分析源码,探究AWT事件处理机制
2012-02-21 23:36
555 查看
Java中的事件处理机制,实际是一种委托模型。比如按钮,当我们发出点击按钮的动作之后,真正响应事件的业务逻辑并非按钮本身,而是由按钮委托的相应监听器来完成的。
在探究之前,必须先了解事件的三个重要概念:
1)事件(event)
比如,点击按钮,这一动作就会产生一个事件,这个事件包含一些信息,如在什么时候点击,事件源的一些信息(比如按钮上的标签)等等,事件类就是对这些信息的一个封装,比如ActionEvent类;
这些类的继承关系如下:
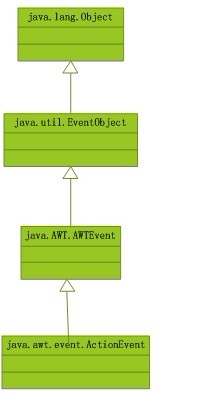
注意:只要是事件,都是类,而不是接口,因为它是对事件信息的一个封装;
(2) 事件源(event source)
就是发生事件的组件,比如说按钮Button就是一个事件源,他可以发生ActionEvent这样的事件。这些事件源类型的父类就是Component。
(3) 事件监听器(event listener)
这是一些相应事件,并完成相应逻辑功能的对象。
比如点击按钮,产生了一个ActionEvent对象,但需要完成相应的业务逻辑。必须使用到ActionListener监听器。但要注意ActionListener并不是类,而是接口,不同的业务逻辑要封装在完成ActionListener接口的不同类中。
这些监听器接口都继承了接口java.util EventListener 。
注意:事件监听器是接口,因为对于特定的事件,需要特定的实现;
Listener是有一个方法:actionPerformed();
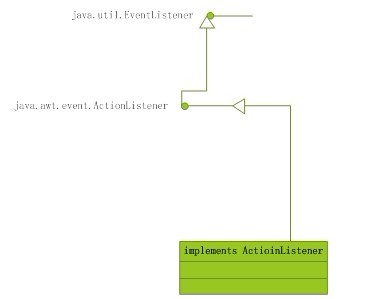
总结:awt事件机制的过程是:
1)。 由事件源(Button)产生一个与动作(按下按钮并释放)相适应的ActionEvent事件。
(2) 事件源会将这个ActionEvent事件发送给监听器,并执行监听器的actionPerformed(e)方法来完成事件响应。
但是事件源并不知道由哪一个监听器来完成,所以重点是探究如何为事件源添加监听器
源码解释最权威:(只选取类中能说明为题的方法)
首先事件源Button
在button类中维护的是一个个监听器Listener
*/
public classButton extends Component
implementsAccessible {
{
transientActionListener actionListener;;
//AWTEvent类既是本地实现的事件(比如单击按钮)
//该方法判断是否有事件发生,并把事件作为参数传入
boolean eventEnabled(AWTEvent e) {
if (e.id == ActionEvent.ACTION_PERFORMED) {
if ((eventMask & AWTEvent.ACTION_EVENT_MASK) != 0 ||
actionListener != null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
return super.eventEnabled(e);
}
//通过该中间方法处理事件
protected void processEvent(AWTEvent e) {
if (e instanceof ActionEvent) {
processActionEvent((ActionEvent)e);
return;
}
super.processEvent(e);
}
//此方法才是真正执行监听器中的方法的方法;
protected void processActionEvent(ActionEvente) {
ActionListener listener = actionListener;
if (listener != null) {
listener.actionPerformed(e);
}
}
//通过此方法添加监听器,但真正添加的算法在AWTEventMulticaster中实现
public synchronized void addActionListener(ActionListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
actionListener = AWTEventMulticaster.add(actionListener, l);
public class AWTEventMulticasterimplements
ComponentListener, ContainerListener,FocusListener, KeyListener,
MouseListener, MouseMotionListener,WindowListener, WindowFocusListener,
WindowStateListener, ActionListener,ItemListener, AdjustmentListener,
TextListener, InputMethodListener,HierarchyListener,
HierarchyBoundsListener, MouseWheelListener{
protected finalEventListener a, b;
protected AWTEventMulticaster(EventListenera, EventListener b) {
this.a = a; this.b = b;
}
//返回EventListener类型
protected static EventListeneraddInternal(EventListener a, EventListener b) {
if (a == null) return b;
if (b == null) return a;
return newAWTEventMulticaster(a, b);
}
public static ActionListener add(ActionListener a, ActionListener b) {
return (ActionListener)addInternal(a,b);
}
以上就是AWT事件机制的实现机制(从一个小的角度观察);
在探究之前,必须先了解事件的三个重要概念:
1)事件(event)
比如,点击按钮,这一动作就会产生一个事件,这个事件包含一些信息,如在什么时候点击,事件源的一些信息(比如按钮上的标签)等等,事件类就是对这些信息的一个封装,比如ActionEvent类;
这些类的继承关系如下:

注意:只要是事件,都是类,而不是接口,因为它是对事件信息的一个封装;
(2) 事件源(event source)
