百度实习生招聘的一道大数据处理题目(下)
2012-07-01 16:11
411 查看
图4为排序阶段CPU的使用率,可以看到只有一个核达到了100%的利用率。下面为一个多线程(线程的数量为核的数量)的排序版本,每个线程只对1G数据中的一部分进行快速排序,排序完成后再由另外一个线程进行归并,将结果写入文件。
多线程排序代码如下:
/*multi_thread_sort.c*/
再编译运行下,以下为测试结果:
下图5为多线程排序时CPU的利用率,可以看到CPU的四个核都已经达到100%的利用率,即:硬件没有白投资:D。当然排序的时间效果也很好,几乎达到了之前的4倍的加速比。另外可以看到文件的加载速度和回写速度也有所提高,这点也是让我比较疑惑的。下面再次运行单线程排序版本。
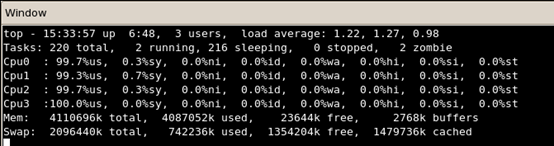
图5 排序阶段CPU的利用率
可以看到加载速度和回写速度有了显著的提升,虽然排序时间还是没有多大变化。
再次运行多线程排序版本试试:
加载速度又延长了,排序速度几乎不变,回写速度也提高了不少。我想这主要是因为文件系统本身提供了缓冲的作用,即上次用过的文件可以放在交换区,便于迅速载入内存吧。这样第二次使用的时候,由于这些文件还存放在交换区中,所以以很高的速度传入内存中。回写的原理应该也一样。对于1G的文件回写到内存,只用了23s,大致的回写速度为50MB/s
假设文件系统一直起作用,并能达到第二次实验的效果,即分块排序22s,归并排序并回写文件系统23s,那么计算和归并回写是能够重合的。对于200G的文件A来说,分块排序的处理时间大致为:200*22s =~1.2h,就扩大为1小时15分钟吧。这样对文件B来说也差不多为1小时15分钟,一共需要2个半小时,接下来开始归并比较了,假设文件的缓冲系统能够启作用,即速度能达到50MB/s,这样,对于2个200G的文件都需要在内存中过一遍,大致时间应该为400*10^3/50 = 8000s,大致为2小时15分钟,所以加上前面的2个半小时,对于2个200G的文件寻找相同值共需要的时间为 5个小时左右,至少比300万年好点。
PS: =~这个符号表示约等于。
本文出自 “相信并热爱着” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://hipercomer.blog.51cto.com/4415661/915110
多线程排序代码如下:
/*multi_thread_sort.c*/
/*
* Author: Chaos Lee
* Date: 2012-06-30
* Description: load, merge , store data with single core, but sorting data with all the cores provided by the SMP
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<sys/sysinfo.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<stdint.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include "../error.h"
#include "timer.h"
uint64_t * buffer = NULL;
pthread_mutex_t counter_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t merge_start = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
int cores_number;
int counter;
int uint64_compare(const void * ptr1,const void * ptr2)
{
return *((uint64_t *)ptr1) > *((uint64_t *)ptr2) ? 1 : *((uint64_t *)ptr1) < *((uint64_t *)ptr2) ? -1 : 0;
}
typedef struct segment_tag
{
uint64_t start;
uint64_t end;
}segment_t,*segment_p;
void barrier()
{
int status;
status = pthread_mutex_lock(&counter_mutex);
if(0 != status)
err_abort("locking error.",status);
counter++;
if(cores_number == counter)
{
pthread_cond_signal(&merge_start);
}
status = pthread_mutex_unlock(&counter_mutex);
if(0 != status)
err_abort("unlocking error.",status);
}
void * sort_thread_routin(void * args)
{
DPRINTF(("%s","sorting thread start...\n"));
segment_p seg = (segment_p) args;
assert(buffer != NULL);
DPRINTF(("%s","begin to sort...\n"));
qsort(buffer+seg->start,seg->end-seg->start,sizeof(uint64_t),uint64_compare);
DPRINTF(("%s","Entering barrier...\n"));
barrier();
pthread_exit((void *)0);
}
void * merge_thread_routin(void * args)
{
int status,i,finish_count,elapsed_seconds;
FILE * fp_result;
uint64_t tmp;
restart_timer();
DPRINTF(("%s","merging thread start...\n"));
fp_result = fopen("multi-result.dat","wb");
while(cores_number != counter)
{
status = pthread_cond_wait(&merge_start,&counter_mutex);
if(0 != status)
err_abort("waiting condition error.",status);
}
elapsed_seconds = get_elapsed_time();
fprintf(stdout,"sorting cost %d seconds.\n",elapsed_seconds);
status = pthread_mutex_unlock(&counter_mutex);
