vc++上的MFC的对象序列化和反序列化
2012-05-01 10:27
429 查看
注意点:
1. 必须类型序列化声明
DECLARE_SERIAL( Person )
2. 必须写出实现宏
IMPLEMENT_SERIAL(Person, CObject, VERSIONABLE_SCHEMA | 2)
3. 重写CObject中的Serialize函数
void Person::Serialize( CArchive& ar )
{
CObject::Serialize(ar);
//关键代码
if(ar.IsStoring()) {
//序列化
ar << this->age << this->sex << this->name;
} else {
//反序列化
ar >> this->age >> this->sex >> this->name;
}
}
序列化后的数据
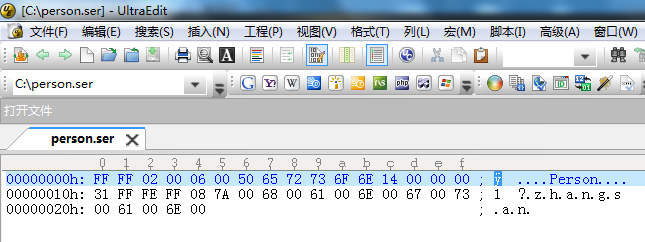
1. 必须类型序列化声明
DECLARE_SERIAL( Person )
2. 必须写出实现宏
IMPLEMENT_SERIAL(Person, CObject, VERSIONABLE_SCHEMA | 2)
3. 重写CObject中的Serialize函数
void Person::Serialize( CArchive& ar )
{
CObject::Serialize(ar);
//关键代码
if(ar.IsStoring()) {
//序列化
ar << this->age << this->sex << this->name;
} else {
//反序列化
ar >> this->age >> this->sex >> this->name;
}
}
序列化后的数据

//Person.h
#pragma once
#include <afx.h>
#include <string>
#include <atlstr.h>
using namespace std;
class Person: public CObject
{
private:
//注意MFC 不支持 标准std:string对象序列化, boost库支持std:string
CString name;
int age;
char sex;
public:
DECLARE_SERIAL( Person )
Person(void);
Person(CString name, int age, char sex);
virtual ~Person(void);
virtual void Serialize(CArchive& ar);
void setName(CString pName);
CString getName();
void setAge(int age);
int getAge();
void setSex(char sex);
char getSex();
};
//Person.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "Person.h"
#include <afx.h>
#include <string>
//必须写出实现宏
IMPLEMENT_SERIAL(Person, CObject, VERSIONABLE_SCHEMA | 2)
Person::Person(void)
{
}
Person::Person( CString name, int age, char sex )
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
this->sex = sex;
}
Person::~Person(void)
{
}
void Person::setName( CString name)
{
this->name = name;
}
CString Person::getName()
{
return this->name;
}
void Person::setAge( int age )
{
this->age = age;
}
int Person::getAge()
{
return this->age;
}
void Person::setSex( char sex )
{
this->sex = sex;
}
char Person::getSex()
{
return this->sex;
}
void Person::Serialize( CArchive& ar )
{
CObject::Serialize(ar);
//关键代码
if(ar.IsStoring()) {
//序列化
ar << this->age << this->sex << this->name;
} else {
//反序列化
ar >> this->age >> this->sex >> this->name;
}
}
// main.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <tchar.h>
#include <afx.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Person person;
person.setAge(20);
person.setName("zhangsan");
person.setSex('1');
CFile myFile(_T("c:/person.ser"), CFile::modeCreate | CFile::modeReadWrite);
// Create a storing archive.
CArchive arStore(&myFile, CArchive::store);
// Write the object to the archive
arStore.WriteObject(&person);
arStore.Flush();
// Close the storing archive
arStore.Close();
// Create a loading archive.
myFile.SeekToBegin();
CArchive arLoad(&myFile, CArchive::load);
// Verify the object is in the archive.
Person* p = (Person*) arLoad.ReadObject(person.GetRuntimeClass());
arLoad.Close();
//wcout << "姓名:" << name.GetBuffer(name.GetLength()) << endl;
CString name = p->getName();
wchar_t* pch = name.GetBuffer(0);
wcout << "姓名:" << pch << endl;
name.ReleaseBuffer(); //注意内在释放
cout << "性别:" << p->getSex() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << p->getAge() << endl;
delete p;
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- vc++上的MFC的对象序列化和反序列化
- vc++上的MFC的对象序列化和反序列化
- vc的序列化和MFC各对象的关系
- JavaScript对象也玩序列化和反序列化
- Java基础学习总结——Java对象的序列化和反序列化
- Java对对象的序列化和反序列化
- 将对象序列化和反序列化
- java IO之对象的序列化和反序列化
- XmlSerializer 对象的Xml序列化和反序列化
- 对象的序列化和反序列化
- Java对象的序列化和反序列化
- 类的序列化和反序列化、对象的归档个解档
- 对象的序列化和反序列化
- Java对象的序列化和反序列化
- .NET对象的XML序列化和反序列化
- 在内存中序列化,反序列化对象实体 来完成对象实体的深拷贝
- xml序列化及反序列化.net对象
- Io流——将对象序列化和反序列化
- C# DataSet对象序列化并压缩和反序列化及解压缩
