C++ 嵌入 Python3 -==- 2
2011-12-01 16:51
239 查看
--=============================================================================---
1. C++ 嵌入 Python3 -==- 2
下面我们让情况在复杂一点
1.1 在c++里面执行一段 Python 脚本
1.2 从c++往Python传递数据,Python计算的结果返回给C++
--=============================================================================---
2. 上程序把,注释我写好点
来自于Python3 文档里面的例子,稍微改动了一点点
// pyD.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Python.h"
// 下面的例子。来自于帮助文档,让我们先原汁原味
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//--===========================================---
Py_Initialize();
//--===========================================---
//5.1. Very High Level Embedding -- 直接执行一段Python语句
/*
相当于在Python里面执行 图1
from time import time,ctime
print('today is',ctime(time()))
*/
PyRun_SimpleString("from time import time,ctime \n"
"print('today is',ctime(time())) \n");
/* 5.2 Pure Embedding
文档说的很明确
To show this, consider what the extension code from Python to C really does:
Convert data values from Python to C,
从Python往C传递数据
Perform a function call to a C routine using the converted values, and
Convert the data values from the call from C to Python.
When embedding Python, the interface code does:
Convert data values from C to Python,
从C往Python传递数据
Perform a function call to a Python interface routine using the converted values, and
Convert the data values from the call from Python to C.
*/
PyObject *pName, *pModule, *pDict, *pFunc;
PyObject *pArgs, *pValue;
int i;
if (argc < 3) {
fprintf(stderr,"Usage: call pythonfile funcname [args]\n");
return 1;
}
Py_Initialize();
pName = PyUnicode_FromString(argv[1]);
/* Error checking of pName left out */
pModule = PyImport_Import(pName);
Py_DECREF(pName);
if (pModule != NULL) {
//--==得到第三个参数, 就是那个multiply==--
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, argv[2]);
/* pFunc is a new reference */
printf("function name is %s \n", argv[2]);
// 得到参数元组
if (pFunc && PyCallable_Check(pFunc)) {
pArgs = PyTuple_New(argc - 3);
for (i = 0; i < argc - 3; ++i) {
pValue = PyLong_FromLong(atoi(argv[i + 3]));
if (!pValue) {
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot convert argument\n");
return 1;
}
/* pValue reference stolen here: */
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, i, pValue);
}
//--====call multiply function=====--
// 这里从C往Python 传
pValue = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, pArgs);
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
if (pValue != NULL) {
int iPythonRet = PyLong_AsLong(pValue);
printf("Result of call: %ld\n", PyLong_AsLong(pValue));
Py_DECREF(pValue);
}
else {
Py_DECREF(pFunc);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr,"Call failed\n");
return 1;
}
}
else {
if (PyErr_Occurred())
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot find function \"%s\"\n", argv[2]);
}
Py_XDECREF(pFunc);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
}
else {
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to load \"%s\"\n", argv[1]);
return 1;
}
//--===========================================---
Py_Finalize();
//--===========================================---
return 0;
}
--=============================================================================---
思考的问题:
增加一个add方法,你应该怎么做? 减法呢?
--=============================================================================---
总结一下:
1. 得到模块名字
Py_Initialize();
pName = PyString_FromString(argv[1]);
/* Error checking of pName left out */
pModule = PyImport_Import(pName);
2.得到函数名字
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, argv[2]);
/* pFunc is a new reference */
if (pFunc && PyCallable_Check(pFunc))
{
...
}
Py_XDECREF(pFunc);
3.调用函数并传递参数
pValue = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, pArgs);
4.必须完成的清理工作
Py_Finalize();
附上我测试的Python脚本
###########################################################
#
#
# iQSRobots Research
# 使用范围:Python3 + T4
#
#
__filename__= "Hello.py"
__author__ = "Eagle Zhao(eaglezzb@gmail.com"
__version__ = "$Revision: 1.0 $"
__date__ = "$Date: 2011/11/15 21:57:19 $"
__copyright__ = "Copyright (c) 2011 Eagle"
__license__ = "iQS"
###########################################################
def HelloPyhton3():
print("Hello, Python3.2.2!")
def multiply(a,b):
print("Will compute", a, "times", b)
c = 0
for i in range(0, a):
c = c + b
return c
def add(a, b):
return (a+b)
最后上一张图把:
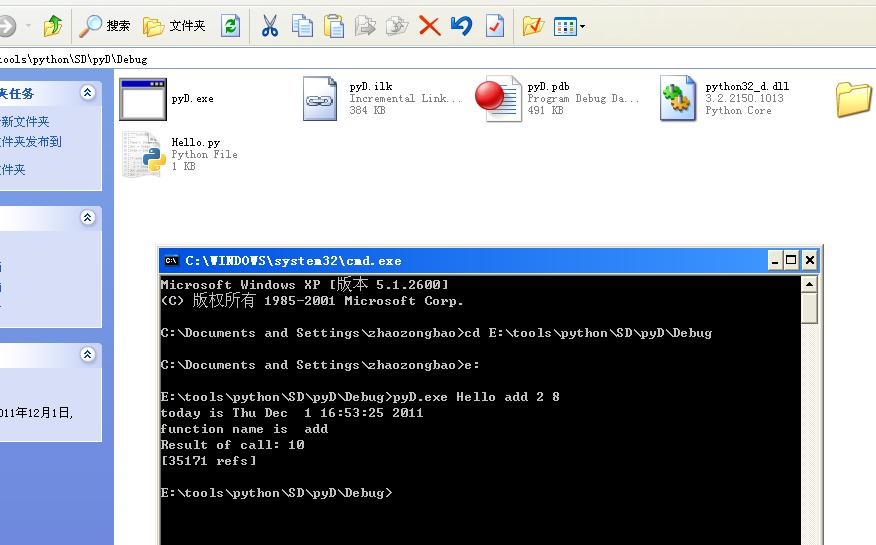
1. C++ 嵌入 Python3 -==- 2
下面我们让情况在复杂一点
1.1 在c++里面执行一段 Python 脚本
1.2 从c++往Python传递数据,Python计算的结果返回给C++
--=============================================================================---
2. 上程序把,注释我写好点
来自于Python3 文档里面的例子,稍微改动了一点点
// pyD.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Python.h"
// 下面的例子。来自于帮助文档,让我们先原汁原味
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//--===========================================---
Py_Initialize();
//--===========================================---
//5.1. Very High Level Embedding -- 直接执行一段Python语句
/*
相当于在Python里面执行 图1
from time import time,ctime
print('today is',ctime(time()))
*/
PyRun_SimpleString("from time import time,ctime \n"
"print('today is',ctime(time())) \n");
/* 5.2 Pure Embedding
文档说的很明确
To show this, consider what the extension code from Python to C really does:
Convert data values from Python to C,
从Python往C传递数据
Perform a function call to a C routine using the converted values, and
Convert the data values from the call from C to Python.
