Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
2012-05-21 20:44
369 查看
最近的一个模块正好用到字体的相关内容,整理出来。
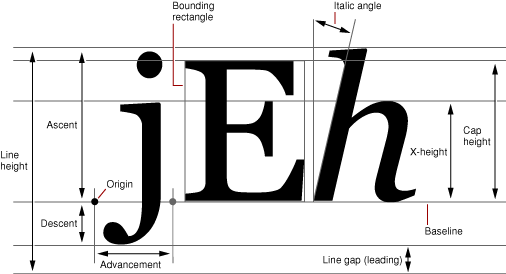
(一) 字体的几个参数 ,以Android API文档定义为准,见下图

要点如下:
1. 基准点是baseline
2. Ascent是baseline之上至字符最高处的距离
3. Descent是baseline之下至字符最低处的距离
4. Leading文档说的很含糊,其实是上一行字符的descent到下一行的ascent之间的距离
5. Top指的是指的是最高字符到baseline的值,即ascent的最大值
6. 同上,bottom指的是最下字符到baseline的值,即descent的最大值
Note:网上有很多错误的图,如果有疑问,就参看文档,区分对错。
为了帮助理解,我特此搜索了不同的示意图。对照示意图,会很容易理解FontMetrics的参数。
pic-1
pic-2

pic-3

pic-4

pic-5

pic-6

(二) 测试
1,测试的代码直接使用网上的代码,因为重复着众多,无所给出原始出处,故不注出。
我增加了Bitmap作为输出显示,完整代码如下:
log显示如下:

Note1:注意到各个数值都是整数,这是建立在baseY=100的情况下,去掉baseY,重新运行代码,log如下:

Note2: 参照线为baseline,即baseline=0的情况下,其他各线的数值。leading = 0,即行间距=0
2,以上是根据paint设置,获取相关的FontMetrics属性,并且只绘制了一行字符串,我们猜想,如果是多行,是否可以获得行间距leanding,代码如下:
log如下:

Note:显然,即使是多行的情况下,仍不能获得leading。
3,如果text是单行,获得各个属性将会怎样,代码如下:
log如下图所示:

Note:与多行获得的属性都相同。
结论:
A:虽然paint和textView所设置的textSize均为55,且为相同的字符串,但是两个获得的FontMetrics属性值并不相同。但是,我们发现,做除法之后,均为1.5倍关系。做出猜测,即Paint下,为mdpi对应的size,而TextView的size已经关联到了显示屏幕本身的320dip。所以获得属性值均为整1.5倍数
B:各种情况下,均未获得leading值。
本文出自 “小新专栏” 博客,转载请与作者联系!
(一) 字体的几个参数 ,以Android API文档定义为准,见下图

要点如下:
1. 基准点是baseline
2. Ascent是baseline之上至字符最高处的距离
3. Descent是baseline之下至字符最低处的距离
4. Leading文档说的很含糊,其实是上一行字符的descent到下一行的ascent之间的距离
5. Top指的是指的是最高字符到baseline的值,即ascent的最大值
6. 同上,bottom指的是最下字符到baseline的值,即descent的最大值
Note:网上有很多错误的图,如果有疑问,就参看文档,区分对错。
为了帮助理解,我特此搜索了不同的示意图。对照示意图,会很容易理解FontMetrics的参数。
pic-1

