Struts 2 + Spring + Hibernate 集成
2011-12-09 11:16
597 查看
Download it – Struts2-Spring-Hibernate-Integration-Example.zip
In this tutorial, it shows the integration between “Struts2 + Spring + Hibernate“. Make sure you check the following tutorials before continue.
Struts 2 + Hibernate integration example
Struts 2 + Spring integration example
Struts 1.x + Spring + Hibernate integration example
See the summary of integration steps :
Get all the dependency libraries (a lot).
Register Spring’s ContextLoaderListener to integrate Struts 2 and Spring.
Use Spring’s LocalSessionFactoryBean to integrate Spring and Hibernate.
Done, all connected.
See the relationship :
This will be a very long tutorial with little explanation, make sure you check the above 3 articles for details explanation.
It will going to create a customer page, with add customer and list customer function. Front end is using Struts 2 to display, Spring as the dependency injection engine, and Hibernate to
doing the database operation. Let start…
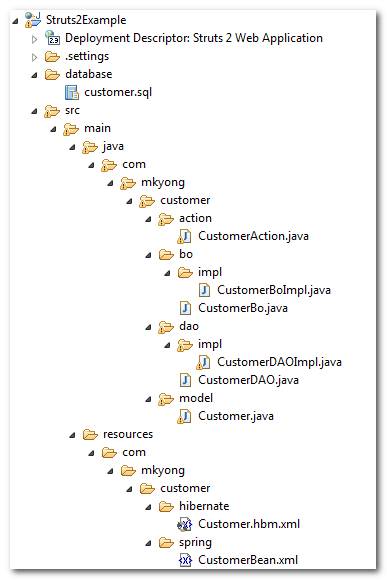
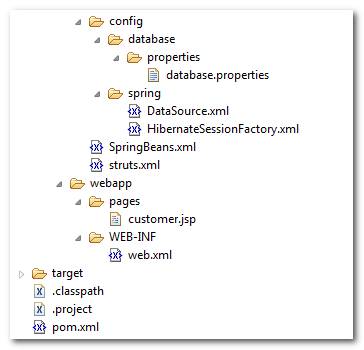
Project folder structure.
Customer’s table script.
This tutorials request many dependency libraries.
Struts 2…
MySQL…
Spring…
Hibernate…
Only the model and mapping files are required, because Spring will handle the Hibernate configuration.
Customer.java – Create a class for customer table.
Customer.hbm.xml – Hibernate mapping file for customer.
Implements the Bo and DAO design pattern. All the Bo and DAO will be DI by Spring in the Spring bean configuration file. In the DAO, make it extends Spring’s HibernateDaoSupport to integrate Spring and Hibernate integration.
CustomerBo.java
CustomerBoImpl.java
CustomerDAO.java
CustomerDAOImpl.java
CustomerAction.java – The Struts2 action is no longer need to extends the ActionSupport, Spring will handle it.
Almost all the configuration is done here, at all, Spring is specialized in integration work

.
CustomerBean.xml – Declare the Spring’s beans : Action, BO and DAO.
database.properties – Declare the database details.
DataSource.xml – Create a datasource bean.
HibernateSessionFactory.xml – Create a sessionFactory bean to integrate Spring and Hibernate.
SpringBeans.xml – Create a core Spring’s bean configuration file, act as the central bean management.
JSP page to display the element with Struts 2 tags.
customer.jsp
Link it all ~
To integrate Struts 2 and Spring, just register the ContextLoaderListener listener class, define a “contextConfigLocation” parameter to ask Spring container to parse the “SpringBeans.xml”
instead of the default “applicationContext.xml“.
