebService服务器发送XML数据获取相关服务
- 提交数据使用json代替xml
- Android中webservice的简单使用以及使用handle在UI线程和子线程中传递数据
- 通过webservice使用jquery访问数据(包含显示,验证,修改)
- flask 如何使用接口以及通过json传递数据
- Query ajax()使用serialize()提交form数据 以及如何防止中文乱码
- Java 通过HttpURLConnection Post方式提交xml,并从服务端返回数据
- Android之通过向WebService服务器发送XML数据获取相关服务
- android中通过GET方法接收数据并通过xml解析数据,POST方法向服务器提交数据
- string.xml中占位符的使用以及动态改变字符串数据
- 在使用validate时遇到的问题,不通过Submit提交数据