pic-2

pic-3

pic-4

pic-5

pic-6

(二) 测试
1,测试的代码直接使用网上的代码,因为重复着众多,无所给出原始出处,故不注出。
我增加了Bitmap作为输出显示,完整代码如下:
public class FontMetricsDemoActivity extends Activity {
private Canvas canvas;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Paint textPaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
textPaint.setTextSize( 55);
textPaint.setColor( Color.WHITE);
// FontMetrics对象
FontMetrics fontMetrics = textPaint.getFontMetrics();
String text = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstu";
// 计算每一个坐标
float baseX = 0;
float baseY = 100;
float topY = baseY + fontMetrics.top;
float ascentY = baseY + fontMetrics.ascent;
float descentY = baseY + fontMetrics.descent;
float bottomY = baseY + fontMetrics.bottom;
float leading = baseY + fontMetrics.leading;
Log.d("fontMetrics", "baseX is:" + 0);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "baseY is:" + 100);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "topY is:" + topY);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "ascentY is:" + ascentY);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "descentY is:" + descentY);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "bottomY is:" + bottomY);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "leading is:" + leading);
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.fontmetrics);
Bitmap mutableBitmap = bitmap.copy(Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888, true);
canvas = new Canvas(mutableBitmap);
// 绘制文本
canvas.drawText(text, baseX, baseY, textPaint);
// BaseLine描画
Paint baseLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
baseLinePaint.setColor( Color.RED);
canvas.drawLine(0, baseY, canvas.getWidth(), baseY, baseLinePaint);
// Base描画
canvas.drawCircle( baseX, baseY, 5, baseLinePaint);
// TopLine描画
Paint topLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
topLinePaint.setColor( Color.LTGRAY);
canvas.drawLine(0, topY, canvas.getWidth(), topY, topLinePaint);
// AscentLine描画
Paint ascentLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
ascentLinePaint.setColor( Color.GREEN);
canvas.drawLine(0, ascentY, canvas.getWidth(), ascentY, ascentLinePaint);
// DescentLine描画
Paint descentLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
descentLinePaint.setColor( Color.YELLOW);
canvas.drawLine(0, descentY, canvas.getWidth(), descentY, descentLinePaint);
// ButtomLine描画
Paint bottomLinePaint = new Paint( Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
bottomLinePaint.setColor( Color.MAGENTA);
canvas.drawLine(0, bottomY, canvas.getWidth(), bottomY, bottomLinePaint);
ImageView imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imageView1);
imageView.setImageBitmap(mutableBitmap);
}
}log显示如下:

Note1:注意到各个数值都是整数,这是建立在baseY=100的情况下,去掉baseY,重新运行代码,log如下:

Note2: 参照线为baseline,即baseline=0的情况下,其他各线的数值。leading = 0,即行间距=0
2,以上是根据paint设置,获取相关的FontMetrics属性,并且只绘制了一行字符串,我们猜想,如果是多行,是否可以获得行间距leanding,代码如下:
//test_multiply_lines
TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
String textMultiLines = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuabcdefghijklmnopqrstuabcdefghijklmnopqrstuabcdefghijklmnopqrstuabcdefghijklmnopqrstu";
textView.setTextSize(55);
textView.setText(textMultiLines);
FontMetrics fontMetrics2 = textView.getPaint().getFontMetrics();
// 计算每一个坐标
float topY = fontMetrics2.top;
float ascentY = fontMetrics2.ascent;
float descentY = fontMetrics2.descent;
float bottomY = fontMetrics2.bottom;
float leading = fontMetrics2.leading;
Log.d("fontMetrics", "topY is:" + topY);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "ascentY is:" + ascentY);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "descentY is:" + descentY);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "bottomY is:" + bottomY);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "leading is:" + leading);log如下:

Note:显然,即使是多行的情况下,仍不能获得leading。
3,如果text是单行,获得各个属性将会怎样,代码如下:
String text = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstu";
TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView1);
textView.setTextSize(55);
textView.setText(text);
FontMetrics fontMetrics = textView.getPaint().getFontMetrics();
// 计算每一个坐标
float baseX = 0;
float baseY = 100;
float topY = baseY + fontMetrics.top;
float ascentY = baseY + fontMetrics.ascent;
float descentY = baseY + fontMetrics.descent;
float bottomY = baseY + fontMetrics.bottom;
float leading = fontMetrics.leading;
Log.d("fontMetrics", "topY is:" + fontMetrics.top);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "ascentY is:" + fontMetrics.ascent);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "descentY is:" + fontMetrics.descent);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "bottomY is:" + fontMetrics.bottom);
Log.d("fontMetrics", "leading is:" + fontMetrics.leading);log如下图所示:

Note:与多行获得的属性都相同。
结论:
A:虽然paint和textView所设置的textSize均为55,且为相同的字符串,但是两个获得的FontMetrics属性值并不相同。但是,我们发现,做除法之后,均为1.5倍关系。做出猜测,即Paint下,为mdpi对应的size,而TextView的size已经关联到了显示屏幕本身的320dip。所以获得属性值均为整1.5倍数
B:各种情况下,均未获得leading值。
本文出自 “小新专栏” 博客,转载请与作者联系!
相关文章推荐
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串进阶之三:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字符串:字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android踩坑日记:Android字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
- Android 字体属性及测量 确定字体大小
- Android字符串进阶之二:字符及字符串的测量和处理
- 字体属性及测量(FontMetrics)