web.xml
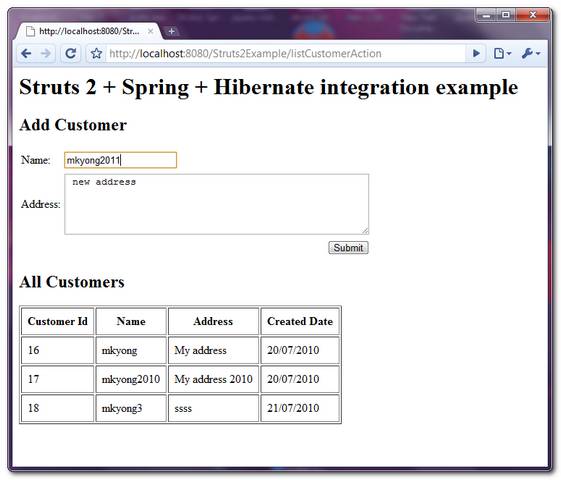
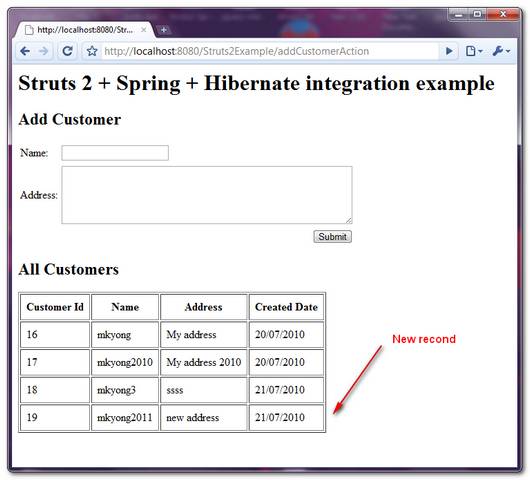
Test it : http://localhost:8080/Struts2Example/listCustomerAction.action
In this tutorial, it shows the integration between “Struts2 + Spring + Hibernate“. Make sure you check the following tutorials before continue.
Struts 2 + Hibernate integration example
Struts 2 + Spring integration example
Struts 1.x + Spring + Hibernate integration example
See the summary of integration steps :
Get all the dependency libraries (a lot).
Register Spring’s ContextLoaderListener to integrate Struts 2 and Spring.
Use Spring’s LocalSessionFactoryBean to integrate Spring and Hibernate.
Done, all connected.
See the relationship :
Struts 2 <-- (ContextLoaderListener) --> Spring <-- (LocalSessionFactoryBean) --> Hibernate
This will be a very long tutorial with little explanation, make sure you check the above 3 articles for details explanation.
Tutorials Start…
It will going to create a customer page, with add customer and list customer function. Front end is using Struts 2 to display, Spring as the dependency injection engine, and Hibernate todoing the database operation. Let start…
1. Project structure
Project folder structure.

2. MySQL table script
Customer’s table script.DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `mkyong`.`customer`; CREATE TABLE `mkyong`.`customer` ( `CUSTOMER_ID` BIGINT(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `NAME` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL, `ADDRESS` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, `CREATED_DATE` datetime NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`CUSTOMER_ID`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=17 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
3.Dependency libraries
This tutorials request many dependency libraries.Struts 2…
<!-- Struts 2 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId> <artifactId>struts2-core</artifactId> <version>2.1.8</version> </dependency> <!-- Struts 2 + Spring plugins --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId> <artifactId>struts2-spring-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.1.8</version> </dependency>
MySQL…
<!-- MySQL database driver --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.9</version> </dependency>
Spring…
<!-- Spring framework --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring</artifactId> <version>2.5.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>2.5.6</version> </dependency>
Hibernate…
<!-- Hibernate core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate</artifactId> <version>3.2.7.ga</version> </dependency> <!-- Hibernate core library dependency start --> <dependency> <groupId>dom4j</groupId> <artifactId>dom4j</artifactId> <version>1.6.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-logging</groupId> <artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId> <version>1.1.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-collections</groupId> <artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId> <version>3.2.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>cglib</groupId> <artifactId>cglib</artifactId> <version>2.2</version> </dependency> <!-- Hibernate core library dependency end --> <!-- Hibernate query library dependency start --> <dependency> <groupId>antlr</groupId> <artifactId>antlr</artifactId> <version>2.7.7</version> </dependency> <!-- Hibernate query library dependency end -->
4. Hibernate…
Only the model and mapping files are required, because Spring will handle the Hibernate configuration.Customer.java – Create a class for customer table.
