Windows Workflow Foundation(4)- Workflow实例
2008-12-25 10:50
399 查看
Workflow实例介绍
当在工作流宿主进程中运行工作流时,不仅需要WorkflowRuntime,而且需要加载workflow实例。workflow实例由一个或多个活动组成。我们在workflow集成环境中设计符合我们业务需求的workflow实例,通过workflow实例完成业务需求,当然workflow实例需要在workflow宿主中调用。workflow实例是一个 WF 对象,它为你提供了我们的独立的workflow 任务上下文(环境)。我们可使用这个对象去找到在我们的处理任务中事情将是如何进行的。就像我们有方法和属性去控制workflow 运行时一样,我们也有方法和属性并用它们和我们的workflow 实例进行交互。
下表列出了大多数 WorkflowInstance 属性
| 属性 | 功能 |
| InstanceId | 得到workflow 实例的唯一标识(一个Guid) |
| WorkflowRuntime | 得到本workflow 实例的WorkflowRuntime |
| 方法 | 功能 |
| ApplyWorkflowChanges | 通过WorkflowChanges 对象申请对workflow 实例进行更改。这允许你在workflow 执行时修改它(增加、移出或更改活动),当动态的更改实施时,workflow 实例会被暂停。 |
| GetWorkflowDefinition | 检索本workflow 实例的根(root)活动。 |
| Resume | 恢复执行先前被暂停的workflow 实例。假如workflow 实例并未处于暂停状态,则不做任何事情。假如workflow 实例处在暂停状态,workflow 运行时就会在workflow 实例刚被恢复后触发WorkflowResumed 事件。 |
| Start | 启动一个workflow 实例的执行,在这个workflow 实例根活动上调用ExecuteActivity。假如Start 发生异常,它通过调用Terminate终止这个workflow 实例,并附加异常相关信息作为终止的原因。 |
| Suspend | 同步暂停本workflow 实例。假如workflow 实例本就处于暂停状态,则不做任何事情。假如workflow 实 例正在运行,则workflow 运行时就暂停该实例,然后设置SuspendOrTerminateInfoProperty(说明原因)并进入 Suspend,触发WorkflowSuspended 事件。 |
| Terminate | 同步终止本workflow 实例。当宿主需要终止workflow 实例时,workflow 运行时就终止这个实例并试图 持久化实例的最终状态。然后WorkflowInstance 设置SuspendOrTerminateInfoProperty(说明原因)并进入 Terminate。最后,它触发WorkflowTerminated 事件并把终止原因传到WorkflowTerminateException 中的 Message 属性并包含到WorkflowTerminatedEventArgs 事件参数中。另外,假如在持久化时发生异常,workflow 运行时 取而代之地就把异常传到WorkflowTerminatedEventArgs 事件参数中。 |
创建一个工作流实例
当我们启动一个workflow 实例前,我们必须有一个 workflow 任务让WF 去执行。在前面,我们通过Visual Studio 2008为我们创建了一个基于workflow 的项目,它自动包含一个workflow 任务。下面我们创建包含workflow实例的project。1、 新建一个SequentianWorkflowlibrary工程。
2、 从Toolbox里向workflow设计里拖拽两个code和一个delay。
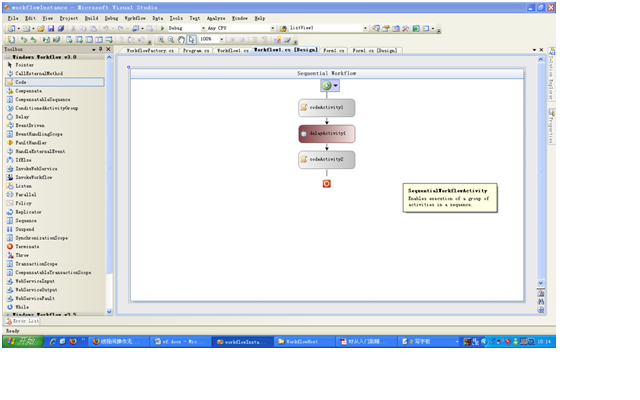
3、 将codeActivity1的executeCode设成PreDelayMsg,delayActivity1的TimeoutDuration设成00:00:05,codeActivity2的executeCode设成PostDelayMsg。
4、 添加引用System.Windows.Forms,编译工程。Workflow1.cs的代码如下
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.ComponentModel.Design;
using System.Collections;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Workflow.ComponentModel.Compiler;
using System.Workflow.ComponentModel.Serialization;
using System.Workflow.ComponentModel;
using System.Workflow.ComponentModel.Design;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.Activities.Rules;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WFInstanceLib
{
public sealed partial class Workflow1: SequentialWorkflowActivity
{
public Workflow1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void PreDelayMsg(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("Pre-delay code is being executed.");
}
private void PostDelayMsg(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("Post-delay code is being executed.");
}
// The delay field.
