Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(二)
2011-10-24 21:56
701 查看
在上一篇讲到了TabActivity和TabHost的结合的分页实现方式一。这里,将讲到方式二。其实,方式一、二大同小异,只是方式二的布局文件可以是独立的。当然,也有些差别,例如点击顶部Tab标签时页面跳转事件响应的实现也不同。具体,看源代码。
二、TabActivity和TabHost的结合实现分页标签--------方式二
细节分析:
1.主类继承TabActivity
public class Pagination extends TabActivity
2.获取当前TabHost对象
TabHost tabHost = getTabHost();
3.添加Tab分页标签
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab1")
.setIndicator("Tab1", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.a1))
.setContent(this));
........
这里,你会疑问,布局文件不用添加吗!确实,要添加,但是动态添加。即点击哪个Tab标签时,动态添加对应的布局文件。
public View createTabContent(String tag){..........}

1、布局文件:secondpage.xml
view plain
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/widget30"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="EditText"
android:textSize="18sp"
>
</EditText>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_show"
android:layout_width="149px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="显示"
>
</Button>
</LinearLayout>
2、代码文件:
view plain
package com.myandroid.test;
import android.app.TabActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TabHost;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class TabPage extends TabActivity implements TabHost.TabContentFactory {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//setContentView(R.layout.main); 这里不需要加载主页面
final TabHost tabHost = getTabHost(); //tab控制对象
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab1") //添加顶部的分页符
.setIndicator("Tab1", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.a1))
.setContent(this));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab2")
.setIndicator("Tab2", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.a2))
.setContent(this));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab3")
.setIndicator("Tab3", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.a3))
.setContent(this));
}
/**
* 点击Tab,跳转页面时激发的事件处理
*/
public View createTabContent(String tag) {
Log.e("tag", tag); //这里的tag字符串是tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab1") 定义的字符串
int tabPage = Integer.parseInt(tag.substring(tag.length()-1)); //获取最后面的数字
final TextView tv = new TextView(this); //要用final修饰,否则报错
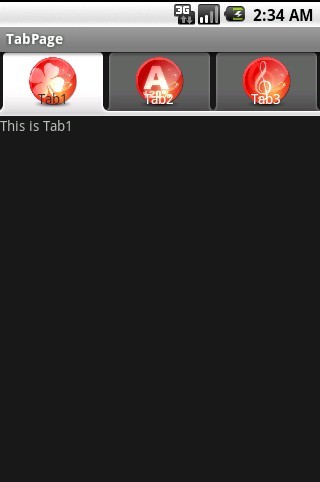
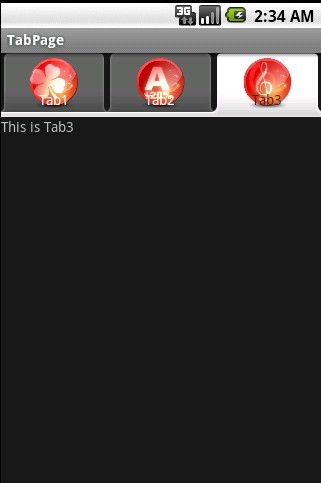
tv.setText("This is " + tag);
switch(tabPage) {
case 1: //分页一
break;
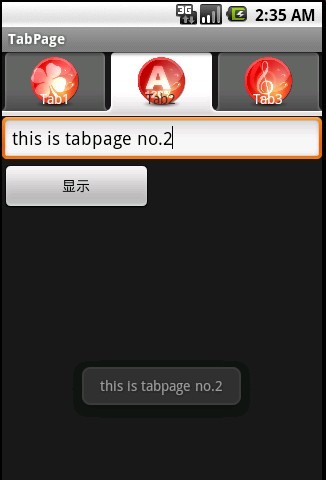
case 2: //分页二
final LayoutInflater layout = LayoutInflater.from(TabPage.this); //用于加载XML的对象,要使用final修饰
final View customView = layout.inflate(R.layout.secondpage, null); //创建自定义的View,要使用final修饰
final Button bt_show = (Button)customView.findViewById(R.id.bt_show);
final EditText et_text = (EditText)customView.findViewById(R.id.et_text);
bt_show.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(TabPage.this, et_text.getText(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
return customView;
case 3: //分页三
break;
default:
break;
}
//不可以返回null
return tv;
}
}
在下一篇,将继续讲到TabActivity和TabHost的结合实现分页标签--------方式三,也是较前两种方式好很多。
二、TabActivity和TabHost的结合实现分页标签--------方式二
细节分析:
1.主类继承TabActivity
public class Pagination extends TabActivity
2.获取当前TabHost对象
TabHost tabHost = getTabHost();
3.添加Tab分页标签
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab1")
.setIndicator("Tab1", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.a1))
.setContent(this));
........
这里,你会疑问,布局文件不用添加吗!确实,要添加,但是动态添加。即点击哪个Tab标签时,动态添加对应的布局文件。
public View createTabContent(String tag){..........}




1、布局文件:secondpage.xml
view plain
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/widget30"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="EditText"
android:textSize="18sp"
>
</EditText>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_show"
android:layout_width="149px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="显示"
>
</Button>
</LinearLayout>
2、代码文件:
view plain
package com.myandroid.test;
import android.app.TabActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TabHost;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class TabPage extends TabActivity implements TabHost.TabContentFactory {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//setContentView(R.layout.main); 这里不需要加载主页面
final TabHost tabHost = getTabHost(); //tab控制对象
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab1") //添加顶部的分页符
.setIndicator("Tab1", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.a1))
.setContent(this));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab2")
.setIndicator("Tab2", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.a2))
.setContent(this));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab3")
.setIndicator("Tab3", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.a3))
.setContent(this));
}
/**
* 点击Tab,跳转页面时激发的事件处理
*/
public View createTabContent(String tag) {
Log.e("tag", tag); //这里的tag字符串是tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab1") 定义的字符串
int tabPage = Integer.parseInt(tag.substring(tag.length()-1)); //获取最后面的数字
final TextView tv = new TextView(this); //要用final修饰,否则报错
tv.setText("This is " + tag);
switch(tabPage) {
case 1: //分页一
break;
case 2: //分页二
final LayoutInflater layout = LayoutInflater.from(TabPage.this); //用于加载XML的对象,要使用final修饰
final View customView = layout.inflate(R.layout.secondpage, null); //创建自定义的View,要使用final修饰
final Button bt_show = (Button)customView.findViewById(R.id.bt_show);
final EditText et_text = (EditText)customView.findViewById(R.id.et_text);
bt_show.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(TabPage.this, et_text.getText(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
return customView;
case 3: //分页三
break;
default:
break;
}
//不可以返回null
return tv;
}
}
在下一篇,将继续讲到TabActivity和TabHost的结合实现分页标签--------方式三,也是较前两种方式好很多。
相关文章推荐
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(二)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(一)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(一)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(三)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(二)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(三)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(二)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(二)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(三)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(一)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(一)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(三)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(三)
- 转:Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(一)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法一-----TabActivity和TabHost的结合(三)
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法--------采用ActivityGroup和GridView的结合
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法--------采用ActivityGroup和GridView的结合
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法--------采用ActivityGroup和GridView的结合
- Android之Tab分页标签的实现方法--------采用ActivityGroup和GridView的结合