package com.mkyong.customer.model;
import java.util.Date;
public class Customer implements java.io.Serializable {
private Long customerId;
private String name;
private String address;
private Date createdDate;
//getter and setter methods
}Customer.hbm.xml – Hibernate mapping file for customer.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- Generated 20 Julai 2010 11:40:18 AM by Hibernate Tools 3.2.5.Beta --> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.mkyong.customer.model.Customer" table="customer" catalog="mkyong"> <id name="customerId" type="java.lang.Long"> <column name="CUSTOMER_ID" /> <generator class="identity" /> </id> <property name="name" type="string"> <column name="NAME" length="45" not-null="true" /> </property> <property name="address" type="string"> <column name="ADDRESS" not-null="true" /> </property> <property name="createdDate" type="timestamp"> <column name="CREATED_DATE" length="19" not-null="true" /> </property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
5. Struts 2…
Implements the Bo and DAO design pattern. All the Bo and DAO will be DI by Spring in the Spring bean configuration file. In the DAO, make it extends Spring’s HibernateDaoSupport to integrate Spring and Hibernate integration.CustomerBo.java
package com.mkyong.customer.bo;
import java.util.List;
import com.mkyong.customer.model.Customer;
public interface CustomerBo{
void addCustomer(Customer customer);
List<Customer> listCustomer();
}CustomerBoImpl.java
package com.mkyong.customer.bo.impl;
import java.util.List;
import com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo;
import com.mkyong.customer.dao.CustomerDAO;
import com.mkyong.customer.model.Customer;
public class CustomerBoImpl implements CustomerBo{
CustomerDAO customerDAO;
//DI via Spring
public void setCustomerDAO(CustomerDAO customerDAO) {
this.customerDAO = customerDAO;
}
//call DAO to save customer
public void addCustomer(Customer customer){
customerDAO.addCustomer(customer);
}
//call DAO to return customers
public List<Customer> listCustomer(){
return customerDAO.listCustomer();
}
}CustomerDAO.java
package com.mkyong.customer.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.mkyong.customer.model.Customer;
public interface CustomerDAO{
void addCustomer(Customer customer);
List<Customer> listCustomer();
}CustomerDAOImpl.java
package com.mkyong.customer.dao.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport;
import com.mkyong.customer.dao.CustomerDAO;
import com.mkyong.customer.model.Customer;
public class CustomerDAOImpl extends HibernateDaoSupport
implements CustomerDAO{
//add the customer
public void addCustomer(Customer customer){
getHibernateTemplate().save(customer);
}
//return all the customers in list
public List<Customer> listCustomer(){
return getHibernateTemplate().find("from Customer");
}
}CustomerAction.java – The Struts2 action is no longer need to extends the ActionSupport, Spring will handle it.
package com.mkyong.customer.action;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import com.mkyong.customer.bo.CustomerBo;
import com.mkyong.customer.model.Customer;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ModelDriven;
public class CustomerAction implements ModelDriven{
Customer customer = new Customer();
List<Customer> customerList = new ArrayList<Customer>();
CustomerBo customerBo;
//DI via Spring
public void setCustomerBo(CustomerBo customerBo) {
this.customerBo = customerBo;
}
public Object getModel() {
return customer;
}
public List<Customer> getCustomerList() {
return customerList;
}
public void setCustomerList(List<Customer> customerList) {
this.customerList = customerList;
}
//save customer
public String addCustomer() throws Exception{
//save it
customer.setCreatedDate(new Date());
customerBo.addCustomer(customer);
//reload the customer list
customerList = null;
customerList = customerBo.listCustomer();
return "success";
}
//list all customers
public String listCustomer() throws Exception{
customerList = customerBo.listCustomer();
return "success";
}
}
6. Spring…
Almost all the configuration is done here, at all, Spring is specialized in integration work.
CustomerBean.xml – Declare the Spring’s beans : Action, BO and DAO.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="customerAction" class="com.mkyong.customer.action.CustomerAction"> <property name="customerBo" ref="customerBo" /> </bean> <bean id="customerBo" class="com.mkyong.customer.bo.impl.CustomerBoImpl" > <property name="customerDAO" ref="customerDAO" /> </bean> <bean id="customerDAO" class="com.mkyong.customer.dao.impl.CustomerDAOImpl" > <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean> </beans>
database.properties – Declare the database details.