if(0 != status)
err_abort("unlocking error.",status);
DPRINTF(("begin to merge...\n"));
finish_count = 0;
segment_p segs = (segment_p) args;
restart_timer();
while(finish_count<cores_number)
{
int i,first=0,j;
for(i=0;i<cores_number;i++)
{
if( 0 == first)
{
if(segs[i].start<segs[i].end)
{
tmp = buffer[segs[i].start];
j = i;
first = 1;
}
}
else
{
if(segs[i].start<segs[i].end && buffer[segs[i].start]<tmp)
{
tmp = buffer[segs[i].start];
j = i;
}
}
}
segs[j].start++;
if(segs[j].start >= segs[j].end)
{
finish_count++;
}
fwrite(&tmp,sizeof(uint64_t),1,fp_result);
}
elapsed_seconds = get_elapsed_time();
fprintf(stdout,"merging cost %d seconds.\n",elapsed_seconds);
DPRINTF(("merging is over\n"));
fclose(fp_result);
pthread_exit((void *)0);
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int elapsed_seconds,status,i;
segment_p segments;
pthread_t * sort_threads;
pthread_t * merge_thread;
uint64_t size,length,seg_len;
FILE * fp;
struct stat data_stat;
cores_number = get_nprocs();
status = stat("data.dat",&data_stat);
if(0 != status)
error_abort("stat file error.\n");
size = data_stat.st_size;
length = size / sizeof(uint64_t);
seg_len = length / cores_number;
buffer = (uint64_t *) malloc(size);
if(NULL == buffer)
{
fprintf(stderr,"mallocing error.\n");
exit(1);
}
fp = fopen("data.dat","rb");
if(NULL == fp)
{
fprintf(stderr,"file open error.\n");
exit(1);
}
start_timer();
fread(buffer,size,1,fp);
elapsed_seconds = get_elapsed_time();
fprintf(stdout,"loading cost %d seconds\n",elapsed_seconds);
segments = (segment_p)malloc(sizeof(segment_t)*cores_number);
if(NULL == segments)
{
fprintf(stderr,"at %s:%d : %s",__FILE__,__LINE__,"malloc error.\n");
exit(1);
}
for(i=0;i<cores_number;i++)
{
segments[i].start = i * seg_len;
if(i != cores_number-1)
segments[i].end = (i + 1 ) * seg_len;
else
segments[i].end = length;
}
sort_threads = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * cores_number);
if(NULL == sort_threads)
{
fprintf(stderr,"at %s:%d :%s",__FILE__,__LINE__,"malloc failuer.\n");
exit(1);
}
merge_thread = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t));
if(NULL == merge_thread)
{
fprintf(stderr,"at %s:%d :%s",__FILE__,__LINE__,"malloc failuer.\n");
exit(1);
}
for(i=0;i<cores_number;i++)
{
status = pthread_create(&sort_threads[i],NULL,sort_thread_routin,(void *)&segments[i]);
if(0 != status)
err_abort("creating threads faulire.\n",status);
}
status = pthread_create(merge_thread,NULL,merge_thread_routin,(void *)segments);
if(0 != status)
err_abort("creating thread faulier.\n",status);
for(i=0;i<cores_number;i++)
{
status = pthread_join(sort_threads[i],NULL);
if(0 != status)
err_abort("joining threads error.\n",status);
}
status = pthread_join(*merge_thread,NULL);
if(0 != status)
err_abort("joining thread error.\n",status);
free(buffer);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}再编译运行下,以下为测试结果:
[lichao@sg01 thread_power]$ gcc multi_thread_sort.c -o multi_thread_sort timer.o -lpthread [lichao@sg01 thread_power]$ ./multi_thread_sort loading cost 14 seconds sorting cost 22 seconds. merging cost 44 seconds.