private Int32 _delay = 10;
// The delay property. This is set when the workflow instance
// is started.
public Int32 Delay
{
get { return _delay; }
set
{
// Check bounds...inject default values if out of range.
if (value < 0 || value > 120)
{
value = 10;
} // if
// Assign value, if we're initialized and ready to execute.
if (ExecutionStatus == ActivityExecutionStatus.Initialized)
{
_delay = value;
delayActivity1.TimeoutDuration = new TimeSpan(0, 0, _delay);
} // if
}
}
}
}
5、 向解决方案中添加一个Windows Forms Application项目,并添加System.Workflow.Activities, System.Workflow.ComponentModel,System.Workflow.Runtime引用。
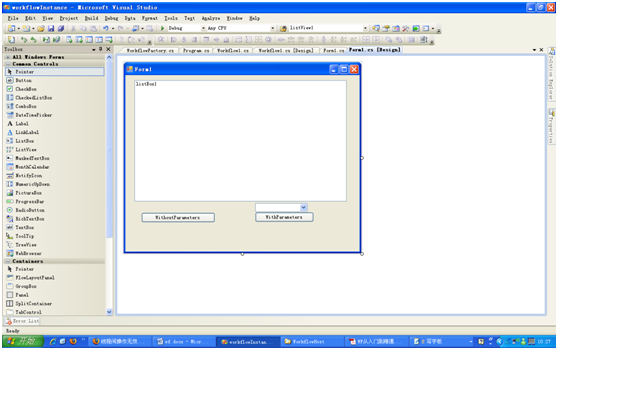
6、 添加上面创建workflow library的引用,From1.cs代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Workflow.Activities;
using System.Workflow.ComponentModel;
using System.Workflow.Runtime;
using System.Threading;
namespace workflowInstance
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
// The auto-reset event that will cause the main thread to wait
// until the workflow completes or is terminated.
private static AutoResetEvent waitHandle = new AutoResetEvent(false);
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
System.Windows.Forms.Control.CheckForIllegalCrossThreadCalls = false;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Obtain a workflow runtime object.
listBox1.Items.Clear();
WorkflowRuntime workflowRuntime = WorkflowFactory.GetWorkflowRuntime();
// Add the event handlers.
workflowRuntime.WorkflowIdled += new EventHandler<WorkflowEventArgs>(workflowIdled);
workflowRuntime.WorkflowCompleted += new EventHandler<WorkflowCompletedEventArgs>(workflowCompleted);
workflowRuntime.WorkflowTerminated += new EventHandler<WorkflowTerminatedEventArgs>(workflowTerminated);
// Print banner.
listBox1.Items.Add("Waiting for workflow completion.");
// Create the workflow instance.
WorkflowInstance instance = workflowRuntime.CreateWorkflow(typeof(WFInstanceLib.Workflow1));
// Start the workflow instance.
instance.Start();
// Wait for the workflow to complete.
waitHandle.WaitOne();
// Print banner.
listBox1.Items.Add("Done.");
}
// The "terminated" event handler (we killed it or it had an exception).
private void workflowTerminated(object sender, WorkflowTerminatedEventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add("Workflow instance terminated.");
waitHandle.Set();
}
// The "completed" event handler (ran to completion, no errors).
private void workflowCompleted(object sender, WorkflowCompletedEventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add("Workflow instance completed.");
waitHandle.Set();
}
// The "idled" event handler.
private void workflowIdled(object sender, WorkflowEventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add("Workflow instance idled.");
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create an instance of the workflow runtime.
listBox1.Items.Clear();
WorkflowRuntime workflowRuntime = WorkflowFactory.GetWorkflowRuntime();
// Add the event handlers.
workflowRuntime.WorkflowIdled += new EventHandler<WorkflowEventArgs>(workflowIdled);
workflowRuntime.WorkflowCompleted += new EventHandler<WorkflowCompletedEventArgs>(workflowCompleted);
workflowRuntime.WorkflowTerminated += new EventHandler<WorkflowTerminatedEventArgs>(workflowTerminated);
// Process the command line for a delay. Use default of 10 seconds
// if no argument is present.