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mkyong jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=password
DataSource.xml – Create a datasource bean.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="location"> <value>WEB-INF/classes/config/database/properties/database.properties</value> </property> </bean> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" /> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> </bean> </beans>
HibernateSessionFactory.xml – Create a sessionFactory bean to integrate Spring and Hibernate.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <!-- Hibernate session factory --> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="dataSource"> <ref bean="dataSource"/> </property> <property name="hibernateProperties"> <props> <prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop> <prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop> </props> </property> <property name="mappingResources"> <list> <value>com/mkyong/customer/hibernate/Customer.hbm.xml</value> </list> </property> </bean> </beans>
SpringBeans.xml – Create a core Spring’s bean configuration file, act as the central bean management.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <!-- Database Configuration --> <import resource="config/spring/DataSource.xml"/> <import resource="config/spring/HibernateSessionFactory.xml"/> <!-- Beans Declaration --> <import resource="com/mkyong/customer/spring/CustomerBean.xml"/> </beans>
7. JSP page
JSP page to display the element with Struts 2 tags.customer.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %> <html> <head> </head> <body> <h1>Struts 2 + Spring + Hibernate integration example</h1> <h2>Add Customer</h2> <s:form action="addCustomerAction" > <s:textfield name="name" label="Name" value="" /> <s:textarea name="address" label="Address" value="" cols="50" rows="5" /> <s:submit /> </s:form> <h2>All Customers</h2> <s:if test="customerList.size() > 0"> <table border="1px" cellpadding="8px"> <tr> <th>Customer Id</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Address</th> <th>Created Date</th> </tr> <s:iterator value="customerList" status="userStatus"> <tr> <td><s:property value="customerId" /></td> <td><s:property value="name" /></td> <td><s:property value="address" /></td> <td><s:date name="createdDate" format="dd/MM/yyyy" /></td> </tr> </s:iterator> </table> </s:if> <br/> <br/> </body> </html>
8. struts.xml
Link it all ~<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"> <struts> <constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" /> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="addCustomerAction" class="customerAction" method="addCustomer" > <result name="success">pages/customer.jsp</result> </action> <action name="listCustomerAction" class="customerAction" method="listCustomer" > <result name="success">pages/customer.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
9. Struts 2 + Spring
To integrate Struts 2 and Spring, just register the ContextLoaderListener listener class, define a “contextConfigLocation” parameter to ask Spring container to parse the “SpringBeans.xml”instead of the default “applicationContext.xml“.
web.xml
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" > <web-app> <display-name>Struts 2 Web Application</display-name> <filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter-class> org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter </filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/classes/SpringBeans.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class> org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener </listener-class> </listener> </web-app>
10. Demo
Test it : http://localhost:8080/Struts2Example/listCustomerAction.action 

相关文章推荐
- Struts + Spring + Hibernate集成
- Spring, Hibernate与Struts集成的大概思路
- osgi与流行的框架(spring,struts,hibernate等)的集成
- 集成 Hibernate,Spring,Struts Portlet 框架构建 Portlet 应用
- spring与struts、hibernate的集成
- Spring+Struts+Hibernate集成
- osgi与流行的框架(spring,struts,hibernate等)的集成
- Spring, Hibernate与Struts集成的大概思路
- Spring+struts+hibernate 集成方案
- struts_spring_hibernate集成
- Struts+Hibernate+Spring 集成
- Ssh为 struts+spring+hibernate的一个集成框架
- Spring, Hibernate与Struts集成思路
- 传智播客-spring2.5(5)-struts、spring、hibernate集成
- osgi与流行的框架(spring,struts,hibernate等)的集成
- 给STRUTS2+SPRING项目集成HIBERNATE,DBUNIT
- Spring, Hibernate与Struts集成的大概思路
- Struts2.1&Hibernate3.2&Spring2.5集成[基于Annotation]--案例结构
- Struts+Spring+Hibernate (一) 集成原理和搭建环境
- Struts,Hibernate,Spring集成开发宝典
