Struts 2架构图以及说明
2011-03-22 19:37
239 查看
此文件copy自struts2 reference.个人认为这个图对理解struts2非常有帮助,所以就拿来放到自己的博客上了。
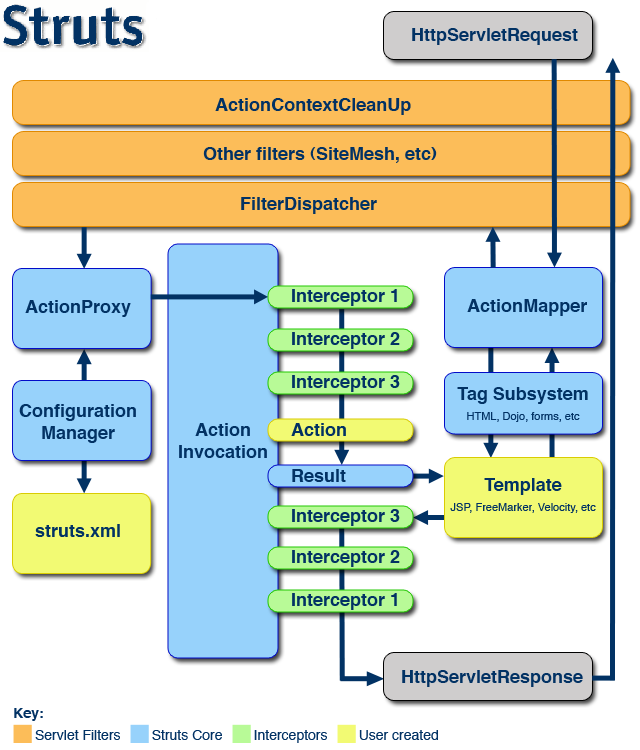
In the diagram, an initial request goes to the Servlet container (such as Jetty or Resin) which is passed through a standard filter chain. The chain includes the (optional)ActionContextCleanUp filter, which is useful when integrating technologies such as SiteMesh Plugin . Next, the required FilterDispatcher is called, which in turn consults theActionMapper to determine if the request should invoke an action.
If the ActionMapper determines that an Action should be invoked, the FilterDispatcher delegates control to the ActionProxy . The ActionProxy consults the frameworkConfiguration Files manager (initialized from the struts.xml file). Next, the ActionProxy creates an ActionInvocation , which is responsible for the command pattern implementation. This includes invoking any Interceptors (the before clause) in advance of invoking the Action itself.
Once the Action returns, the ActionInvocation is responsible for looking up the proper result associated with the Action result code mapped in struts.xml . The result is then executed, which often (but not always, as is the case for Action Chaining ) involves a template written in JSP or FreeMarker to be rendered. While rendering, the templates can use the Struts Tags provided by the framework. Some of those components will work with the ActionMapper to render proper URLs for additional requests.
Interceptors are executed again (in reverse order, calling the after clause). Finally, the response returns through the filters configured in the web.xml . If the ActionContextCleanUp filter is present, the FilterDispatcher will not clean up the ThreadLocal ActionContext . If the ActionContextCleanUp filter is not present, the FilterDispatcher will cleanup all ThreadLocals.
注意:与struts1不同,struts2对用户的每一次请求都会创建一个action,所以struts2的action是线程安全的。
struts1中的action是singleton(单例)的,struts2中的action是prototype(原型)的。

In the diagram, an initial request goes to the Servlet container (such as Jetty or Resin) which is passed through a standard filter chain. The chain includes the (optional)ActionContextCleanUp filter, which is useful when integrating technologies such as SiteMesh Plugin . Next, the required FilterDispatcher is called, which in turn consults theActionMapper to determine if the request should invoke an action.
If the ActionMapper determines that an Action should be invoked, the FilterDispatcher delegates control to the ActionProxy . The ActionProxy consults the frameworkConfiguration Files manager (initialized from the struts.xml file). Next, the ActionProxy creates an ActionInvocation , which is responsible for the command pattern implementation. This includes invoking any Interceptors (the before clause) in advance of invoking the Action itself.
Once the Action returns, the ActionInvocation is responsible for looking up the proper result associated with the Action result code mapped in struts.xml . The result is then executed, which often (but not always, as is the case for Action Chaining ) involves a template written in JSP or FreeMarker to be rendered. While rendering, the templates can use the Struts Tags provided by the framework. Some of those components will work with the ActionMapper to render proper URLs for additional requests.
| All objects in this architecture (Actions, Results , Interceptors , and so forth) are created by an ObjectFactory . This ObjectFactory is pluggable. We can provide our own ObjectFactory for any reason that requires knowing when objects in the framework are created. A popular ObjectFactory implementation uses Spring as provided by the Spring Plugin . |
注意:与struts1不同,struts2对用户的每一次请求都会创建一个action,所以struts2的action是线程安全的。
struts1中的action是singleton(单例)的,struts2中的action是prototype(原型)的。
相关文章推荐
- MFC原创:三层架构03(人事管理系统)BLL以及总体说明
- struts2配置文件的加载顺序以及 struts.xml package 的配置说明
- 概述struts,以及struts如何实现MVC架构的
- Java后台架构篇--Struts2.0体系结构图以及详解
- Java Struts2 框架入门详解(一)MVC架构详解以及Struts基本概述
- 关于“幽灵架构”的补充说明2:Struct以及Copy - on -Write
- 概述struts,以及struts如何实现MVC架构的?
- struts 2.1+Spring3.0 +hibernate 3.3整合所需要的JAR库 以及 作用说明
- Java三大框架之struts的上传文件出错信息配置(允许上传的类型,上传文件的大小,以及大文件上传说明等等)
- OpenCv3.0架构的详细解释以及新增新功能的说明(当然OpenCv3.2.0中的很多新功能更加强大,比如CNN,DNN的实现)
- MFC原创:三层架构03(人事管理系统)BLL以及总体说明
- 算法服务平台-整体架构以及说明
- Spring+Struts2+Hibernate 架构分层原理说明
- java struts常见错误以及原因分析
- HSSA总体架构(HSSA=Hibernate+Spring+Struts+Ajax)
- struts2 struts.xml配置中常见配置选项及说明
- Nova 各个组件介绍以及功能分析(逻辑架构,运行架构,开发架构以及数据库)
- scrollTo 以及 scrollBy方法使用说明
- iOS各框架使用场景以及系统架构层次
- 整理的一些java中常使用jar包以及说明
