HDU 1506 Largest Rectangle in a Histogram 最大矩形的面积
2012-08-10 16:12
447 查看
Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 5445 Accepted Submission(s): 1558
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
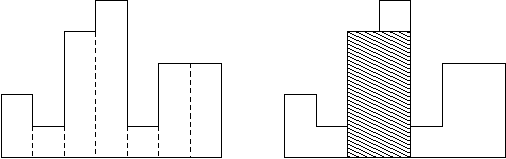
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
[align=left]Input[/align]
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1 <= n <= 100000. Then follow n integers h1, ..., hn, where 0 <= hi <= 1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3 4 1000 1000 1000 1000 0
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
8 4000
思路:
对于每一块木板,Area=height[i]*(j-k+1) 设其中任一块x, j<=x<=k, height[x]>=height[i]; 找j,k成为关键。
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 100005
#define MX(a,b) (a>b?a:b)
int l
,r
;
__int64 h
;
__int64 max;
int n;
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n),n)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%I64d",&h[i]);
l[i]=r[i]=i;
}
h[0]=h[n+1]=-1;//高度可能为0,防止死循环;
//利用动态规划,如果它左边高度大于等于它本身,那么它左边的左边界一定满足这个性质,再从这个边界的左边迭代下去;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
while(h[l[i]-1]>=h[i])
l[i]=l[l[i]-1];
}
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--)
{
while(h[r[i]+1]>=h[i])
r[i]=r[r[i]+1];
}
max=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
max=MX(max, (r[i]-l[i]+1)*h[i] );
printf("%I64d\n",max);
}
return 0;
}
链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1506
相关文章推荐
- 51nod 1102 面积最大的矩形【单调栈、预处理】
- HDU 2830 Matrix Swapping II (最大列可移动子矩形面积)
- 寻找直方图中面积最大的矩形
- 寻找直方图中面积最大的矩形
- Arithmetic problem | 找二维矩阵权值为1的最大矩形面积
- 计算直方图中面积最大的矩形
- Poj 2559 最大矩形面积 v单调栈 分类: Brush Mode 2014-11-13 20:48 81人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
- 最大矩形面积
- 寻找直方图中面积最大的矩形
- poj 1964 DP 求最大子矩形面积
- 面积最大的矩形
- 有一个直方图,用一个整数数组表示,其中每列的宽度为1,求所给直方图包含的最大矩形面积。比如,对于直方图[2,7,9,4],它所包含的最大矩形的面积为14(即[7,9]包涵的7x2的矩形)。给定一个直方图A及它的总宽度n,请返回最大矩形面积。保证直方图宽度小于等于500。保证结果在int范围内。
- 9715 相邻最大矩形面积 单调栈
- HDU 1056 Largest Rectangle in a Histogram(dp)(求最大的矩形面积)
- 找出最大矩形面积(枚举)
- Poj 2559 最大矩形面积 v单调栈
- CSDN编程挑战之寻找直方图中面积最大的矩形
- POJ 2559最大矩形面积
- 寻找直方图中面积最大的矩形
- 寻找直方图中面积最大的矩形