下图5为多线程排序时CPU的利用率,可以看到CPU的四个核都已经达到100%的利用率,即:硬件没有白投资:D。当然排序的时间效果也很好,几乎达到了之前的4倍的加速比。另外可以看到文件的加载速度和回写速度也有所提高,这点也是让我比较疑惑的。下面再次运行单线程排序版本。

图5 排序阶段CPU的利用率
[lichao@sg01 thread_power]$ ./single_thread_sort loading cost 17 seconds sorting cost 81 seconds writing results cost 12 seconds
可以看到加载速度和回写速度有了显著的提升,虽然排序时间还是没有多大变化。
再次运行多线程排序版本试试:
[lichao@sg01 thread_power]$ ./multi_thread_sort loading cost 31 seconds sorting cost 22 seconds. merging cost 23 seconds.
加载速度又延长了,排序速度几乎不变,回写速度也提高了不少。我想这主要是因为文件系统本身提供了缓冲的作用,即上次用过的文件可以放在交换区,便于迅速载入内存吧。这样第二次使用的时候,由于这些文件还存放在交换区中,所以以很高的速度传入内存中。回写的原理应该也一样。对于1G的文件回写到内存,只用了23s,大致的回写速度为50MB/s
假设文件系统一直起作用,并能达到第二次实验的效果,即分块排序22s,归并排序并回写文件系统23s,那么计算和归并回写是能够重合的。对于200G的文件A来说,分块排序的处理时间大致为:200*22s =~1.2h,就扩大为1小时15分钟吧。这样对文件B来说也差不多为1小时15分钟,一共需要2个半小时,接下来开始归并比较了,假设文件的缓冲系统能够启作用,即速度能达到50MB/s,这样,对于2个200G的文件都需要在内存中过一遍,大致时间应该为400*10^3/50 = 8000s,大致为2小时15分钟,所以加上前面的2个半小时,对于2个200G的文件寻找相同值共需要的时间为 5个小时左右,至少比300万年好点。
PS: =~这个符号表示约等于。
本文出自 “相信并热爱着” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://hipercomer.blog.51cto.com/4415661/915110
相关文章推荐
- 百度实习生招聘的一道大数据处理题目(上)
- 百度实习生招聘的一道大数据处理题目(上)
- 百度实习生招聘的一道大数据处理题目(上)
- 百度实习生招聘的一道大数据处理题目(下)
- 2011百度数据挖掘研发工程师实习生笔试面试题
- 腾讯2014实习生招聘一道附加题 DP和分治两种解法
- C语言 数据结构题目一道 在线等答案~快~试写一符合上述要求的LocateNode运算的算法。
- 2017百度实习生招聘算法题
- 网易2017实习生招聘笔试题编程题(双核处理)
- 百度---2011年校园招聘笔试题 C++类题目
- 微软实习生招聘笔试题目
- ACM题目中输入数据的处理(C++版)
- 2012年百度实习生招聘——java开发
- hdu4318 Power transmission 最短路 当数据很大的时候的解决办法 一道题目的解题全过程记录 小水
- 网易2009年校园招聘--一道关于<list>的STL题目
- [原创]今天看到一RPG处理数据的题目,不知各位将如何解答和解释这几条常见的指令?
- 第十二周 项目二-OJ平台题目中多种输入形式的处理--输入多组数据,知道文件尾(EOF)--分离正整数中的各位数
- 百度2015春季实习生招聘附加题
- ACM题目中输入数据的处理(C++版)
- 如何在百度站内搜索前对数据或都其它内容进行处理?