When embedding Python, the interface code does:
Convert data values from C to Python,
从C往Python传递数据
Perform a function call to a Python interface routine using the converted values, and
Convert the data values from the call from Python to C.
*/
PyObject *pName, *pModule, *pDict, *pFunc;
PyObject *pArgs, *pValue;
int i;
if (argc < 3) {
fprintf(stderr,"Usage: call pythonfile funcname [args]\n");
return 1;
}
Py_Initialize();
pName = PyUnicode_FromString(argv[1]);
/* Error checking of pName left out */
pModule = PyImport_Import(pName);
Py_DECREF(pName);
if (pModule != NULL) {
//--==得到第三个参数, 就是那个multiply==--
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, argv[2]);
/* pFunc is a new reference */
printf("function name is %s \n", argv[2]);
// 得到参数元组
if (pFunc && PyCallable_Check(pFunc)) {
pArgs = PyTuple_New(argc - 3);
for (i = 0; i < argc - 3; ++i) {
pValue = PyLong_FromLong(atoi(argv[i + 3]));
if (!pValue) {
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot convert argument\n");
return 1;
}
/* pValue reference stolen here: */
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, i, pValue);
}
//--====call multiply function=====--
// 这里从C往Python 传
pValue = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, pArgs);
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
if (pValue != NULL) {
int iPythonRet = PyLong_AsLong(pValue);
printf("Result of call: %ld\n", PyLong_AsLong(pValue));
Py_DECREF(pValue);
}
else {
Py_DECREF(pFunc);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr,"Call failed\n");
return 1;
}
}
else {
if (PyErr_Occurred())
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot find function \"%s\"\n", argv[2]);
}
Py_XDECREF(pFunc);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
}
else {
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to load \"%s\"\n", argv[1]);
return 1;
}
//--===========================================---
Py_Finalize();
//--===========================================---
return 0;
}
--=============================================================================---
思考的问题:
增加一个add方法,你应该怎么做? 减法呢?
--=============================================================================---
总结一下:
1. 得到模块名字
Py_Initialize();
pName = PyString_FromString(argv[1]);
/* Error checking of pName left out */
pModule = PyImport_Import(pName);
2.得到函数名字
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, argv[2]);
/* pFunc is a new reference */
if (pFunc && PyCallable_Check(pFunc))
{
...
}
Py_XDECREF(pFunc);
3.调用函数并传递参数
pValue = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, pArgs);
4.必须完成的清理工作
Py_Finalize();
附上我测试的Python脚本
###########################################################
#
#
# iQSRobots Research
# 使用范围:Python3 + T4
#
#
__filename__= "Hello.py"
__author__ = "Eagle Zhao(eaglezzb@gmail.com"
__version__ = "$Revision: 1.0 $"
__date__ = "$Date: 2011/11/15 21:57:19 $"
__copyright__ = "Copyright (c) 2011 Eagle"
__license__ = "iQS"
###########################################################
def HelloPyhton3():
print("Hello, Python3.2.2!")
def multiply(a,b):
print("Will compute", a, "times", b)
c = 0
for i in range(0, a):
c = c + b
return c
def add(a, b):
return (a+b)
最后上一张图把:

相关文章推荐
- boost.python学习之----python 嵌入c++
- Python/C API使用方法简介 (在C/C++中嵌入Python)
- 用c++和python写GUI程序(python嵌入方式)
- C++使用ffpython嵌入和扩展python
- Python嵌入C++来弥补C++本身不足之处的方案介绍
- C、C++中如何成功嵌入python
- C++ 扩展和嵌入 Python
- 使用 Boost.Python 嵌入 Python 模块到 C++
- C++中嵌入python程序——命令行模式
- Python嵌入C++详解(3)--Import Class
- Python嵌入C++
- boost C++中嵌入python
- 把Python嵌入C++的具体操作方案的介绍
- 使用 Boost.Python 嵌入 Python 模块到 C++
- C++中嵌入python入门2
- C++中嵌入python程序——命令行模式
- 谈谈自己对“将Python嵌入到C/C++程序,让你的程序的用户获得"脚本化"的能力”一这句话中脚本化的理解
- boost.python入门教程 ----python 嵌入c++
- C++代码中嵌入Python之后程序的发布问题
- Python嵌入C/C++ (Python核心编程)