就是发生事件的组件,比如说按钮Button就是一个事件源,他可以发生ActionEvent这样的事件。这些事件源类型的父类就是Component。
(3) 事件监听器(event listener)
这是一些相应事件,并完成相应逻辑功能的对象。
比如点击按钮,产生了一个ActionEvent对象,但需要完成相应的业务逻辑。必须使用到ActionListener监听器。但要注意ActionListener并不是类,而是接口,不同的业务逻辑要封装在完成ActionListener接口的不同类中。
这些监听器接口都继承了接口java.util EventListener 。
注意:事件监听器是接口,因为对于特定的事件,需要特定的实现;
Listener是有一个方法:actionPerformed();

总结:awt事件机制的过程是:
1)。 由事件源(Button)产生一个与动作(按下按钮并释放)相适应的ActionEvent事件。
(2) 事件源会将这个ActionEvent事件发送给监听器,并执行监听器的actionPerformed(e)方法来完成事件响应。
但是事件源并不知道由哪一个监听器来完成,所以重点是探究如何为事件源添加监听器
源码解释最权威:(只选取类中能说明为题的方法)
首先事件源Button
在button类中维护的是一个个监听器Listener
*/
public classButton extends Component
implementsAccessible {
{
transientActionListener actionListener;;
//AWTEvent类既是本地实现的事件(比如单击按钮)
//该方法判断是否有事件发生,并把事件作为参数传入
boolean eventEnabled(AWTEvent e) {
if (e.id == ActionEvent.ACTION_PERFORMED) {
if ((eventMask & AWTEvent.ACTION_EVENT_MASK) != 0 ||
actionListener != null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
return super.eventEnabled(e);
}
//通过该中间方法处理事件
protected void processEvent(AWTEvent e) {
if (e instanceof ActionEvent) {
processActionEvent((ActionEvent)e);
return;
}
super.processEvent(e);
}
//此方法才是真正执行监听器中的方法的方法;
protected void processActionEvent(ActionEvente) {
ActionListener listener = actionListener;
if (listener != null) {
listener.actionPerformed(e);
}
}
//通过此方法添加监听器,但真正添加的算法在AWTEventMulticaster中实现
public synchronized void addActionListener(ActionListener l) {
if (l == null) {
return;
}
actionListener = AWTEventMulticaster.add(actionListener, l);
public class AWTEventMulticasterimplements
ComponentListener, ContainerListener,FocusListener, KeyListener,
MouseListener, MouseMotionListener,WindowListener, WindowFocusListener,
WindowStateListener, ActionListener,ItemListener, AdjustmentListener,
TextListener, InputMethodListener,HierarchyListener,
HierarchyBoundsListener, MouseWheelListener{
protected finalEventListener a, b;
protected AWTEventMulticaster(EventListenera, EventListener b) {
this.a = a; this.b = b;
}
//返回EventListener类型
protected static EventListeneraddInternal(EventListener a, EventListener b) {
if (a == null) return b;
if (b == null) return a;
return newAWTEventMulticaster(a, b);
}
public static ActionListener add(ActionListener a, ActionListener b) {
return (ActionListener)addInternal(a,b);
}
以上就是AWT事件机制的实现机制(从一个小的角度观察);
相关文章推荐
- 从源码角度分析android事件分发处理机制
- Android事件处理机制轻量级源码分析
- 从源码角度分析android事件分发处理机制
- view的事件的处理机制-源码分析
- Android触摸事件分发处理机制详解与源码分析一(View篇)
- 源码分析Android触摸事件处理机制
- 【Cocos2d-x 3.x】 事件处理机制源码分析
- libevent源码分析(7)--2.1.8--信号事件处理机制分析
- android的消息处理机制(图+源码分析)——Looper,Handler,Message
- Android源码分析-点击事件派发机制
- ExtJs源码分析与学习—ExtJs事件机制(三)
- jQuery 1.9.1源码分析系列(十)事件系统之主动触发事件和模拟冒泡处理
- Android源码分析-点击事件派发机制
- Android消息处理机制源码分析(一):整体过程
- 从源码的角度分析Android消息处理机制
- Android触摸屏事件派发机制详解与源码分析一(View篇)
- View的事件分发机制(源码分析)
- libevent高性能网络库源码分析——事件处理框架(四)
- Android触摸屏事件派发机制详解与源码分析二(ViewGroup篇)
- Android异步消息处理机制详解及源码分析 Handler