Int32 delay = 0;
string val = comboBox1.SelectedText == "" ? "10" : comboBox1.SelectedText;
if (!Int32.TryParse(val, out delay))
{
// Not an integer value.
Console.WriteLine("You must pass in an integer value!");
return;
} // if
// Create the argument.
Dictionary<string, object> parms = new Dictionary<string, object>();
parms.Add("Delay", delay);
// Print banner.
listBox1.Items.Add("Waiting for workflow completion.");
// Create instance.
WorkflowInstance instance = workflowRuntime.CreateWorkflow(typeof(WFInstanceLib.Workflow1), parms);
// Start instance.
instance.Start();
// Wait until the workflow instance is done.
waitHandle.WaitOne();
// Print banner.
listBox1.Items.Add("Done.");
}
}
}
7、 将windows froms项目设成启动项目,编译并运行。
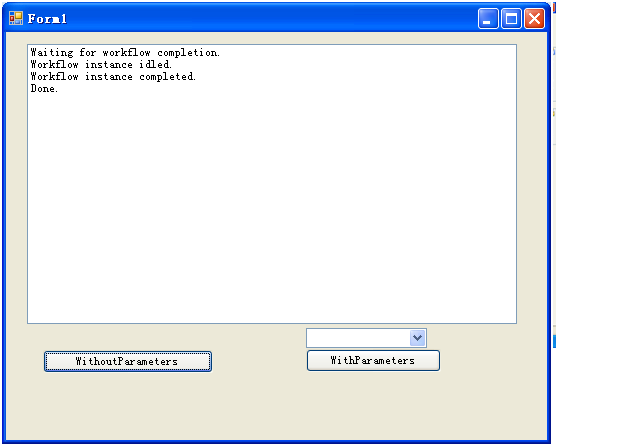
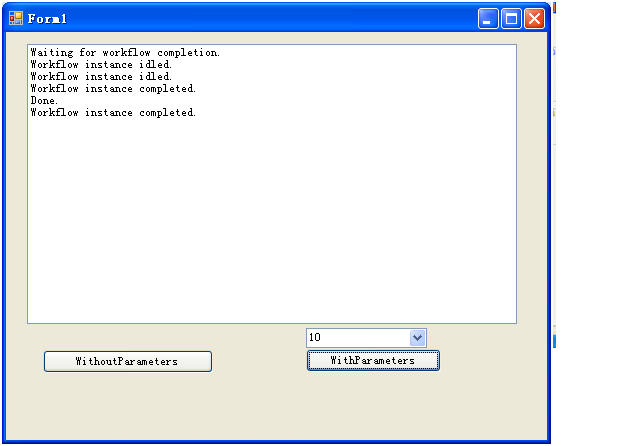
下面是本节实例的下载地址
/Files/chkff_01/workflowInstance.rar
相关文章推荐
- 和我一起学Windows Workflow Foundation(1)-----创建和调试一个WF实例
- 和我一起学Windows Workflow Foundation(1) 创建和调试一个WF实例
- Windows Workflow Foundation(1)-----创建和调试一个WF实例
- 和我一起学Windows Workflow Foundation(1)-----创建和调试一个WF实例
- 和我一起学Windows Workflow Foundation(1)-----创建和调试一个WF实例
- 和我一起学Windows Workflow Foundation(1)-----创建和调试一个WF实例 [转]
- Windows Workflow Foundation (wwf) 在宿主中使用参数与实例通信 --学习笔记(二)
- [转帖]Windows Workflow Foundation之旅(七)——顺序工作流、状态机工作流
- Windows Workflow Foundation能带来什么
- Windows Workflow Foundation之旅(一)——概况
- 现在可用:Workflow Foundation Activity Pack for Windows Azure CTP 1
- 现在可用:Workflow Foundation Activity Pack for Windows Azure CTP 1
- Windows Workflow Foundation 4.0
- Windows Workflow Foundation(四)——(创建自定义活动)(转载)
- 跟我一起学Windows Workflow Foundation(5)-----使用activity设计器创建一个整合的定制activity
- Windows Workflow Foundation开发环境配置
- Windows Workflow Foundation之旅(八)——使用活动控制流程、在工作流中使用条件
- 跟我一起学Windows Workflow Foundation(4)-----使用Listen,Delay,和其他envnt-based定制活动(转)
- “Windows Workflow Foundation开发实战系列课程”中的数据库恢复
- Windows Workflow Foundation Web Workflow Approvals Starter Kit(转)
